Combinations of resistors and non-ideal meters
... Recall that to measure the voltage drop across a given resistor, you place a voltmeter in parallel with it. The resistance of the voltmeter should be large so that it does not change significantly the current through the resistor (and in turn the voltage drop across the resistor). Create a circuit c ...
... Recall that to measure the voltage drop across a given resistor, you place a voltmeter in parallel with it. The resistance of the voltmeter should be large so that it does not change significantly the current through the resistor (and in turn the voltage drop across the resistor). Create a circuit c ...
Compact Device Modelling for System Simulation - Mos-AK
... • IGBT turn-on (left), IGBT turn-off shown to validate switching (right). energies. ...
... • IGBT turn-on (left), IGBT turn-off shown to validate switching (right). energies. ...
Combining Light Bulbs in Parallel
... 1. The graph below shows the I-V characteristics of two conductors, X and Y. The conductors are connected in series to a battery whose voltage is such that the power dissipated in each of the two resistors is the same. ...
... 1. The graph below shows the I-V characteristics of two conductors, X and Y. The conductors are connected in series to a battery whose voltage is such that the power dissipated in each of the two resistors is the same. ...
MOSFETs: Linear Model
... where the drain-source voltage is replaced by the change in channel voltage over a distance dx, namely dVC. Both sides of the equation can be integrated from the source to the drain, so that x varies from 0 to the gate length, L, and the channel voltage VC varies from 0 to the drain-source voltage, ...
... where the drain-source voltage is replaced by the change in channel voltage over a distance dx, namely dVC. Both sides of the equation can be integrated from the source to the drain, so that x varies from 0 to the gate length, L, and the channel voltage VC varies from 0 to the drain-source voltage, ...
Capacitors and RC circuits
... 1. Connect a cylindrical capacitor to the power supply in DC and apply a voltage between 5 and 10 V. 2. Disconnect the capacitor before turning the power supply off. (The capacitor should now have a charge.) 3. Connect two wires to the capacitor – one to each terminal. The wire should just be hangin ...
... 1. Connect a cylindrical capacitor to the power supply in DC and apply a voltage between 5 and 10 V. 2. Disconnect the capacitor before turning the power supply off. (The capacitor should now have a charge.) 3. Connect two wires to the capacitor – one to each terminal. The wire should just be hangin ...
Ohm`s Law states that current is proportional to voltage
... be interpreted as the voltage drop across a resistor produced by the flow of current I. The phrase IR drop is often used for this voltage. If voltage is measured at various points in a circuit, it will be seen to increase at the voltage source and decrease at the resistor. Voltage is similar to flui ...
... be interpreted as the voltage drop across a resistor produced by the flow of current I. The phrase IR drop is often used for this voltage. If voltage is measured at various points in a circuit, it will be seen to increase at the voltage source and decrease at the resistor. Voltage is similar to flui ...
CURRENT, RESISTANCE AND ELECTROMOTIVE FORCE Electric
... CURRENT, RESISTANCE AND ELECTROMOTIVE FORCE Electric current Up to now, we have considered charges at rest (ELECTROSTATICS) But E exerts a force ⇒ charges move if they are free to do so. Definition: ELECTRIC CURRENT is the rate of flow of charge: I = Units of current: ...
... CURRENT, RESISTANCE AND ELECTROMOTIVE FORCE Electric current Up to now, we have considered charges at rest (ELECTROSTATICS) But E exerts a force ⇒ charges move if they are free to do so. Definition: ELECTRIC CURRENT is the rate of flow of charge: I = Units of current: ...
RL Circuit - Kuniv.edu.kw
... a result of changing current in its windings. It depends on the length, size, shape, number of turns and the kind of core material. It does not depend on the value of frequency of the applied voltage. The mathematical symbol for inductance is L and the unit of inductance is Henry (H). In AC circuits ...
... a result of changing current in its windings. It depends on the length, size, shape, number of turns and the kind of core material. It does not depend on the value of frequency of the applied voltage. The mathematical symbol for inductance is L and the unit of inductance is Henry (H). In AC circuits ...
psaa electromotive force worksheet
... On some devices, resistance is lowered as the temperature is increased. These devices are called thermistors or surgistors. Thermistors are used to control current and also as temperature sensors. Surgistors are used to prevent a large current in a device when it is first turned on. Surgistors are o ...
... On some devices, resistance is lowered as the temperature is increased. These devices are called thermistors or surgistors. Thermistors are used to control current and also as temperature sensors. Surgistors are used to prevent a large current in a device when it is first turned on. Surgistors are o ...
eet 307 power electronics 2005-2006
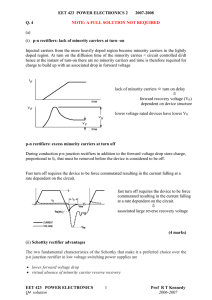
... (i) p-n rectifiers: lack of minority carriers at turn -on Injected carriers from the more heavily doped region become minority carriers in the lightly doped region. At turn on the diffusion time of the minority carries < circuit controlled di/dt hence at the instant of turn-on there are no minority ...
... (i) p-n rectifiers: lack of minority carriers at turn -on Injected carriers from the more heavily doped region become minority carriers in the lightly doped region. At turn on the diffusion time of the minority carries < circuit controlled di/dt hence at the instant of turn-on there are no minority ...
Memristor
The memristor (/ˈmɛmrɨstər/; a portmanteau of memory resistor) was a term coined in 1971 by circuit theorist Leon Chua as a missing non-linear passive two-terminal electrical component relating electric charge and magnetic flux linkage. The operation of RRAM devices was recently connected to the memristor concept According to the characterizing mathematical relations, the memristor would hypothetically operate in the following way: The memristor's electrical resistance is not constant but depends on the history of current that had previously flowed through the device, i.e., its present resistance depends on how much electric charge has flowed in what direction through it in the past. The device remembers its history - the so-called non-volatility property: When the electric power supply is turned off, the memristor remembers its most recent resistance until it is turned on again.Leon Chua has more recently argued that the definition could be generalized to cover all forms of two-terminal non-volatile memory devices based on resistance switching effects although some experimental evidence contradicts this claim, since a non-passive nanobattery effect is observable in resistance switching memory. Chua also argued that the memristor is the oldest known circuit element, with its effects predating the resistor, capacitor and inductor.In 2008, a team at HP Labs claimed to have found Chua's missing memristor based on an analysis of a thin film of titanium dioxide; the HP result was published in Nature. The memristor is currently under development by various teams including Hewlett-Packard, SK Hynix and HRL Laboratories.These devices are intended for applications in nanoelectronic memories, computer logic and neuromorphic/neuromemristive computer architectures. In October 2011, the HP team announced the commercial availability of memristor technology within 18 months, as a replacement for Flash, SSD, DRAM and SRAM. Commercial availability of new memory was more recently estimated as 2018. In March 2012, a team of researchers from HRL Laboratories and the University of Michigan announced the first functioning memristor array built on a CMOS chip.