SYSC4203: Amplifier Circuits
... What kinds of interference causes a large CM signal? Sketch a block diagram of a driver right leg circuit? How does a driver right leg circuit help improve CM response? What causes signal saturation (clipping)? How can you detect it? Describe how an infusion pump near a biomedical amplifier can caus ...
... What kinds of interference causes a large CM signal? Sketch a block diagram of a driver right leg circuit? How does a driver right leg circuit help improve CM response? What causes signal saturation (clipping)? How can you detect it? Describe how an infusion pump near a biomedical amplifier can caus ...
Op-Amp Characteristics
... You will be familiar with the term resistance from your GCSE Science courses as being the property of a circuit which reduces the flow of electricity. Impedance is the name given to a similar property for a.c. circuits. If we think of the input terminal to the amplifier we really don’t want to have ...
... You will be familiar with the term resistance from your GCSE Science courses as being the property of a circuit which reduces the flow of electricity. Impedance is the name given to a similar property for a.c. circuits. If we think of the input terminal to the amplifier we really don’t want to have ...
Sedona Series D (2010)
... twisted pair cables is recommended to decrease the possibility of radiated noise entering the system. ...
... twisted pair cables is recommended to decrease the possibility of radiated noise entering the system. ...
100V Input DC/DC Controller Generates Positive or Negative
... applications, capable of generating either positive or negative regulated output voltages. The LT3758 has two voltage feedback error amplifiers and reference voltages. One set is for positive output voltages, the other is for negative output voltages, both off a single feedback pin, making the LT375 ...
... applications, capable of generating either positive or negative regulated output voltages. The LT3758 has two voltage feedback error amplifiers and reference voltages. One set is for positive output voltages, the other is for negative output voltages, both off a single feedback pin, making the LT375 ...
INSTRUCTION MANUAL
... McIntosh Model A-116 30 watt amplifiers and includes all of the rigid electrical specifications and features found in these earlier units plus: less than 1 / 3 % harmonic distortion at any power output up to 30 watts and at any frequency in the audio spectrum, 20 to 20,000 cps; less than 1/2% interm ...
... McIntosh Model A-116 30 watt amplifiers and includes all of the rigid electrical specifications and features found in these earlier units plus: less than 1 / 3 % harmonic distortion at any power output up to 30 watts and at any frequency in the audio spectrum, 20 to 20,000 cps; less than 1/2% interm ...
Physics 517/617 Experiment 4 Transistors - 1 R I
... d) The AC input impedance of the transistor is ≈ βrBE (or hferbe ). A typical β is 100. Remember that β = hfe = IC/IB so for 1 mA of collector current the AC input impedance is ≈ (100)(25) = 2500 Ω. e) The DC input impedance of the transistor is ≈ βRE (or hfeRE). A typical value of RE is 1 kΩ. So th ...
... d) The AC input impedance of the transistor is ≈ βrBE (or hferbe ). A typical β is 100. Remember that β = hfe = IC/IB so for 1 mA of collector current the AC input impedance is ≈ (100)(25) = 2500 Ω. e) The DC input impedance of the transistor is ≈ βRE (or hfeRE). A typical value of RE is 1 kΩ. So th ...
hood_ss-amp.pdf
... The circuit shown in Fig. 3 may be used, with very little modification to the component values, to drive load impedances in the range 3-15 ohms. However, the chosen output power is represented by a different current/voltage relationship in each case, and the current through the output transistors an ...
... The circuit shown in Fig. 3 may be used, with very little modification to the component values, to drive load impedances in the range 3-15 ohms. However, the chosen output power is represented by a different current/voltage relationship in each case, and the current through the output transistors an ...
Wisnu Electronics Pemancar Rf-Kits
... changing supply voltage, varyingthe drive level, and changing the bias voltage. Changing drive power work well for amplifier in linear range operation. Changing bias voltage works better but can produce rise of harmonic. Best results can be obstained by changing supply voltage to the power amplifier ...
... changing supply voltage, varyingthe drive level, and changing the bias voltage. Changing drive power work well for amplifier in linear range operation. Changing bias voltage works better but can produce rise of harmonic. Best results can be obstained by changing supply voltage to the power amplifier ...
