ASSEMBLY INSTRUCTIONS & USER’S MANUAL Analog Synthesizer / Moogfest 2014 Kit
... NOTE: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can ...
... NOTE: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can ...
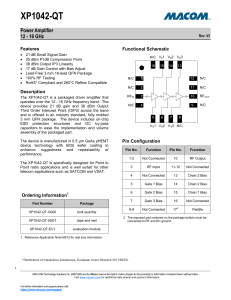
XP1042-QT
... at 5 V with 125, 125, 250 mA respectively. It is recommended to use active bias to keep the currents constant in order to maintain the best performance over temperature. Depending on the supply voltage available and the power dissipation constraints, the bias circuit may be a single transistor or a ...
... at 5 V with 125, 125, 250 mA respectively. It is recommended to use active bias to keep the currents constant in order to maintain the best performance over temperature. Depending on the supply voltage available and the power dissipation constraints, the bias circuit may be a single transistor or a ...
LTM8020 - 200mA, 36V DC/DC uModule
... is diode ORed with the LTM8020’s output. If the VIN pin is allowed to float and the SHDN pin is held high (either by a logic signal or because it is tied to VIN), then the LTM8020’s internal circuitry will pull its quiescent current from its output. This is fine if your system can tolerate a few mil ...
... is diode ORed with the LTM8020’s output. If the VIN pin is allowed to float and the SHDN pin is held high (either by a logic signal or because it is tied to VIN), then the LTM8020’s internal circuitry will pull its quiescent current from its output. This is fine if your system can tolerate a few mil ...
SN65HVD11-HT - Texas Instruments
... The SN65HVD11-HT device combines a 3-state differential line driver and differential input line receiver that operates with a single 3.3-V power supply. It is designed for balanced transmission lines and meets or exceeds ANSI TIA/EIA-485-A and ISO 8482:1993, with the exception that the thermal shutd ...
... The SN65HVD11-HT device combines a 3-state differential line driver and differential input line receiver that operates with a single 3.3-V power supply. It is designed for balanced transmission lines and meets or exceeds ANSI TIA/EIA-485-A and ISO 8482:1993, with the exception that the thermal shutd ...
MP174 - Monolithic Power System
... Start-Up and Under-Voltage Lockout The internal high-voltage regulator self-supplies the IC from the Drain pin. When VCC voltage reaches 5.6V, the IC starts switching and the internal high voltage regulator turns off. The internal high-voltage regulator turns on to charge the external VCC capacitor ...
... Start-Up and Under-Voltage Lockout The internal high-voltage regulator self-supplies the IC from the Drain pin. When VCC voltage reaches 5.6V, the IC starts switching and the internal high voltage regulator turns off. The internal high-voltage regulator turns on to charge the external VCC capacitor ...
36-W, Universal Input, >90% Efficiency, Dual Output, Auxiliary
... is independent of the MOSFET RDS(on), parasitic inductance or ringing allowing flexibility to designers in component selection and PCB layout. This control method enables maximum SR conduction time and highest rectifier efficiency for a given MOSFET. The controller’s built-in intelligence to detect ...
... is independent of the MOSFET RDS(on), parasitic inductance or ringing allowing flexibility to designers in component selection and PCB layout. This control method enables maximum SR conduction time and highest rectifier efficiency for a given MOSFET. The controller’s built-in intelligence to detect ...
lab-manual-electronic-devices-and
... negative half cycle no voltage is available across the load. This explains the unidirectional pulsating dc waveform obtained as output. The process of removing one half the input signal to establish a dc level is aptly called half wave rectification. The Full Wave Rectifier In the previous Power Dio ...
... negative half cycle no voltage is available across the load. This explains the unidirectional pulsating dc waveform obtained as output. The process of removing one half the input signal to establish a dc level is aptly called half wave rectification. The Full Wave Rectifier In the previous Power Dio ...
stnrgpf01 - STMicroelectronics
... The STNRGPF01 is a digital controller designed specifically for interleaved PFC boost topologies and intended for use in high power applications. The controller is capable of driving up to 3 interleaved channels, generating the proper signals in each condition. Moreover, it implements a flexible pha ...
... The STNRGPF01 is a digital controller designed specifically for interleaved PFC boost topologies and intended for use in high power applications. The controller is capable of driving up to 3 interleaved channels, generating the proper signals in each condition. Moreover, it implements a flexible pha ...
TLC251, TLC251A, TLC251B, TLC251Y LinCMOS PROGRAMMABLE LOW-POWER OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
... This series of parts is available in selected grades of input offset voltage and can be nulled with one external potentiometer. Because the input common-mode range extends to the negative rail and the power consumption is extremely low, this family is ideally suited for battery-powered or energy-con ...
... This series of parts is available in selected grades of input offset voltage and can be nulled with one external potentiometer. Because the input common-mode range extends to the negative rail and the power consumption is extremely low, this family is ideally suited for battery-powered or energy-con ...
MAX1772 Low-Cost, Multichemistry Battery- Charger Building Block General Description
... Operating Temperature Range ...........................-40°C to +85°C Junction Temperature ........................................................150°C Storage Temperature Range .............................-60°C to +150°C Lead Temperature (soldering, 10s) .................................+300°C ...
... Operating Temperature Range ...........................-40°C to +85°C Junction Temperature ........................................................150°C Storage Temperature Range .............................-60°C to +150°C Lead Temperature (soldering, 10s) .................................+300°C ...
