1296 MHz SSPA with XRF286
... The MRF286 and the XRF286 are electrically the same device and differ only by their mounting method. The MRF286 has a traditional flange that is screwed to a heatsink, whilst the XRF286 is flangeless and requires the base (Source) to be soldered to a heat spreader before mounting on a heatsink. Elec ...
... The MRF286 and the XRF286 are electrically the same device and differ only by their mounting method. The MRF286 has a traditional flange that is screwed to a heatsink, whilst the XRF286 is flangeless and requires the base (Source) to be soldered to a heat spreader before mounting on a heatsink. Elec ...
TDA2040 - Micropik
... - increased impedance seen by the loudspeaker (lower damping) - difficulty of precise design due to variable loudspeaker impedance Obviously, active crossovers can only be used if a ...
... - increased impedance seen by the loudspeaker (lower damping) - difficulty of precise design due to variable loudspeaker impedance Obviously, active crossovers can only be used if a ...
1. Pre-Lab Introduction
... domain. The resistor RI shown in the two circuits is included to help with stability and for general circuit protection. The value for RI is nominally set equal to the feedback resistor (Figure 7-1) or the input resistor (Figure 7-2). The purpose of the optional resistor is left for student investig ...
... domain. The resistor RI shown in the two circuits is included to help with stability and for general circuit protection. The value for RI is nominally set equal to the feedback resistor (Figure 7-1) or the input resistor (Figure 7-2). The purpose of the optional resistor is left for student investig ...
File tda2040 | allcomponents.ru
... - increased impedance seen by the loudspeaker (lower damping) - difficulty of precise design due to variable loudspeaker impedance Obviously, active crossovers can only be used if a ...
... - increased impedance seen by the loudspeaker (lower damping) - difficulty of precise design due to variable loudspeaker impedance Obviously, active crossovers can only be used if a ...
…closing the gap
... Automatic Gain Control (AGC), dual duplexers, and bias tee’s. The BDA can be powered by a conventional 110/220 VAC source using a built in power supply or, alternatively, DC voltage can be supplied to the BDA via an external DC input or via the center conductor of the RF coax cable. Automatic Gain C ...
... Automatic Gain Control (AGC), dual duplexers, and bias tee’s. The BDA can be powered by a conventional 110/220 VAC source using a built in power supply or, alternatively, DC voltage can be supplied to the BDA via an external DC input or via the center conductor of the RF coax cable. Automatic Gain C ...
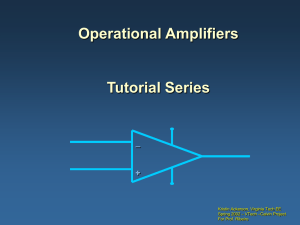
OpAmp-tutorial
... Note: The actual value of AOL is given for the specific device and usually ranges from 50k 500k. is the feedback factor and by assuming open-loop gain is infinite: ...
... Note: The actual value of AOL is given for the specific device and usually ranges from 50k 500k. is the feedback factor and by assuming open-loop gain is infinite: ...
ATP-Y/Analog Input to Pulse (Relay)
... Analog input, digital input, and analog output circuits should not be earth grounded at two points. Any field device connected to this transformer must use the same common. If you are not sure of other field device configuration, use separate transformers for isolation. 2.) If the 24 volt AC or DC p ...
... Analog input, digital input, and analog output circuits should not be earth grounded at two points. Any field device connected to this transformer must use the same common. If you are not sure of other field device configuration, use separate transformers for isolation. 2.) If the 24 volt AC or DC p ...
Document
... many sensors produce signals of the order of milli volts. This low level input signals from sensors must be amplified to use them for further control action. Operational amplifiers (op-amp) are widely used for amplification of input signals. The details are as follows. ...
... many sensors produce signals of the order of milli volts. This low level input signals from sensors must be amplified to use them for further control action. Operational amplifiers (op-amp) are widely used for amplification of input signals. The details are as follows. ...
Name of the participant: D .Padma Subhashini
... second emitter to the base of first through the resistor Rf. • The input current is the difference of the current at the base of transistor due to Vs and the current If. • This is smaller than the magnitude of current without ...
... second emitter to the base of first through the resistor Rf. • The input current is the difference of the current at the base of transistor due to Vs and the current If. • This is smaller than the magnitude of current without ...
Jun 1999 LTC2400 Differential Bridge Digitizers
... single-ended, ground referred signals for input to the LTC2400 delta-sigma ADC. These circuits were designed to have a minimal effect on the LTC2400’s 1ppm typical accuracy. The circuit in Figure 1 is ideal for low level differential bridge outputs in applications that have ±5V supplies. The circuit ...
... single-ended, ground referred signals for input to the LTC2400 delta-sigma ADC. These circuits were designed to have a minimal effect on the LTC2400’s 1ppm typical accuracy. The circuit in Figure 1 is ideal for low level differential bridge outputs in applications that have ±5V supplies. The circuit ...
BIO-ELECTRIC MEASUREMENTS
... The output of the differential amplifier goes to the input stage of the optical coupler, which converts the electrical signal to a light signal by pulsing a light-emitting diode (LED). The light signal is detected by a phototransistor and converted back to an electrical signal in the output stage. T ...
... The output of the differential amplifier goes to the input stage of the optical coupler, which converts the electrical signal to a light signal by pulsing a light-emitting diode (LED). The light signal is detected by a phototransistor and converted back to an electrical signal in the output stage. T ...
TWO TONE TESTING
... from either end of the audio pass band. The result, in a properly adjusted transmitter, is an RF output that varies from zero to maximum at a rate determined by the difference in frequency between the two audio inputs. Consequently, overdrive (which causes splatter), non-linearity, instability and a ...