Energy Efficient and High Performance Current-Mode Neural
... memory [1-3]. The Resistive-Crossbar Memory (RCM) technology has led to interesting possibilities of combining memory with computation [1-5]. RCM can be highly suitable for a class of non-Boolean computing applications that involve pattern-matching [5, 11]. Such applications employ highly memory in ...
... memory [1-3]. The Resistive-Crossbar Memory (RCM) technology has led to interesting possibilities of combining memory with computation [1-5]. RCM can be highly suitable for a class of non-Boolean computing applications that involve pattern-matching [5, 11]. Such applications employ highly memory in ...
Class B Amplifier
... obtained before for the same vi(t), but with RL=22Ω. Are the two waveforms different? Suggestion: For example, in the positive half-wave of vi(t) and vo(t), we must check if the current through R1 is large enough to ensure a sufficiently large base current for T1, to keep T1 in aF. In aF consider ...
... obtained before for the same vi(t), but with RL=22Ω. Are the two waveforms different? Suggestion: For example, in the positive half-wave of vi(t) and vo(t), we must check if the current through R1 is large enough to ensure a sufficiently large base current for T1, to keep T1 in aF. In aF consider ...
Analogue Electronic Circuit - Federal University Oye
... Tell the operational differences between the Common-Emitter amplifier, CommonBase amplifier, and Common-Collector amplifier as well as identify the similarities between the operations of the following pairs of amplifiers: Common-Emitter & Common Source amplifiers, Common-Collector and Common-Drain ...
... Tell the operational differences between the Common-Emitter amplifier, CommonBase amplifier, and Common-Collector amplifier as well as identify the similarities between the operations of the following pairs of amplifiers: Common-Emitter & Common Source amplifiers, Common-Collector and Common-Drain ...
Slide 1
... hybrid parameters and are the components of a small-signal equivalent circuit. The description of the hybrid equivalent model begins with the general two-port system. ...
... hybrid parameters and are the components of a small-signal equivalent circuit. The description of the hybrid equivalent model begins with the general two-port system. ...
The PLH Amplifier By Nelson Pass Introduction
... In Figure 2 additional details of setting up the DC bias for each device are shown, where capacitors are used to separate DC values from AC values. C1 separates feedback from bias current. C2 separates input signal from input DC bias voltage and C3 blocks the output DC of the amplifier from the load ...
... In Figure 2 additional details of setting up the DC bias for each device are shown, where capacitors are used to separate DC values from AC values. C1 separates feedback from bias current. C2 separates input signal from input DC bias voltage and C3 blocks the output DC of the amplifier from the load ...
60V Zero-Drift Operational Amplifier with 220nVP
... dynamic range enables tiny signals to be amplified in the presence of much larger signals without saturating the amplifier or losing precision. For applications requiring supply voltages up to 36V, a lower supply version of LTC2057 is available. Specified over a -40°C to 125°C temperature range, the ...
... dynamic range enables tiny signals to be amplified in the presence of much larger signals without saturating the amplifier or losing precision. For applications requiring supply voltages up to 36V, a lower supply version of LTC2057 is available. Specified over a -40°C to 125°C temperature range, the ...
the Enclosed DC Drives product datasheet.
... e.g multi setpoint systems, closed loop control, field weakening processor, signal buffering. CHANNELS 1 AND 2. High accuracy differential amplifier with adjustable gain. Uses include inverting, non-inverting, amplification, attenuation, buffering, rectifying, filtering, load cell amplifier etc. ...
... e.g multi setpoint systems, closed loop control, field weakening processor, signal buffering. CHANNELS 1 AND 2. High accuracy differential amplifier with adjustable gain. Uses include inverting, non-inverting, amplification, attenuation, buffering, rectifying, filtering, load cell amplifier etc. ...
AMZ-40 Driver Amplifier Operation Guide
... with broadband 50 Ω systems. Prior to any DC bias connection, connect the input to a broadband 50 Ω source impedence and connect the output to a broadband 50 Ω load impedence. Applying DC bias to a non‐50 Ω terminated amplifier can result in damage to the device—especially when operating the ampl ...
... with broadband 50 Ω systems. Prior to any DC bias connection, connect the input to a broadband 50 Ω source impedence and connect the output to a broadband 50 Ω load impedence. Applying DC bias to a non‐50 Ω terminated amplifier can result in damage to the device—especially when operating the ampl ...
