ENG 220
... 16. Be able to calculate the gain for an Inverting Op-Amp circuit and a Non-inverting Op-Amp circuit. 17. Understand Virtual Ground and the affect on input resistance of an inverting op-amp. 18. Understand an op-amp summing circuit. 19. Understand the function of “bypass” capacitors. ...
... 16. Be able to calculate the gain for an Inverting Op-Amp circuit and a Non-inverting Op-Amp circuit. 17. Understand Virtual Ground and the affect on input resistance of an inverting op-amp. 18. Understand an op-amp summing circuit. 19. Understand the function of “bypass” capacitors. ...
Lab 8: Series RC Circuit
... Plot of the voltage across the capacitor as a function time – Use either Vpulse or Digclock as the voltage source • Instructions on setting up a transient simulation using these sources are posted under Resources/Technical Support: Circuit Simulation • Include the input voltage in the plot and show ...
... Plot of the voltage across the capacitor as a function time – Use either Vpulse or Digclock as the voltage source • Instructions on setting up a transient simulation using these sources are posted under Resources/Technical Support: Circuit Simulation • Include the input voltage in the plot and show ...
Spirit 2
... Putting “Electric Current” in Recognizable terms: Electric current is the flow of electric charge from one location to another. This flow of charge is usually electrons, but it can actually be any charge that is in motion. It is measured in amperes, “A”, which is the flow of 1 Coulomb of charge per ...
... Putting “Electric Current” in Recognizable terms: Electric current is the flow of electric charge from one location to another. This flow of charge is usually electrons, but it can actually be any charge that is in motion. It is measured in amperes, “A”, which is the flow of 1 Coulomb of charge per ...
Define and Explain on Current and Resistance
... Experimentally, it was found that current is proportional to voltage for conductors. The proportionality constant is the resistance in the circuit. This relationship is called Ohm's law: V = IR. Resistance is measured in ohms ( W): an ohm is equal to 1 volt/1 ampere. The resistance of a conductor de ...
... Experimentally, it was found that current is proportional to voltage for conductors. The proportionality constant is the resistance in the circuit. This relationship is called Ohm's law: V = IR. Resistance is measured in ohms ( W): an ohm is equal to 1 volt/1 ampere. The resistance of a conductor de ...
34-3 Voltage Sources 34-4 Electric Resistance 34
... Because our wall sockets run on AC and many of electrical appliances we use run on battery which is a DC current, we need to convert between the two current types in order to plug these devices in. o To convert we use a diode which is an electronic device that acts as a one way valve for electron fl ...
... Because our wall sockets run on AC and many of electrical appliances we use run on battery which is a DC current, we need to convert between the two current types in order to plug these devices in. o To convert we use a diode which is an electronic device that acts as a one way valve for electron fl ...
Electricity Study Guide KEY
... 12. What can you predict would happen to the resistance in a device if the voltage decreases, but the current stays the same? Explain how you arrived at this answer. You can show an example if necessary. Resistance decreases 13. What can you predict would happen to the voltage in a device if the res ...
... 12. What can you predict would happen to the resistance in a device if the voltage decreases, but the current stays the same? Explain how you arrived at this answer. You can show an example if necessary. Resistance decreases 13. What can you predict would happen to the voltage in a device if the res ...
Lesson 2 - UC Berkeley IEEE
... Calculating Resistance • It’s possible to calculate resistance of a resistor using the color bands on it – AB represent a 2 digit number – C represents the magnitude – Resistance = AB * 10C + D ...
... Calculating Resistance • It’s possible to calculate resistance of a resistor using the color bands on it – AB represent a 2 digit number – C represents the magnitude – Resistance = AB * 10C + D ...
References
... The cell circuit configuration of a DT-CNN implemented with MOBILE’s. Here, the cell with positive feedback and an inverting state of MOBILE are clocked with the VA clock, the states of inverter are clocked with the VB clock. VA and VB are complementary clocks. Hence, the output A is complementary w ...
... The cell circuit configuration of a DT-CNN implemented with MOBILE’s. Here, the cell with positive feedback and an inverting state of MOBILE are clocked with the VA clock, the states of inverter are clocked with the VB clock. VA and VB are complementary clocks. Hence, the output A is complementary w ...
MS Word
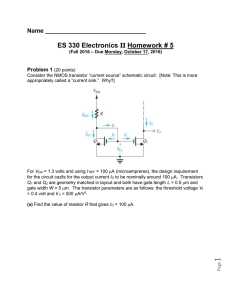
... For VDD = 1.3 volts and using I REF = 100 A (microampreres), the design requirement for the circuit cazlls for the output current IO to be nominally around 100 A. Transistors Q1 and Q2 are geometry matched in layout and both have gate length L = 0.5 m and gate width W = 5 m. The transistor param ...
... For VDD = 1.3 volts and using I REF = 100 A (microampreres), the design requirement for the circuit cazlls for the output current IO to be nominally around 100 A. Transistors Q1 and Q2 are geometry matched in layout and both have gate length L = 0.5 m and gate width W = 5 m. The transistor param ...
Memristor
The memristor (/ˈmɛmrɨstər/; a portmanteau of memory resistor) was a term coined in 1971 by circuit theorist Leon Chua as a missing non-linear passive two-terminal electrical component relating electric charge and magnetic flux linkage. The operation of RRAM devices was recently connected to the memristor concept According to the characterizing mathematical relations, the memristor would hypothetically operate in the following way: The memristor's electrical resistance is not constant but depends on the history of current that had previously flowed through the device, i.e., its present resistance depends on how much electric charge has flowed in what direction through it in the past. The device remembers its history - the so-called non-volatility property: When the electric power supply is turned off, the memristor remembers its most recent resistance until it is turned on again.Leon Chua has more recently argued that the definition could be generalized to cover all forms of two-terminal non-volatile memory devices based on resistance switching effects although some experimental evidence contradicts this claim, since a non-passive nanobattery effect is observable in resistance switching memory. Chua also argued that the memristor is the oldest known circuit element, with its effects predating the resistor, capacitor and inductor.In 2008, a team at HP Labs claimed to have found Chua's missing memristor based on an analysis of a thin film of titanium dioxide; the HP result was published in Nature. The memristor is currently under development by various teams including Hewlett-Packard, SK Hynix and HRL Laboratories.These devices are intended for applications in nanoelectronic memories, computer logic and neuromorphic/neuromemristive computer architectures. In October 2011, the HP team announced the commercial availability of memristor technology within 18 months, as a replacement for Flash, SSD, DRAM and SRAM. Commercial availability of new memory was more recently estimated as 2018. In March 2012, a team of researchers from HRL Laboratories and the University of Michigan announced the first functioning memristor array built on a CMOS chip.