The Laramide Orogeny: What Were the Driving Forces?
... American plate must have been driven by ridgepush from the Atlantic spreading-center or by basal drag caused by mantle convection. Basal drag is not considered to be an important factor in driving plate motions (e.g. Stüwe, 2002); this model, therefore, requires that horizontal normal compressive st ...
... American plate must have been driven by ridgepush from the Atlantic spreading-center or by basal drag caused by mantle convection. Basal drag is not considered to be an important factor in driving plate motions (e.g. Stüwe, 2002); this model, therefore, requires that horizontal normal compressive st ...
The Laramide Orogeny - University of Nevada, Reno
... American plate must have been driven by ridgepush from the Atlantic spreading-center or by basal drag caused by mantle convection. Basal drag is not considered to be an important factor in driving plate motions (e.g. Stüwe, 2002); this model, therefore, requires that horizontal normal compressive st ...
... American plate must have been driven by ridgepush from the Atlantic spreading-center or by basal drag caused by mantle convection. Basal drag is not considered to be an important factor in driving plate motions (e.g. Stüwe, 2002); this model, therefore, requires that horizontal normal compressive st ...
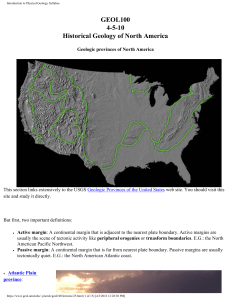
GEOL100 4-5-10 Historical Geology of North America
... (aka Great Basin): Image Here, the Earth's crust and upper mantle has been stretched up to 100% of its original width. Beginning in the Paleogene, the entire region was subjected to extension that thinned and cracked the crust as it was pulled apart, creating long parallel normal faults. Along these ...
... (aka Great Basin): Image Here, the Earth's crust and upper mantle has been stretched up to 100% of its original width. Beginning in the Paleogene, the entire region was subjected to extension that thinned and cracked the crust as it was pulled apart, creating long parallel normal faults. Along these ...
7.1
... joined as part of Pangaea 250 million years ago. The lighter area on the map shows where Glossopteris fossils have been found. Notice that the plant once grew in parts of five continents—South America, Africa, India, Antarctica, and Australia. Because these plants grew in a swampy environment, this ...
... joined as part of Pangaea 250 million years ago. The lighter area on the map shows where Glossopteris fossils have been found. Notice that the plant once grew in parts of five continents—South America, Africa, India, Antarctica, and Australia. Because these plants grew in a swampy environment, this ...
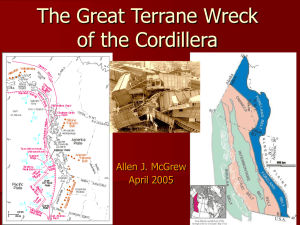
An Introduction to Terrane Analysis in the Western North American
... and related terranes shift SE as Atlantic and Proto-Caribbean expand; transform fault and oblique rift systems developed along waning continental arc (McCoy-Bisbee; Mojave-Sonoran megashear); early Franciscan mÈlange formed farther outboard Nutzotin Ocean between northern Wrangellia and North Americ ...
... and related terranes shift SE as Atlantic and Proto-Caribbean expand; transform fault and oblique rift systems developed along waning continental arc (McCoy-Bisbee; Mojave-Sonoran megashear); early Franciscan mÈlange formed farther outboard Nutzotin Ocean between northern Wrangellia and North Americ ...
The Initial Break Up
... • Parts of Appalachian Mountains are found in Greenland and Western Europe. ...
... • Parts of Appalachian Mountains are found in Greenland and Western Europe. ...
Plate Tectonic Constraints on the Biogeography of Middle America
... are also not known but could have included a largelysubmarinemagmaticarc, parts of which may have subsequentlydispersed eastward as the GreaterAntilles.Much of what is now Middle America is apparentlyunderlainby oceanic crustat least as young as Late Cretaceous in age. By Late Cretaceous time the Gr ...
... are also not known but could have included a largelysubmarinemagmaticarc, parts of which may have subsequentlydispersed eastward as the GreaterAntilles.Much of what is now Middle America is apparentlyunderlainby oceanic crustat least as young as Late Cretaceous in age. By Late Cretaceous time the Gr ...
olivia Earthquake Re..
... This subduction is responsible for the majority of the tectonic activity experienced in South America. In addition to shallow (0–70 km), intermediate (70-300km) and great (~600km) depth earthquakes, active volcanic chains are present along South America’s west coast due to the melting of the Nazca p ...
... This subduction is responsible for the majority of the tectonic activity experienced in South America. In addition to shallow (0–70 km), intermediate (70-300km) and great (~600km) depth earthquakes, active volcanic chains are present along South America’s west coast due to the melting of the Nazca p ...
Plate Tectonics: The Rocky History of an Idea
... Close examination of a globe often results in the observation that most of the continents seem to fit together like a puzzle: the west African coastline seems to snuggle nicely into the east coast of South America and the Caribbean sea; and a similar fit appears across the Pacific. The fit is even m ...
... Close examination of a globe often results in the observation that most of the continents seem to fit together like a puzzle: the west African coastline seems to snuggle nicely into the east coast of South America and the Caribbean sea; and a similar fit appears across the Pacific. The fit is even m ...
