Ch. 19
... a) Sketch the situation. b) What is the work done by the electric field on the charge if it moves 5.5 m? c) What is the change in electrostatic potential energy of the charge? ...
... a) Sketch the situation. b) What is the work done by the electric field on the charge if it moves 5.5 m? c) What is the change in electrostatic potential energy of the charge? ...
X PS EM - deo kadapa
... Ans:- The specific heat capacity of water is large so, water requires large amount of heat for a given rise in temperature. Thus acting a very good coolant. (5) State the principle of calorimeter or method of mixture? Ans:- When two or more bodies at different temperature are brought into thermal co ...
... Ans:- The specific heat capacity of water is large so, water requires large amount of heat for a given rise in temperature. Thus acting a very good coolant. (5) State the principle of calorimeter or method of mixture? Ans:- When two or more bodies at different temperature are brought into thermal co ...
maitland/5230/41270 Ideas Part 2
... television picture tubes have a layer of the phosphor coated on the inside of the glass screen. The beam of electrons projected by the cathode excites the fluorescent phosphor layer on the screen. That is, the phosphors glow. Most cathode ray tubes use zinc sulfide that glows with a characteristic b ...
... television picture tubes have a layer of the phosphor coated on the inside of the glass screen. The beam of electrons projected by the cathode excites the fluorescent phosphor layer on the screen. That is, the phosphors glow. Most cathode ray tubes use zinc sulfide that glows with a characteristic b ...
Pdf - Text of NPTEL IIT Video Lectures
... So, in this case when we are considering the spring mass system we are always taking this small spring mass system as very representative problem; it is very easy to understand the concept of this. So, all the basic concepts we are trying to understand using this simple problem. So, in this particul ...
... So, in this case when we are considering the spring mass system we are always taking this small spring mass system as very representative problem; it is very easy to understand the concept of this. So, all the basic concepts we are trying to understand using this simple problem. So, in this particul ...
Faraday and the Electromagnetic Theory of Light
... Michael Faraday (1791-1867) is probably best known for his discovery of electromagnetic induction, his contributions to electrical engineering and electrochemistry or due to the fact that he was responsible for introducing the concept of field in physics to describe electromagnetic interaction. But ...
... Michael Faraday (1791-1867) is probably best known for his discovery of electromagnetic induction, his contributions to electrical engineering and electrochemistry or due to the fact that he was responsible for introducing the concept of field in physics to describe electromagnetic interaction. But ...
SCHLOSS RINGBERG
... of a gold single crystal.[1] The most probable scattering channel for an initially highly vibrationally excited molecule (vibrational quantum number v = 16) involves the transfer of nearly 2 eV of energy from the molecule to the surface.[2] Due to the large energy mismatch between the vibrational sp ...
... of a gold single crystal.[1] The most probable scattering channel for an initially highly vibrationally excited molecule (vibrational quantum number v = 16) involves the transfer of nearly 2 eV of energy from the molecule to the surface.[2] Due to the large energy mismatch between the vibrational sp ...
The Structure of Aether and the Mechanics of the Electromagnetic
... fractal plenum (AFP) fits into the illustration for the first generation of electromagnetic waves as presented last year at the 15th NPA Conference. First of all, it was proposed that the electromagnetic wave spectrum is divided into roughly three equal logarithmic segments for each of the three gen ...
... fractal plenum (AFP) fits into the illustration for the first generation of electromagnetic waves as presented last year at the 15th NPA Conference. First of all, it was proposed that the electromagnetic wave spectrum is divided into roughly three equal logarithmic segments for each of the three gen ...
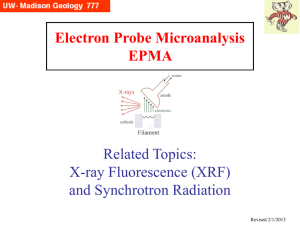
x-rays
... There are other techniques, similar in some ways, that are worth discussing, that utilize x-rays for secondary x-ray fluorescence. Two in particular are: • XRF (X-Ray Fluorescence), where x-rays from a sealed tube are used to produce x-rays by secondary fluorescence in samples of interest (tradition ...
... There are other techniques, similar in some ways, that are worth discussing, that utilize x-rays for secondary x-ray fluorescence. Two in particular are: • XRF (X-Ray Fluorescence), where x-rays from a sealed tube are used to produce x-rays by secondary fluorescence in samples of interest (tradition ...