Galaxy Notes File
... member of a small cluster called the Local Group which contains about 40 galaxies. The largest member of the Local Group is M 31, with the Milky Way coming in second in size. ...
... member of a small cluster called the Local Group which contains about 40 galaxies. The largest member of the Local Group is M 31, with the Milky Way coming in second in size. ...
Galaxy / Cluster Ecosystem Ming Sun (University of Alabama in Huntsville)
... Radio AGN in clusters and groups that do not reside in large cool cores are generally associated with small coronae. Strong radio AGN in groups do not co-exist with strong, large cool cores. They are generally associated with coronae. ...
... Radio AGN in clusters and groups that do not reside in large cool cores are generally associated with small coronae. Strong radio AGN in groups do not co-exist with strong, large cool cores. They are generally associated with coronae. ...
December - Rose City Astronomers
... scanty star grouping of DolidzeDžimšelejšvili 1 (Do-Dž 1). This triple star and open cluster combo is a remarkable stroke of cosmic serendipity in an area nearly devoid of other major deep-sky objects. The refractor at 44x shows the 12' diameter star cluster as six stars (9th to 11thmagnitude) embed ...
... scanty star grouping of DolidzeDžimšelejšvili 1 (Do-Dž 1). This triple star and open cluster combo is a remarkable stroke of cosmic serendipity in an area nearly devoid of other major deep-sky objects. The refractor at 44x shows the 12' diameter star cluster as six stars (9th to 11thmagnitude) embed ...
81 KB - CSIRO Publishing
... II. Contains Stars An additional key requirement is that a galaxy be a stellar system, (i.e. it must include some stars). In the case of recently discovered ultra-faint dwarf spheroidal galaxies, the number of stars inferred can be as low as a few hundred. It is possible, and indeed predicted by som ...
... II. Contains Stars An additional key requirement is that a galaxy be a stellar system, (i.e. it must include some stars). In the case of recently discovered ultra-faint dwarf spheroidal galaxies, the number of stars inferred can be as low as a few hundred. It is possible, and indeed predicted by som ...
Chapter 16
... 2. The center portion was the first to become dense enough for stars to form. Dense pockets in orbit around the center became globular clusters. 3. The initial cloud had some rotation, and as it contracted it spun faster. The rotating matter formed into a disk. 4. Density waves formed in the Galaxy’ ...
... 2. The center portion was the first to become dense enough for stars to form. Dense pockets in orbit around the center became globular clusters. 3. The initial cloud had some rotation, and as it contracted it spun faster. The rotating matter formed into a disk. 4. Density waves formed in the Galaxy’ ...
24.1 Hubble`s Galaxy Classification
... clusters in the halo of our Galaxy, while Cepheid variables, being so much brighter, allow measurement of galaxies to about 25 Mpc away. The image below shows a Cepheid variable spotted in a galaxy in the Virgo Cluster of galaxies. You can see it getting fainter and brighter in the insets. ...
... clusters in the halo of our Galaxy, while Cepheid variables, being so much brighter, allow measurement of galaxies to about 25 Mpc away. The image below shows a Cepheid variable spotted in a galaxy in the Virgo Cluster of galaxies. You can see it getting fainter and brighter in the insets. ...
Sample Exam for 3 rd Astro Exam
... A. In the galactic halo. B. In the galactic nuclear bulge C. Beyond the Sun above and below the galactic mid-plane D. Perpendicular to the galactic plane. E. In the galactic mid-plane 16. True or false: The Sun is located within the galactic gas layer of the Milky Way A. True B. False C. I have no @ ...
... A. In the galactic halo. B. In the galactic nuclear bulge C. Beyond the Sun above and below the galactic mid-plane D. Perpendicular to the galactic plane. E. In the galactic mid-plane 16. True or false: The Sun is located within the galactic gas layer of the Milky Way A. True B. False C. I have no @ ...
Milky Way Galaxy
... called the Local Group which contains about 40 galaxies. The largest member of the Local Group is M 31, with the Milky Way coming in second in size. (NOAO/AURA Photo) ...
... called the Local Group which contains about 40 galaxies. The largest member of the Local Group is M 31, with the Milky Way coming in second in size. (NOAO/AURA Photo) ...
Extragalactic Distances from Planetary Nebulae
... The real problem comes from the absolute luminosity of the PNLF cutoff … M* = 4.47 corresponds to a luminosity of 600 L To produce 600 L of [O III] emission, a central star must have a luminosity of L > 6,000 L. A central star with L > 6,000 L must be more massive than M > 0.6 M. Such st ...
