ES636 True RMS-to-DC Converters Features
... is chosen, the additional error at 30Hz will be 1%. If the DC error can be rejected, a capacitor should be connected in series with the input, as would typically be the case in single-supply operation. The input and output signal ranges are a function of the supply voltages. Refer to the electrical ...
... is chosen, the additional error at 30Hz will be 1%. If the DC error can be rejected, a capacitor should be connected in series with the input, as would typically be the case in single-supply operation. The input and output signal ranges are a function of the supply voltages. Refer to the electrical ...
ElectronicsPrimer
... Enable and Direction Logic • Critical that transistors in either vertical leg of “H” are never turned on at same time – If Q1 and Q2 were turned on together, current would flow straight down through the two transistors – There would be no load in this circuit other than the transistors themselves, s ...
... Enable and Direction Logic • Critical that transistors in either vertical leg of “H” are never turned on at same time – If Q1 and Q2 were turned on together, current would flow straight down through the two transistors – There would be no load in this circuit other than the transistors themselves, s ...
Lecture 15
... In fact the Q-point could be at any of the intersection points between the load line and the transistor curves. We have chosen the Q-point corresponding to I B 2 on the plot of Figure 8 since that point is at about the midpoint of the load line. In amplifier design applications the Q-point correspo ...
... In fact the Q-point could be at any of the intersection points between the load line and the transistor curves. We have chosen the Q-point corresponding to I B 2 on the plot of Figure 8 since that point is at about the midpoint of the load line. In amplifier design applications the Q-point correspo ...
A SiGe PA With Dual Dynamic Bias Control and Handset Applications
... peak power efficiency may be high at high output powers, it drops quickly with the power back-off, resulting in a poor average power efficiency. To increase power efficiencies in the low-power region, different dynamic biasing techniques [5]–[8] have been developed. Altering the DC bias current in r ...
... peak power efficiency may be high at high output powers, it drops quickly with the power back-off, resulting in a poor average power efficiency. To increase power efficiencies in the low-power region, different dynamic biasing techniques [5]–[8] have been developed. Altering the DC bias current in r ...
ADN2890ACPZ-RL Datasheet
... output signals to minimize reflections: PIN, NIN, OUTP and OUTN. It is also necessary for the PIN/NIN input traces to be matched in length, and OUTP/OUTN output traces to be matched in length to avoid skew between the differential traces. C1, C2, C3, and C4 are ac-coupling capacitors in series with ...
... output signals to minimize reflections: PIN, NIN, OUTP and OUTN. It is also necessary for the PIN/NIN input traces to be matched in length, and OUTP/OUTN output traces to be matched in length to avoid skew between the differential traces. C1, C2, C3, and C4 are ac-coupling capacitors in series with ...
design of low power low voltage bulk driven operational
... Low-voltage (LV) and low-power (LP) CMOS circuits have received considerable attention recently due to several reasons: a) Many of today's integrated circuit (IC) applications such as portable communication, remote computing and wireless communication systems require high performance IC's that opera ...
... Low-voltage (LV) and low-power (LP) CMOS circuits have received considerable attention recently due to several reasons: a) Many of today's integrated circuit (IC) applications such as portable communication, remote computing and wireless communication systems require high performance IC's that opera ...
BCR405U
... The BCR405U is a cost efficient LED driver to drive low power LED’s. The advantages towards resistor biasing are: • homogenous light output despite varying forward voltages in different LED strings • homogenous light output of LED’s despite voltage drop across long supply lines • homogenous light ou ...
... The BCR405U is a cost efficient LED driver to drive low power LED’s. The advantages towards resistor biasing are: • homogenous light output despite varying forward voltages in different LED strings • homogenous light output of LED’s despite voltage drop across long supply lines • homogenous light ou ...
EL5174, EL5374
... The EL5374 can be disabled and its outputs placed in a high impedance state. The turn-off time is about 1.2µs and the turn-on time is about 130ns. When disabled, the amplifier's supply current is reduced to 1.7µA for IS+ and 120µA for IStypically, thereby effectively eliminating the power consumptio ...
... The EL5374 can be disabled and its outputs placed in a high impedance state. The turn-off time is about 1.2µs and the turn-on time is about 130ns. When disabled, the amplifier's supply current is reduced to 1.7µA for IS+ and 120µA for IStypically, thereby effectively eliminating the power consumptio ...
Lecture January 27
... Amplifier Basics • An amplifier scales the magnitude of an analog input signal: Eo(t) = h { Ei(t) } ...
... Amplifier Basics • An amplifier scales the magnitude of an analog input signal: Eo(t) = h { Ei(t) } ...
File
... The 741 is a versatile chip and it can be used in the design of a wide variety of sound-effect generators. This circuit produces a siren that can be used in conjunction with other circuits. You can also use an LM358 dual op-amp chip. The operation of the op-amp was not discussed correctly in the ori ...
... The 741 is a versatile chip and it can be used in the design of a wide variety of sound-effect generators. This circuit produces a siren that can be used in conjunction with other circuits. You can also use an LM358 dual op-amp chip. The operation of the op-amp was not discussed correctly in the ori ...
Hitachi SJ200 Series Inverter Instruction Manual
... CAUTION: It is possible to damage the inverter or other devices if your application exceeds the maximum current or voltage characteristics of a connection point. ...
... CAUTION: It is possible to damage the inverter or other devices if your application exceeds the maximum current or voltage characteristics of a connection point. ...