Moss Flora of Central America
... from southeastern Australia, New Zealand, South Africa, and Patagonia, with isolated mountain stations in Borneo, eastern Africa, and the Andes of Colombia and Bolivia. A somewhat similar distribution pattern is shown by Tristichium mirabile and Aongstroemia julacea, which are present at high elevat ...
... from southeastern Australia, New Zealand, South Africa, and Patagonia, with isolated mountain stations in Borneo, eastern Africa, and the Andes of Colombia and Bolivia. A somewhat similar distribution pattern is shown by Tristichium mirabile and Aongstroemia julacea, which are present at high elevat ...
Geología Norteamerica
... was only a part of it. The name of the huge ocean that surrounded the Pangea supercontinent is Panthalassa. ...
... was only a part of it. The name of the huge ocean that surrounded the Pangea supercontinent is Panthalassa. ...
Rocking our world - University of Victoria
... mountains of BC and Alberta looks more like a train derailment than a wrinkle. There are huge shards of land folded up against each other—and they contain mineral deposits unlike the surrounding land.” Johnston believes this is evidence that what is now the western edge of North America was once a c ...
... mountains of BC and Alberta looks more like a train derailment than a wrinkle. There are huge shards of land folded up against each other—and they contain mineral deposits unlike the surrounding land.” Johnston believes this is evidence that what is now the western edge of North America was once a c ...
Continental drift script (version 2) File
... ✦ There is fossilized evidence of primitive flora and fauna found on continents that have drifted far apart. Fossils of Lystrosaurus have been found in India, South Africa and Australia while those of Mesosaurus have been found in Western countries of Africa and Brazil. Fossils of predecessors of Os ...
... ✦ There is fossilized evidence of primitive flora and fauna found on continents that have drifted far apart. Fossils of Lystrosaurus have been found in India, South Africa and Australia while those of Mesosaurus have been found in Western countries of Africa and Brazil. Fossils of predecessors of Os ...
Historical Geology and the history of the continents
... Sea level was very high and much of North America was covered by a shallow sea. ...
... Sea level was very high and much of North America was covered by a shallow sea. ...
Middle America
... - Mexico, Central America, and the Caribbean Islands. Geographically it is still part of North America, but culturally it is called Latin America. The heritage of Middle America is mainly Spanish because Spain once controlled most of Middle America. ...
... - Mexico, Central America, and the Caribbean Islands. Geographically it is still part of North America, but culturally it is called Latin America. The heritage of Middle America is mainly Spanish because Spain once controlled most of Middle America. ...
Geography Page 1
... Coastal Plain: The Coastal Plain of North America is located along the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Mexico. The land of this region is made up of broad lowlands that provide many excellent harbors. These busy harbors connect North America with the rest of the world. Appalachian Highlands: The Appa ...
... Coastal Plain: The Coastal Plain of North America is located along the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Mexico. The land of this region is made up of broad lowlands that provide many excellent harbors. These busy harbors connect North America with the rest of the world. Appalachian Highlands: The Appa ...
Where in the World Wednesday?
... • Western North America dominated by the Rocky Mountains – Also the Pacific Ranges: Sierra Nevada, Coast Range, and Cascades ...
... • Western North America dominated by the Rocky Mountains – Also the Pacific Ranges: Sierra Nevada, Coast Range, and Cascades ...
physical geography of latin america
... coasts of Central and South America • South America has vast grasslands • Llanos: Colombia and Venezuela • Pampas: Argentina and ...
... coasts of Central and South America • South America has vast grasslands • Llanos: Colombia and Venezuela • Pampas: Argentina and ...
Americas
The Americas, or America, also known as the Western Hemisphere and the New World, comprise the totality of territories in North America and South America. Along with their associated islands, they cover 8.3% of the Earth's total surface area (28.4% of its land area). The topography is dominated by the American Cordillera, a long chain of mountains that run the length of the west coast. The flatter eastern side of the Americas is dominated by large river basins, such as the Amazon, Mississippi, and La Plata. Since the Americas extend 14,000 km (8,700 mi) from north to south, the climate and ecology vary widely, from the arctic tundra of Northern Canada, Greenland, and Alaska, to the tropical rain forests in Central America and South America.Humans first settled the Americas from Asia between 42,000 and 17,000 years ago. A second migration of Na-Dene speakers followed later from Asia. The subsequent migration of the Inuit into the neoarctic around 3500 BCE completed what is generally regarded as the settlement by the indigenous peoples of the Americas.The first known European settlement in the Americas was by the Norse explorer Leif Ericson. However the colonization never became permanent and was later abandoned. The voyages of Christopher Columbus from 1492 to 1502 resulted in permanent contact with European (and subsequently, other Old World) powers, which led to the Columbian exchange. Diseases introduced from Europe and Africa devastated the indigenous peoples, and the European powers colonised the Americas. Mass emigration from Europe, including large numbers of indentured servants, and forced immigration of African slaves largely replaced the indigenous peoples.Decolonization of the Americas began with the American Revolution in 1776 and Haitian Revolution in 1791. Currently, almost all of the population of the Americas resides in independent countries; however, the legacy of the colonisation and settlement by Europeans is that the Americas share many common cultural traits, most notably Christianity and the use of Indo-European languages; primarily Spanish, English, Portuguese, French and to a lesser extent, Dutch. The population is approaching 1 billion, with over 65% of them living in one of the three most populous countries (the United States, Brazil, and Mexico). The most populous cities are São Paulo, Mexico City, New York City, Buenos Aires and Los Angeles.