... The real problem comes from the absolute luminosity of the PNLF cutoff … M* = 4.47 corresponds to a luminosity of 600 L To produce 600 L of [O III] emission, a central star must have a luminosity of L > 6,000 L. A central star with L > 6,000 L must be more massive than M > 0.6 M. Such st ...
Chapter 12 Quiz, Nov. 28, 2012, Astro 162, Section 4 12-1
... 12-31. The time for a fluctuation in brightness of a quasar allows astronomers to place an upper limit on its a) luminosity. b) size. X c) age. d) distance. Chapter 12 Thought/Writing Questions 12-32. Why are the spiral arms of our Galaxy brighter than the regions between them? The O and B stars for ...
... 12-31. The time for a fluctuation in brightness of a quasar allows astronomers to place an upper limit on its a) luminosity. b) size. X c) age. d) distance. Chapter 12 Thought/Writing Questions 12-32. Why are the spiral arms of our Galaxy brighter than the regions between them? The O and B stars for ...
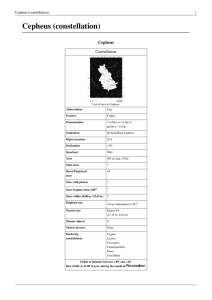
Cepheus (constellation)
... due to its deep red colour. It is a semiregular variable star with a minimum magnitude of 5.1 and a maximum magnitude of 3.4. Its period is approximately 2 years.[1] The star is around 11.8 AU in radius. If it were placed at the centre of our Solar System, it would extend to the orbit of Saturn.[cit ...
... due to its deep red colour. It is a semiregular variable star with a minimum magnitude of 5.1 and a maximum magnitude of 3.4. Its period is approximately 2 years.[1] The star is around 11.8 AU in radius. If it were placed at the centre of our Solar System, it would extend to the orbit of Saturn.[cit ...
M104: The Sombrero Galaxy
... the Sombrero, appearing like a shadow against the bright bulge of stars. In this image, NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope easily resolves the Sombrero’s rich system of star clusters, called globular clusters. Astronomers estimate that the Sombrero contains nearly 2,000 globular clusters —10 times as man ...
... the Sombrero, appearing like a shadow against the bright bulge of stars. In this image, NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope easily resolves the Sombrero’s rich system of star clusters, called globular clusters. Astronomers estimate that the Sombrero contains nearly 2,000 globular clusters —10 times as man ...
M104: The Sombrero Galaxy
... the Sombrero, appearing like a shadow against the bright bulge of stars. In this image, NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope easily resolves the Sombrero’s rich system of star clusters, called globular clusters. Astronomers estimate that the Sombrero contains nearly 2,000 globular clusters —10 times as man ...
... the Sombrero, appearing like a shadow against the bright bulge of stars. In this image, NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope easily resolves the Sombrero’s rich system of star clusters, called globular clusters. Astronomers estimate that the Sombrero contains nearly 2,000 globular clusters —10 times as man ...
OSP2016Level 3 Map - Oregon Star Party
... What is it? V404 Cyg is a black hole (12+/- 3 solar masses) with late K or early G type stellar companion that’s slightly smaller than the Sun, orbiting each other in less than 6.5 days. They are approximately 7800 light years away. Why you want to see it: The stellar companion is distorted into a ...
... What is it? V404 Cyg is a black hole (12+/- 3 solar masses) with late K or early G type stellar companion that’s slightly smaller than the Sun, orbiting each other in less than 6.5 days. They are approximately 7800 light years away. Why you want to see it: The stellar companion is distorted into a ...
Draco: The Dragon - Courtney Stookey
... The Constellation and Stars The Draco constellation is found in the northern hemisphere. Originally, it was charted by Ptolemy in the 2nd century. The constellation is found in an area that is 1083 square degrees. “It can be seen at latitudes between +90° and -15° and is best visible at 9 p.m. durin ...
... The Constellation and Stars The Draco constellation is found in the northern hemisphere. Originally, it was charted by Ptolemy in the 2nd century. The constellation is found in an area that is 1083 square degrees. “It can be seen at latitudes between +90° and -15° and is best visible at 9 p.m. durin ...
M101: The Pinwheel Galaxy
... like Messier 101 (M101) shown in this Hubble Space Telescope image, lasted billions of years. This photograph of M101, nicknamed the Pinwheel Galaxy, showcases a spiral galaxy’s well-known features. A galaxy is a collection of stars, gas, and dust held together by gravity. Galaxies come in three dif ...
... like Messier 101 (M101) shown in this Hubble Space Telescope image, lasted billions of years. This photograph of M101, nicknamed the Pinwheel Galaxy, showcases a spiral galaxy’s well-known features. A galaxy is a collection of stars, gas, and dust held together by gravity. Galaxies come in three dif ...
