Simulation of a Steady-State Electron Shock Wave in a Submicron
... c = T /m, higher electron Mach numbers may also be obtained by lowering the ambient temperature T0 . We present two parameter regimes for the ballistic diode in which there is a transition from subsonic to supersonic electron flow just to the right of the n+ − n junction and from supersonic to subso ...
... c = T /m, higher electron Mach numbers may also be obtained by lowering the ambient temperature T0 . We present two parameter regimes for the ballistic diode in which there is a transition from subsonic to supersonic electron flow just to the right of the n+ − n junction and from supersonic to subso ...
double-slit worksheet
... accelerated by a potential difference of 5 x 104 m/s V. Do the following calculations nonrelativistically. (Details can be found at http://www.hqrd.hitachi.co.jp/em/doubleslit.cfm.) a) How fast were these electrons moving? b) How fast is that compared to the speed of light? 42 %. c) How long would t ...
... accelerated by a potential difference of 5 x 104 m/s V. Do the following calculations nonrelativistically. (Details can be found at http://www.hqrd.hitachi.co.jp/em/doubleslit.cfm.) a) How fast were these electrons moving? b) How fast is that compared to the speed of light? 42 %. c) How long would t ...
Focusing light with the power of 1000 Hoover Dams
... electric field, which can be used to accelerate other particles. The region of high electric field travels through the plasma as a wave trailing in the wake of the light pulse. Charged particles are accelerated to high-energy in laser wake fields just as dolphins gain energy by swimming in phase wit ...
... electric field, which can be used to accelerate other particles. The region of high electric field travels through the plasma as a wave trailing in the wake of the light pulse. Charged particles are accelerated to high-energy in laser wake fields just as dolphins gain energy by swimming in phase wit ...
electricity - Aquinas High School
... Attraction and Repulsion The force of attraction or repulsion between electrically charged objects is electric force Double the charge = double the electric force Quadruple the charge = quadruple the force Double the distance = force is 4 X less Quadruple the distance = force is 16 X less ...
... Attraction and Repulsion The force of attraction or repulsion between electrically charged objects is electric force Double the charge = double the electric force Quadruple the charge = quadruple the force Double the distance = force is 4 X less Quadruple the distance = force is 16 X less ...
Lecture 6
... the dominant decay. Therefore this decay happens at very high probability. In fact the top quark decays before it can even interact with the anti-top quark via QCD and form new quarks out of the vacuum. We say it decays before it can hadronize. Next the W+ will decay. It can decay to a lepton and a ...
... the dominant decay. Therefore this decay happens at very high probability. In fact the top quark decays before it can even interact with the anti-top quark via QCD and form new quarks out of the vacuum. We say it decays before it can hadronize. Next the W+ will decay. It can decay to a lepton and a ...
Notes on electricity - Web Services Overview
... Electrical current is the movement of electrons. Conductors facilitate electrical current because good conductors have valence electrons that can move from atom to atom in the solid. Figure 7 is a graphical representation of current in a conductor represented by a solid cylinder. The two ends of the ...
... Electrical current is the movement of electrons. Conductors facilitate electrical current because good conductors have valence electrons that can move from atom to atom in the solid. Figure 7 is a graphical representation of current in a conductor represented by a solid cylinder. The two ends of the ...
introductory concepts - New Age International
... The distinction between different atoms arises from the varying number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in the atom. Different models have been proposed for the structure of an atom. In the Bohr model, electrons are assumed to revolve round the nucleus, without radiating any energy, in certain di ...
... The distinction between different atoms arises from the varying number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in the atom. Different models have been proposed for the structure of an atom. In the Bohr model, electrons are assumed to revolve round the nucleus, without radiating any energy, in certain di ...
Slide 28
... The quantum model describes the probability of locating an electron at any place. The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle – states it is impossible to know both the velocity (momentum) and the position of an electron at the same time The impact of a photon of light alters the motion of the electron in ...
... The quantum model describes the probability of locating an electron at any place. The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle – states it is impossible to know both the velocity (momentum) and the position of an electron at the same time The impact of a photon of light alters the motion of the electron in ...
Optical Spectra and Atomic Structure
... we see that 13.60 ev of energy must be delivered to a neutral hydrogen atom, in its ground state, to ionize the atom. This is called the ionization potential, for if hydrogen is placed in a gaseous discharge tube which is provided with electrodes, there can be no significant conduction of electricit ...