Design and Simulation of High Speed Low Power CMOS
... The inverter-based amplifier topology shown in Figure 6 uses CMOS inverters as the amplifier input. This input stage design has the advantage of combining the transconductance of the n and p transistors. This combination of the two transconductance should provide 6dB increase in gain over a traditio ...
... The inverter-based amplifier topology shown in Figure 6 uses CMOS inverters as the amplifier input. This input stage design has the advantage of combining the transconductance of the n and p transistors. This combination of the two transconductance should provide 6dB increase in gain over a traditio ...
DEVELOPMENT OF AN AUDIO EVOKED RESPONSE SYSTEM TO FACILITATE ANAESTHESIA MONITORING
... headphone or a loudspeaker and picking up the evoked voltage signals from the brain using electrodes fixed at suitable locations on the patient’s head. The AER signals, which are of the order of 10µV, are usually associated with thousands of time larger mains borne 50Hz noise. This noise will need m ...
... headphone or a loudspeaker and picking up the evoked voltage signals from the brain using electrodes fixed at suitable locations on the patient’s head. The AER signals, which are of the order of 10µV, are usually associated with thousands of time larger mains borne 50Hz noise. This noise will need m ...
Linear Circuit Experiment MAE 171a
... the op-amp is controlled either by negative feedback, which largely determines the magnitude of its output voltage gain. In addition, positive feedback can be used to allow regenerative gain and oscillation circuits. High input impedance at the input terminals and low output impedance are important ...
... the op-amp is controlled either by negative feedback, which largely determines the magnitude of its output voltage gain. In addition, positive feedback can be used to allow regenerative gain and oscillation circuits. High input impedance at the input terminals and low output impedance are important ...
Fairchild Semiconductors
... General Description This device contains four independent gates each of which performs a non-inverting buffer function. The outputs have the 3-STATE feature. When enabled, the outputs exhibit the low impedance characteristics of a standard LS output with additional drive capability to permit the dri ...
... General Description This device contains four independent gates each of which performs a non-inverting buffer function. The outputs have the 3-STATE feature. When enabled, the outputs exhibit the low impedance characteristics of a standard LS output with additional drive capability to permit the dri ...
Unit 5 - VTU e
... • Main disadvantage of fixed bias configuration requires two dc voltage sources. • Self bias circuit requires only one DC supply to establish the desired operating point. ...
... • Main disadvantage of fixed bias configuration requires two dc voltage sources. • Self bias circuit requires only one DC supply to establish the desired operating point. ...
MAX9788 14V , Class G Ceramic Speaker Driver P-P
... making the device compatible with many CODECs, and offering improved noise immunity over a single-ended input amplifier. In devices such as PCs, noisy digital signals can be picked up by the amplifier’s input traces. The signals appear at the amplifier’s inputs as common-mode noise. A differential i ...
... making the device compatible with many CODECs, and offering improved noise immunity over a single-ended input amplifier. In devices such as PCs, noisy digital signals can be picked up by the amplifier’s input traces. The signals appear at the amplifier’s inputs as common-mode noise. A differential i ...
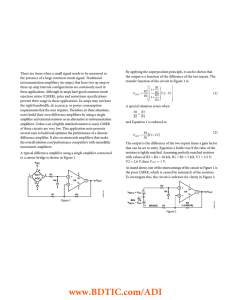
AN-589: Ways to Optimize the Performance of a Difference Amplifier
... the presence of a large common-mode signal. Traditional instrumentation amplifiers (in-amps) that have two op amp or three op amp internal configurations are commonly used in these applications. Although in-amps have good common-mode rejection ratios (CMRR), price and sometimes specifications preven ...
... the presence of a large common-mode signal. Traditional instrumentation amplifiers (in-amps) that have two op amp or three op amp internal configurations are commonly used in these applications. Although in-amps have good common-mode rejection ratios (CMRR), price and sometimes specifications preven ...
Amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that increases the power of a signal.It does this by taking energy from a power supply and controlling the output to match the input signal shape but with a larger amplitude. In this sense, an amplifier modulates the output of the power supply to make the output signal stronger than the input signal. An amplifier is effectively the opposite of an attenuator: while an amplifier provides gain, an attenuator provides loss.An amplifier can either be a separate piece of equipment or an electrical circuit within another device. The ability to amplify is fundamental to modern electronics, and amplifiers are extremely widely used in almost all electronic equipment. The types of amplifiers can be categorized in different ways. One is by the frequency of the electronic signal being amplified; audio amplifiers amplify signals in the audio (sound) range of less than 20 kHz, RF amplifiers amplify frequencies in the radio frequency range between 20 kHz and 300 GHz. Another is which quantity, voltage or current is being amplified; amplifiers can be divided into voltage amplifiers, current amplifiers, transconductance amplifiers, and transresistance amplifiers. A further distinction is whether the output is a linear or nonlinear representation of the input. Amplifiers can also be categorized by their physical placement in the signal chain.The first practical electronic device that amplified was the Audion (triode) vacuum tube, invented in 1906 by Lee De Forest, which led to the first amplifiers. The terms ""amplifier"" and ""amplification"" (from the Latin amplificare, 'to enlarge or expand') were first used for this new capability around 1915 when triodes became widespread. For the next 50 years, vacuum tubes were the only devices that could amplify. All amplifiers used them until the 1960s, when transistors appeared. Most amplifiers today use transistors, though tube amplifiers are still produced.