Pre-Lab
... Galaxy seen from the inside (but not the center). With unaided eyes one other galaxy can be seen in the northern sky, the Andromeda nebulae, as it was called before its true nature was known. It is a faint fuzzy patch in the region of the sky containing the stars of the constellation Andromeda. Two ...
... Galaxy seen from the inside (but not the center). With unaided eyes one other galaxy can be seen in the northern sky, the Andromeda nebulae, as it was called before its true nature was known. It is a faint fuzzy patch in the region of the sky containing the stars of the constellation Andromeda. Two ...
Robert_Minchin_Galaxies_2011_REU
... galaxies are often measured using the 21-cm line of neutral hydrogen. • For elliptical and spheroidal galaxies, which are gas poor, velocity dispersions from stellar spectroscopy can be used ...
... galaxies are often measured using the 21-cm line of neutral hydrogen. • For elliptical and spheroidal galaxies, which are gas poor, velocity dispersions from stellar spectroscopy can be used ...
Spiral Galaxies - Astronomy Centre
... • Spiral disks are relatively blue due to light from hot, massive, young stars • Elliptical galaxies are relatively red due to the dominant population of older, lower-mass stars ...
... • Spiral disks are relatively blue due to light from hot, massive, young stars • Elliptical galaxies are relatively red due to the dominant population of older, lower-mass stars ...
Galaxies Galaxies M81
... galaxies are grouped in clusters ranging in size from a few dozens to thousands of galaxies. The Coma Cluster, shown at right, is 300 million light years from the Milky Way and contains more than 1,000 (and possibly as many as 10,000) galaxies. ...
... galaxies are grouped in clusters ranging in size from a few dozens to thousands of galaxies. The Coma Cluster, shown at right, is 300 million light years from the Milky Way and contains more than 1,000 (and possibly as many as 10,000) galaxies. ...
Galaxy Questions Info
... Spiral arms — Curved extensions beginning at the bulge of a spiral galaxy, giving it a "pinwheel" appearance. Spiral arms contain a lot of gas and dust as well as young blue stars. Spiral arms are found only in spiral galaxies. Halo — The halo primarily contains individual old stars and clusters of ...
... Spiral arms — Curved extensions beginning at the bulge of a spiral galaxy, giving it a "pinwheel" appearance. Spiral arms contain a lot of gas and dust as well as young blue stars. Spiral arms are found only in spiral galaxies. Halo — The halo primarily contains individual old stars and clusters of ...
CONSTELLATION CEPHEUS, KING OF ETHIOPIA Cepheus is a
... NGC 188 is an open cluster first discovered by John Herschel in 1825. It is the oldest known open clusters and the closest to the north celestial pole. NGC 6946 (The Fireworks Galaxy) is a spiral galaxy in which nine supernovae have been observed, more than in any other galaxy. IC 469 is another spi ...
... NGC 188 is an open cluster first discovered by John Herschel in 1825. It is the oldest known open clusters and the closest to the north celestial pole. NGC 6946 (The Fireworks Galaxy) is a spiral galaxy in which nine supernovae have been observed, more than in any other galaxy. IC 469 is another spi ...
Universe 8e Lecture Chapter 24 Galaxies
... cluster of galaxies is not large enough to account for the observed motions of the galaxies; a large amount of unobserved mass must also be present. This situation is called the dark-matter problem. Hot intergalactic gases in rich clusters account for a small part of the unobserved mass. These gases ...
... cluster of galaxies is not large enough to account for the observed motions of the galaxies; a large amount of unobserved mass must also be present. This situation is called the dark-matter problem. Hot intergalactic gases in rich clusters account for a small part of the unobserved mass. These gases ...
PEGASUS, THE FLYING HORSE Pegasus is a constellation in the
... constellation boundaries, as set by Eugène Delporte in 1930, are defined as a polygon of 35 segments. In the equatorial coordinate system, the right ascension coordinates of these borders lie between 21h 12.6m and 00h. Its position in the Northern Celestial Hemisphere means that the whole constellat ...
... constellation boundaries, as set by Eugène Delporte in 1930, are defined as a polygon of 35 segments. In the equatorial coordinate system, the right ascension coordinates of these borders lie between 21h 12.6m and 00h. Its position in the Northern Celestial Hemisphere means that the whole constellat ...
Coma Berenices

Coma Berenices is a traditional asterism that has since been defined as one of the 88 modern constellations. It is located near Arcturus, and the constellation Leo to which it formerly belonged, and contains the North Galactic Pole. Its name means ""Berenice's Hair"" (in Greek, via Latin), and refers to the legend of Queen Berenice II of Egypt, who sacrificed her long hair.