AM Audio PA-60X
... consists of a 3 mm-thick stainless steel frame on which the container/power-supply transformers shield, made of 2 mm-thick, chrome-plated, mirror polished stainless steel, is installed by using rubber decouplers; 12x15 mm aluminium bars make the base even more sturdy. The sides, supporting the heavy ...
... consists of a 3 mm-thick stainless steel frame on which the container/power-supply transformers shield, made of 2 mm-thick, chrome-plated, mirror polished stainless steel, is installed by using rubber decouplers; 12x15 mm aluminium bars make the base even more sturdy. The sides, supporting the heavy ...
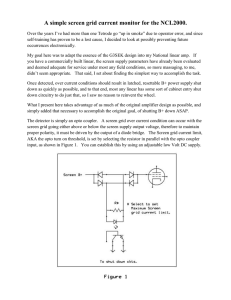
NCL 2000 Screen Grid Protection.
... about AC, DC, Current, or Voltage precautions, AND its simple. Many amplifiers utilize two tubes in parallel, and there are a couple ways to accommodate this. One is to just add a few more diodes to the mix as shown in figure 3. Another approach is to use a second bridge and associated opto coupler, ...
... about AC, DC, Current, or Voltage precautions, AND its simple. Many amplifiers utilize two tubes in parallel, and there are a couple ways to accommodate this. One is to just add a few more diodes to the mix as shown in figure 3. Another approach is to use a second bridge and associated opto coupler, ...
Mar 2003 Triple and Quad RGB Amplifiers Deliver Full Performance on 3.3V
... Even with their limited lifetimes, incandescent lamps are still widely used as low-cost hi-level illumination in many products like automobiles and aircraft. With the trend in products to provide more self-diagnostic information, it is optimal to have a circuit that provides a full-time status of th ...
... Even with their limited lifetimes, incandescent lamps are still widely used as low-cost hi-level illumination in many products like automobiles and aircraft. With the trend in products to provide more self-diagnostic information, it is optimal to have a circuit that provides a full-time status of th ...
8020A Datasheet
... Maximum long term RMS acoustic output in same conditions with IEC-weighted noise (limited by driver ...
... Maximum long term RMS acoustic output in same conditions with IEC-weighted noise (limited by driver ...
Linear Position Sensors: LVDT Sensors | TE Connectivity
... LVC-2401, a user can choose 3, 5, or 10 kHz nominal excitation frequencies at a level of 3 Volts rms for driving normal LVDTs, changeable to 1.3 Volts rms for operating LVDTs with low primary impedance. For multiple channel applications, several LVC-2401 modules can be connected together in master/s ...
... LVC-2401, a user can choose 3, 5, or 10 kHz nominal excitation frequencies at a level of 3 Volts rms for driving normal LVDTs, changeable to 1.3 Volts rms for operating LVDTs with low primary impedance. For multiple channel applications, several LVC-2401 modules can be connected together in master/s ...
Amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that increases the power of a signal.It does this by taking energy from a power supply and controlling the output to match the input signal shape but with a larger amplitude. In this sense, an amplifier modulates the output of the power supply to make the output signal stronger than the input signal. An amplifier is effectively the opposite of an attenuator: while an amplifier provides gain, an attenuator provides loss.An amplifier can either be a separate piece of equipment or an electrical circuit within another device. The ability to amplify is fundamental to modern electronics, and amplifiers are extremely widely used in almost all electronic equipment. The types of amplifiers can be categorized in different ways. One is by the frequency of the electronic signal being amplified; audio amplifiers amplify signals in the audio (sound) range of less than 20 kHz, RF amplifiers amplify frequencies in the radio frequency range between 20 kHz and 300 GHz. Another is which quantity, voltage or current is being amplified; amplifiers can be divided into voltage amplifiers, current amplifiers, transconductance amplifiers, and transresistance amplifiers. A further distinction is whether the output is a linear or nonlinear representation of the input. Amplifiers can also be categorized by their physical placement in the signal chain.The first practical electronic device that amplified was the Audion (triode) vacuum tube, invented in 1906 by Lee De Forest, which led to the first amplifiers. The terms ""amplifier"" and ""amplification"" (from the Latin amplificare, 'to enlarge or expand') were first used for this new capability around 1915 when triodes became widespread. For the next 50 years, vacuum tubes were the only devices that could amplify. All amplifiers used them until the 1960s, when transistors appeared. Most amplifiers today use transistors, though tube amplifiers are still produced.