... we see that 13.60 ev of energy must be delivered to a neutral hydrogen atom, in its ground state, to ionize the atom. This is called the ionization potential, for if hydrogen is placed in a gaseous discharge tube which is provided with electrodes, there can be no significant conduction of electricit ...
The Quantum Atom
... is composed of a tiny nucleus in which a positive charge and nearly all its mass are concentrated, with the electrons at some distance away. It was apparent that since most alpha particles could go right through the gold foil, an atom must be largely an empty space. When an alpha particle came near ...
... is composed of a tiny nucleus in which a positive charge and nearly all its mass are concentrated, with the electrons at some distance away. It was apparent that since most alpha particles could go right through the gold foil, an atom must be largely an empty space. When an alpha particle came near ...
Bonding in Metals and Semiconductors
... Band-Gap energies. Next, we will observe the change induced when these diodes are cooled to liquid Nitrogen temperatures. This will allow us to observe how structural changes in the material also influence the Band-Gap energy. Finally, we will insert Hydrogen atoms into a Tungsten Trioxide (WO3) sol ...
... Band-Gap energies. Next, we will observe the change induced when these diodes are cooled to liquid Nitrogen temperatures. This will allow us to observe how structural changes in the material also influence the Band-Gap energy. Finally, we will insert Hydrogen atoms into a Tungsten Trioxide (WO3) sol ...
Direct observation of electron propagation and dielectric screening
... Direct (time-domain) access to these electronic and optical wave packets promises a unique insight into the photoelectric effect, including underlying electron propagation and phenomena as fundamental as dielectric screening of light fields at solid surfaces. Here we show that this can be achieved b ...
... Direct (time-domain) access to these electronic and optical wave packets promises a unique insight into the photoelectric effect, including underlying electron propagation and phenomena as fundamental as dielectric screening of light fields at solid surfaces. Here we show that this can be achieved b ...
New emerging experimental results (ref) in the last couple of
... reduction in the electronic energetic state by a factor q2 as predicted from equation-10. The CPD data indicated that a dramatic change has occurred in the electrons wave function otherwise the value obtained for the CPD would be high and negative (-4.7V). It is proposed that this change is related ...
... reduction in the electronic energetic state by a factor q2 as predicted from equation-10. The CPD data indicated that a dramatic change has occurred in the electrons wave function otherwise the value obtained for the CPD would be high and negative (-4.7V). It is proposed that this change is related ...
Modern Model
... Since Bohr, the model of the atom has become even more sophisticated. Scientists had to explain why even the thin lines in an emission spectrum could be resolved into more fine lines, and they had to include the discovery of neutrons into their model. The atom is the smallest unit of an element that ...
... Since Bohr, the model of the atom has become even more sophisticated. Scientists had to explain why even the thin lines in an emission spectrum could be resolved into more fine lines, and they had to include the discovery of neutrons into their model. The atom is the smallest unit of an element that ...
Alpha beta gamma decay worksheet April 8, 2008
... 11) During decay 11) ______ A) a proton is ejected from the nucleus. B) a neutron is ejected from the nucleus. C) a proton is transformed to a neutron. D) a neutron is transformed to a proton. 12) During decay 12) ______ A) a neutron is ejected from the nucleus. B) a neutron is transformed to a ...
... 11) During decay 11) ______ A) a proton is ejected from the nucleus. B) a neutron is ejected from the nucleus. C) a proton is transformed to a neutron. D) a neutron is transformed to a proton. 12) During decay 12) ______ A) a neutron is ejected from the nucleus. B) a neutron is transformed to a ...
THE HISTORY OF THE ATOM Table of Contents Black Boxes
... Democritus’ idea of the atom was largely ignored until an English schoolteacher did some experiments over 2000 years later, he was… John Dalton (1766-1804) “The Father of Modern Chemistry” Leading to his atomic theory… Dalton’s Atomic Theory All matter is made up of atoms Atoms are indestructibl ...
... Democritus’ idea of the atom was largely ignored until an English schoolteacher did some experiments over 2000 years later, he was… John Dalton (1766-1804) “The Father of Modern Chemistry” Leading to his atomic theory… Dalton’s Atomic Theory All matter is made up of atoms Atoms are indestructibl ...