TPS255xx Precision Adjustable Current-Limited
... The TPS2552/53 and TPS2552-1/53-1 respond to overcurrent conditions by limiting their output current to the IOS levels shown in Figure 24. When an overcurrent condition is detected, the device maintains a constant output current and reduces the output voltage accordingly. Two possible overload condi ...
... The TPS2552/53 and TPS2552-1/53-1 respond to overcurrent conditions by limiting their output current to the IOS levels shown in Figure 24. When an overcurrent condition is detected, the device maintains a constant output current and reduces the output voltage accordingly. Two possible overload condi ...
ADA4853-1AKSZ-R7中文资料
... 100 MHz, ?3 dB bandwidth 120 V/μs slew rate 0.5 dB flatness: 22 MHz Differential gain: 0.20% Differential phase: 0.10° Single-supply operation Rail-to-rail output ...
... 100 MHz, ?3 dB bandwidth 120 V/μs slew rate 0.5 dB flatness: 22 MHz Differential gain: 0.20% Differential phase: 0.10° Single-supply operation Rail-to-rail output ...
Design and Implementation of Improved Electronic Load Controller
... synchronous frequency constant [12]. Bansal has presented an overview about several solutions for standalone three-phase self-excited generators. A hybrid excited synchronous generator based on the two different types of excitation field is proposed [13]. Singh et al. have demonstrated the behavior ...
... synchronous frequency constant [12]. Bansal has presented an overview about several solutions for standalone three-phase self-excited generators. A hybrid excited synchronous generator based on the two different types of excitation field is proposed [13]. Singh et al. have demonstrated the behavior ...
Single-Phase Full-Wave Rectifier as an Effective Example to Teach
... Analysis of single-phase rectifiers is inevitable part of every general electronics course [4, pp. 179-190], or power electronics course [5, pp. 82-100]. These circuits contain low number of elements, but expose rather complex behavior in the case some sort of filtering is applied. This makes the si ...
... Analysis of single-phase rectifiers is inevitable part of every general electronics course [4, pp. 179-190], or power electronics course [5, pp. 82-100]. These circuits contain low number of elements, but expose rather complex behavior in the case some sort of filtering is applied. This makes the si ...
ADE7762 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... Master Clock for the ADCs and Digital Signal Processing. An external clock can be provided at this logic input. Alternatively, a parallel resonant AT crystal can be connected across CLKIN and CLKOUT to provide a clock source for the ADE7762. The clock frequency for the specified operation is 10 MHz. ...
... Master Clock for the ADCs and Digital Signal Processing. An external clock can be provided at this logic input. Alternatively, a parallel resonant AT crystal can be connected across CLKIN and CLKOUT to provide a clock source for the ADE7762. The clock frequency for the specified operation is 10 MHz. ...
LM5007 - Texas Instruments
... The LM5007 Step Down Switching Regulator features all of the functions needed to implement low cost, efficient, Buck bias regulators. This high voltage regulator contains an 80-V, 0.7-A N-Channel Buck Switch. The device is easy to apply and is provided in the VSSOP-8 and the thermally enhanced WSON- ...
... The LM5007 Step Down Switching Regulator features all of the functions needed to implement low cost, efficient, Buck bias regulators. This high voltage regulator contains an 80-V, 0.7-A N-Channel Buck Switch. The device is easy to apply and is provided in the VSSOP-8 and the thermally enhanced WSON- ...
BDTIC www.BDTIC.com/infineon Application Note No. 018
... The layout size can be reduced by using chip inductors instead of the microstrip lines TrL1 and TrL6 Improved stabilization behaviour versus temperature and reduced variation in amplifier performance due to the device‘s Beta (current gain) distribution can be achieved by using an active bias circuit ...
... The layout size can be reduced by using chip inductors instead of the microstrip lines TrL1 and TrL6 Improved stabilization behaviour versus temperature and reduced variation in amplifier performance due to the device‘s Beta (current gain) distribution can be achieved by using an active bias circuit ...
Amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that increases the power of a signal.It does this by taking energy from a power supply and controlling the output to match the input signal shape but with a larger amplitude. In this sense, an amplifier modulates the output of the power supply to make the output signal stronger than the input signal. An amplifier is effectively the opposite of an attenuator: while an amplifier provides gain, an attenuator provides loss.An amplifier can either be a separate piece of equipment or an electrical circuit within another device. The ability to amplify is fundamental to modern electronics, and amplifiers are extremely widely used in almost all electronic equipment. The types of amplifiers can be categorized in different ways. One is by the frequency of the electronic signal being amplified; audio amplifiers amplify signals in the audio (sound) range of less than 20 kHz, RF amplifiers amplify frequencies in the radio frequency range between 20 kHz and 300 GHz. Another is which quantity, voltage or current is being amplified; amplifiers can be divided into voltage amplifiers, current amplifiers, transconductance amplifiers, and transresistance amplifiers. A further distinction is whether the output is a linear or nonlinear representation of the input. Amplifiers can also be categorized by their physical placement in the signal chain.The first practical electronic device that amplified was the Audion (triode) vacuum tube, invented in 1906 by Lee De Forest, which led to the first amplifiers. The terms ""amplifier"" and ""amplification"" (from the Latin amplificare, 'to enlarge or expand') were first used for this new capability around 1915 when triodes became widespread. For the next 50 years, vacuum tubes were the only devices that could amplify. All amplifiers used them until the 1960s, when transistors appeared. Most amplifiers today use transistors, though tube amplifiers are still produced.