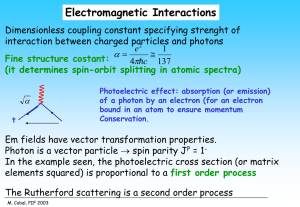
Symmetry in Electron-Atom Collisions and Photoionization Process
... photoionization boundary condition (Eq.13) in relation to the collision boundary condition (Eq.12). This complex conjugation is characteristic of ‘motion reversal’ in quantum mechanics, usually referred to as ‘time reversal’. Using a quantum mechanical operator for ‘time/motion reversal’, one can ...
... photoionization boundary condition (Eq.13) in relation to the collision boundary condition (Eq.12). This complex conjugation is characteristic of ‘motion reversal’ in quantum mechanics, usually referred to as ‘time reversal’. Using a quantum mechanical operator for ‘time/motion reversal’, one can ...
Chapter 7 notes physics 2
... When working on collision problems in order to find specific answers you may have to use both concepts (conservation of momentum and conservation of energy) in order to solve for your variables. For certain situations this can be difficult and time consuming. To simplify your efforts use the given e ...
... When working on collision problems in order to find specific answers you may have to use both concepts (conservation of momentum and conservation of energy) in order to solve for your variables. For certain situations this can be difficult and time consuming. To simplify your efforts use the given e ...
Hooke`s Law - UCSB Physics
... that none of the n solutions can be written as a simple linear combination of the other ones. The most general solution to the differential equation is then given as a linear combination of these n “basis” solutions. In our case, it is clear that neither sine nor cosine can be written as a simple mu ...
... that none of the n solutions can be written as a simple linear combination of the other ones. The most general solution to the differential equation is then given as a linear combination of these n “basis” solutions. In our case, it is clear that neither sine nor cosine can be written as a simple mu ...
Baryon femtoscopy considering residual correlations as a tool to
... These proceedings are based on [1] where all the relevant details may be found. Femtoscopy, the study of particle-correlations at low relative momentum, is a powerful tool extensively used in heavy-ion, proton-nucleus and proton-proton collisions. Such correlations arise due to Quantum Statistics (i ...
... These proceedings are based on [1] where all the relevant details may be found. Femtoscopy, the study of particle-correlations at low relative momentum, is a powerful tool extensively used in heavy-ion, proton-nucleus and proton-proton collisions. Such correlations arise due to Quantum Statistics (i ...
TrackingAndPIDLecture_2
... Cerenkov light and scintillation light needs to be collected somehow. There are now many detectors which can do that. Photo-multiplier tubes (PMT’s) have been around for 50 years and are still used in many applications: A photon hits a photocathode liberating an electron which is accelerated to the ...
... Cerenkov light and scintillation light needs to be collected somehow. There are now many detectors which can do that. Photo-multiplier tubes (PMT’s) have been around for 50 years and are still used in many applications: A photon hits a photocathode liberating an electron which is accelerated to the ...
Scattering_pdf
... based on atomic theories. The first question we pose when studying any condensed matter system is the question concerning the internal structure: what are the building blocks (atoms, colloidal particles, ...) and how are they arranged? The second question concerns the microscopic dynamics: how do th ...
... based on atomic theories. The first question we pose when studying any condensed matter system is the question concerning the internal structure: what are the building blocks (atoms, colloidal particles, ...) and how are they arranged? The second question concerns the microscopic dynamics: how do th ...
File
... • The two equations we need to solve are: • v1 – v2 = v ’2 – v ’1 (derived from conservation of kinetic energy) and • m1v1 + m2v2 = m1v ’1 + m2v ’2 (the conservation of momentum equation • The strategy is to solve the first equation for either v’2 or v ’1 plug that into the second equation. ...
... • The two equations we need to solve are: • v1 – v2 = v ’2 – v ’1 (derived from conservation of kinetic energy) and • m1v1 + m2v2 = m1v ’1 + m2v ’2 (the conservation of momentum equation • The strategy is to solve the first equation for either v’2 or v ’1 plug that into the second equation. ...
Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH)
... Before we consider the details… How do we describe our particle system? Each particle is specified by a state list: ...
... Before we consider the details… How do we describe our particle system? Each particle is specified by a state list: ...