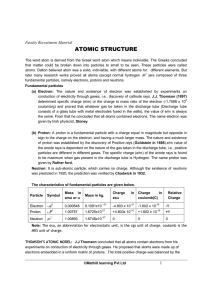
atomic structure
... the same. From that he concluded that all atoms contained electrons. The name electron was given by Irish physicist, Stoney (b) Proton: A proton is a fundamental particle with a charge equal in magnitude but opposite in sign to the charge on the electron, and having a much larger mass. The nature an ...
... the same. From that he concluded that all atoms contained electrons. The name electron was given by Irish physicist, Stoney (b) Proton: A proton is a fundamental particle with a charge equal in magnitude but opposite in sign to the charge on the electron, and having a much larger mass. The nature an ...
Triad Helium Nucleus
... to explain by cause-and-effect what holds the particles together in a structured way to create matter. Three possibilities have been considered. The first two apply only to the nucleus, while the last one has possibilities for holding electrons in place around the nucleus. 1. Strong nuclear force. T ...
... to explain by cause-and-effect what holds the particles together in a structured way to create matter. Three possibilities have been considered. The first two apply only to the nucleus, while the last one has possibilities for holding electrons in place around the nucleus. 1. Strong nuclear force. T ...
Chemistry Final Exam Study Guide
... ____ 75. Who was the man who lived from 460B.C.–370B.C. and was among the first to suggest the idea of atoms? a. Atomos c. Democritus b. Dalton d. Thomson ____ 76. Dalton's atomic theory included which idea? a. All atoms of all elements are the same size. b. Atoms of different elements always combin ...
... ____ 75. Who was the man who lived from 460B.C.–370B.C. and was among the first to suggest the idea of atoms? a. Atomos c. Democritus b. Dalton d. Thomson ____ 76. Dalton's atomic theory included which idea? a. All atoms of all elements are the same size. b. Atoms of different elements always combin ...
Electron

The electron is a subatomic particle, symbol e− or β−, with a negative elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family, and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have no known components or substructure. The electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton. Quantum mechanical properties of the electron include an intrinsic angular momentum (spin) of a half-integer value in units of ħ, which means that it is a fermion. Being fermions, no two electrons can occupy the same quantum state, in accordance with the Pauli exclusion principle. Like all matter, electrons have properties of both particles and waves, and so can collide with other particles and can be diffracted like light. The wave properties of electrons are easier to observe with experiments than those of other particles like neutrons and protons because electrons have a lower mass and hence a higher De Broglie wavelength for typical energies.Many physical phenomena involve electrons in an essential role, such as electricity, magnetism, and thermal conductivity, and they also participate in gravitational, electromagnetic and weak interactions. An electron generates an electric field surrounding it. An electron moving relative to an observer generates a magnetic field. External magnetic fields deflect an electron. Electrons radiate or absorb energy in the form of photons when accelerated. Laboratory instruments are capable of containing and observing individual electrons as well as electron plasma using electromagnetic fields, whereas dedicated telescopes can detect electron plasma in outer space. Electrons have many applications, including electronics, welding, cathode ray tubes, electron microscopes, radiation therapy, lasers, gaseous ionization detectors and particle accelerators.Interactions involving electrons and other subatomic particles are of interest in fields such as chemistry and nuclear physics. The Coulomb force interaction between positive protons inside atomic nuclei and negative electrons composes atoms. Ionization or changes in the proportions of particles changes the binding energy of the system. The exchange or sharing of the electrons between two or more atoms is the main cause of chemical bonding. British natural philosopher Richard Laming first hypothesized the concept of an indivisible quantity of electric charge to explain the chemical properties of atoms in 1838; Irish physicist George Johnstone Stoney named this charge 'electron' in 1891, and J. J. Thomson and his team of British physicists identified it as a particle in 1897. Electrons can also participate in nuclear reactions, such as nucleosynthesis in stars, where they are known as beta particles. Electrons may be created through beta decay of radioactive isotopes and in high-energy collisions, for instance when cosmic rays enter the atmosphere. The antiparticle of the electron is called the positron; it is identical to the electron except that it carries electrical and other charges of the opposite sign. When an electron collides with a positron, both particles may be totally annihilated, producing gamma ray photons.