... from either end of the audio pass band. The result, in a properly adjusted transmitter, is an RF output that varies from zero to maximum at a rate determined by the difference in frequency between the two audio inputs. Consequently, overdrive (which causes splatter), non-linearity, instability and a ...
XA SERIES - Nady Systems, Inc.
... one of the channels. This still allows independent control of each channel. (Note: Do not select this “Parallel” mode when feeding the amplifier 2 separate signals.) (Note: Do not use both unbalanced and balanced cables in the same set-up as that can unbalance all the connections when daisy-chaining ...
... one of the channels. This still allows independent control of each channel. (Note: Do not select this “Parallel” mode when feeding the amplifier 2 separate signals.) (Note: Do not use both unbalanced and balanced cables in the same set-up as that can unbalance all the connections when daisy-chaining ...
EE 1202 Experiment #7 – Signal Amplification
... 3. Exercise: We developed some basic relationships for the negative-feedback operational amplifier circuit described in 3.2.2 and 3.2.3 (Figs. 5 and 6). a. Use the relations ii i f 0 , or ii i f and the definitions of ii and if developed in 3.2.3 to find a value of the output voltage, v0 , i ...
... 3. Exercise: We developed some basic relationships for the negative-feedback operational amplifier circuit described in 3.2.2 and 3.2.3 (Figs. 5 and 6). a. Use the relations ii i f 0 , or ii i f and the definitions of ii and if developed in 3.2.3 to find a value of the output voltage, v0 , i ...
Prog05Goyal_Suba
... which can dynamically adjust to changing Rm of the oscillator, in order to sustain ...
... which can dynamically adjust to changing Rm of the oscillator, in order to sustain ...
ha200 : Optoma USA : http://www2.optoma.com/us
... The Class-A topology is widely recognized as being the purest form of amplification, and this is because other topologies such as Class B and Class-AB require that two output devices be operated in "pushpull" fashion in order for each to handle one half of the musical waveform. At the point where a ...
... The Class-A topology is widely recognized as being the purest form of amplification, and this is because other topologies such as Class B and Class-AB require that two output devices be operated in "pushpull" fashion in order for each to handle one half of the musical waveform. At the point where a ...
GSM15 Medical - SL Power Electronics
... the first ac half-cycle under cold start conditions will not exceed 37 A. ...
... the first ac half-cycle under cold start conditions will not exceed 37 A. ...
Slide 1
... Many class A amplifiers use the same transistor(s) for both halves of the audio waveform. In this configuration, the output transistor(s) always has current flowing through it, even if it has no audio signal (the output transistors never 'turn off'). The current flowing through it is D.C. A pure cla ...
... Many class A amplifiers use the same transistor(s) for both halves of the audio waveform. In this configuration, the output transistor(s) always has current flowing through it, even if it has no audio signal (the output transistors never 'turn off'). The current flowing through it is D.C. A pure cla ...
Heathkit SB-200 - Orange County (California) Amateur Radio Club
... know you could make the contact more easily with a kilowatt. Wouldn’t that mean another Sunit or two? Before SSB became the popular choice for HF voice communications on the ham bands, amplitude modulation (AM) was the mode most often used. Operating a kilowatt on AM was a big deal. There are linear ...
... know you could make the contact more easily with a kilowatt. Wouldn’t that mean another Sunit or two? Before SSB became the popular choice for HF voice communications on the ham bands, amplitude modulation (AM) was the mode most often used. Operating a kilowatt on AM was a big deal. There are linear ...
AD633 Low Cost Analog Multiplier Data Sheet (REV. E)
... The AD633 is a functionally complete, four-quadrant, analog multiplier. It includes high impedance, differential X and Y inputs and a high impedance summing input (Z). The low impedance output voltage is a nominal 10 V full scale provided by a buried Zener. The AD633 is the first product to offer th ...
... The AD633 is a functionally complete, four-quadrant, analog multiplier. It includes high impedance, differential X and Y inputs and a high impedance summing input (Z). The low impedance output voltage is a nominal 10 V full scale provided by a buried Zener. The AD633 is the first product to offer th ...
WEBENCH® Amplifier Designer
... Simulations may be added to PDF report or may be shared with the Design ...
... Simulations may be added to PDF report or may be shared with the Design ...
Amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that increases the power of a signal.It does this by taking energy from a power supply and controlling the output to match the input signal shape but with a larger amplitude. In this sense, an amplifier modulates the output of the power supply to make the output signal stronger than the input signal. An amplifier is effectively the opposite of an attenuator: while an amplifier provides gain, an attenuator provides loss.An amplifier can either be a separate piece of equipment or an electrical circuit within another device. The ability to amplify is fundamental to modern electronics, and amplifiers are extremely widely used in almost all electronic equipment. The types of amplifiers can be categorized in different ways. One is by the frequency of the electronic signal being amplified; audio amplifiers amplify signals in the audio (sound) range of less than 20 kHz, RF amplifiers amplify frequencies in the radio frequency range between 20 kHz and 300 GHz. Another is which quantity, voltage or current is being amplified; amplifiers can be divided into voltage amplifiers, current amplifiers, transconductance amplifiers, and transresistance amplifiers. A further distinction is whether the output is a linear or nonlinear representation of the input. Amplifiers can also be categorized by their physical placement in the signal chain.The first practical electronic device that amplified was the Audion (triode) vacuum tube, invented in 1906 by Lee De Forest, which led to the first amplifiers. The terms ""amplifier"" and ""amplification"" (from the Latin amplificare, 'to enlarge or expand') were first used for this new capability around 1915 when triodes became widespread. For the next 50 years, vacuum tubes were the only devices that could amplify. All amplifiers used them until the 1960s, when transistors appeared. Most amplifiers today use transistors, though tube amplifiers are still produced.