Document
... - The trivial parton model: proton consists of some partons. Interaction between partons are not taken into account - The parton model can be valid if the target p has a sufficiently big momentum, so that: z = x - Measured cross section at any given x is prop. to the probability of finding a parton ...
... - The trivial parton model: proton consists of some partons. Interaction between partons are not taken into account - The parton model can be valid if the target p has a sufficiently big momentum, so that: z = x - Measured cross section at any given x is prop. to the probability of finding a parton ...
webjune
... An approximate solution of the Thomas-Fermi equation for positive ions in a high magnetic field is obtained by making use of the variational principle. The radial wavefunctions of the hydrogen-like atom are used as the trial function that contains some variational parameters and satisfies the approp ...
... An approximate solution of the Thomas-Fermi equation for positive ions in a high magnetic field is obtained by making use of the variational principle. The radial wavefunctions of the hydrogen-like atom are used as the trial function that contains some variational parameters and satisfies the approp ...
Thermalization of photoexcited carriers in bismuth investigated by
... The terahertz spectrometer is driven by a Ti:sapphire laser oscillator delivering 10-fs pulses at a 780-nm center wavelength. Part of the laser output is used to excite the sample with an incident fluence of about 10 μJ cm−2 . The terahertz pulses are obtained from the residual 10% of the laser outp ...
... The terahertz spectrometer is driven by a Ti:sapphire laser oscillator delivering 10-fs pulses at a 780-nm center wavelength. Part of the laser output is used to excite the sample with an incident fluence of about 10 μJ cm−2 . The terahertz pulses are obtained from the residual 10% of the laser outp ...
Physics 200 Class #1 Outline
... Case III: There is an explosion during the collision and the 2kg mass moves to the left at 95m/s, find the speed of the 3kg mass afterwards. (2kg)(10m / s ) (3kg)(0m / s) (2kg)( 95m / s) (3kg)(v final ) 20kgm / s 190kgm / s (3kg)(v final ) v final 70m / s ...
... Case III: There is an explosion during the collision and the 2kg mass moves to the left at 95m/s, find the speed of the 3kg mass afterwards. (2kg)(10m / s ) (3kg)(0m / s) (2kg)( 95m / s) (3kg)(v final ) 20kgm / s 190kgm / s (3kg)(v final ) v final 70m / s ...
Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH)
... Before we consider the details… How do we describe our particle system? Each particle is specified by a state list: ...
... Before we consider the details… How do we describe our particle system? Each particle is specified by a state list: ...
Mass conservation of finite element methods for coupled flow
... incompressibility constraint ∇ · u0 = 0. Different discretization methods for both the instationary, incompressible Navier–Stokes equations and the transport equation have been developed also in the practically important case of ν 1 and ε 1, for an overview see [12]. We study the mass conservati ...
... incompressibility constraint ∇ · u0 = 0. Different discretization methods for both the instationary, incompressible Navier–Stokes equations and the transport equation have been developed also in the practically important case of ν 1 and ε 1, for an overview see [12]. We study the mass conservati ...
Ch 9 - Momentum and Collisions (No 2D)
... right at a velocity of +2.00 m/s on a frictionless table, collides head-on with a stationary 7.50kg ball. Find the final velocities of the balls if the collision is elastic. ...
... right at a velocity of +2.00 m/s on a frictionless table, collides head-on with a stationary 7.50kg ball. Find the final velocities of the balls if the collision is elastic. ...
Notes for Solid State Theory FFF051/FYST25
... Now we investigate the eigenfunctions Ψα (r) of the translation operator, satisfying T̂R Ψα (r) = cα (R)Ψα (r) Let us write without loss of generality cα (ai ) = e2πixi for the primitive lattice vectors ai with xi ∈ C (it will be shown below that only xi ∈ R is of relevance for bulk crystals). From ...
... Now we investigate the eigenfunctions Ψα (r) of the translation operator, satisfying T̂R Ψα (r) = cα (R)Ψα (r) Let us write without loss of generality cα (ai ) = e2πixi for the primitive lattice vectors ai with xi ∈ C (it will be shown below that only xi ∈ R is of relevance for bulk crystals). From ...