LTC1250 - Very Low Noise Zero-Drift Bridge Amplifier
... The LTC1250, like all CMOS amplifiers, exhibits two types of low frequency noise: thermal noise and 1/f noise. The LTC1250 uses several design modifications to minimize these noise sources. Thermal noise is minimized by raising the gM of the front-end transistors by running them at high bias levels ...
... The LTC1250, like all CMOS amplifiers, exhibits two types of low frequency noise: thermal noise and 1/f noise. The LTC1250 uses several design modifications to minimize these noise sources. Thermal noise is minimized by raising the gM of the front-end transistors by running them at high bias levels ...
Exp # (1) Introduction to OrCAD Objectives: • To Be familiar with the
... amplitude and phases for each frequency. When the input amplitude is set to 1V, then the output voltage is basically the transfer function. In contrast to a sinusoidal transient analysis, the AC analysis is not a time domain simulation but rather a simulation of the sinusoidal steady state of the ci ...
... amplitude and phases for each frequency. When the input amplitude is set to 1V, then the output voltage is basically the transfer function. In contrast to a sinusoidal transient analysis, the AC analysis is not a time domain simulation but rather a simulation of the sinusoidal steady state of the ci ...
250MHz, Rail-to-Rail I/O, CMOS Operational
... RAIL-TO-RAIL OUTPUT A class AB output stage with common-source transistors is used to achieve rail-to-rail output. For high-impedance loads (> 200Ω), the output voltage swing is typically 100mV from the supply rails. With 10Ω loads, a useful output swing can be achieved while maintaining high open-l ...
... RAIL-TO-RAIL OUTPUT A class AB output stage with common-source transistors is used to achieve rail-to-rail output. For high-impedance loads (> 200Ω), the output voltage swing is typically 100mV from the supply rails. With 10Ω loads, a useful output swing can be achieved while maintaining high open-l ...
Data Acquisition Fundamentals
... from analog common to both inputs when the inputs are identical. (See Figure 10.) However, when the two input voltages are different (for example, 4.10 V and 4.20 V), the commonmode voltage, Vcm, is 4.10 V, and the differential voltage between the two is 0.10 V. Ideally, the IA ignores the commonmod ...
... from analog common to both inputs when the inputs are identical. (See Figure 10.) However, when the two input voltages are different (for example, 4.10 V and 4.20 V), the commonmode voltage, Vcm, is 4.10 V, and the differential voltage between the two is 0.10 V. Ideally, the IA ignores the commonmod ...
Data Sheet
... sition. With the Output Enable (OE) LOW, the contents of the eight flip-flops are available at the outputs. When the OE is HIGH, the outputs go to the high impedance state. Operation of the OE input does not affect the state of the flip-flops. ...
... sition. With the Output Enable (OE) LOW, the contents of the eight flip-flops are available at the outputs. When the OE is HIGH, the outputs go to the high impedance state. Operation of the OE input does not affect the state of the flip-flops. ...
+ v if
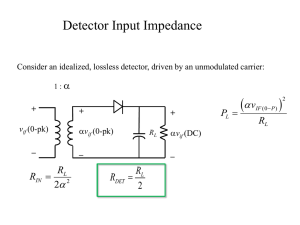
... The previous example uses reasonable numbers, and the result, 15.7 dB, is not a respectable value for dynamic range. If the radio’s maximum range is 50 miles, then the IF will clip at ranges less than 1.5 miles, and this would be unacceptable. The solution is to provide a means for reducing the gain ...
... The previous example uses reasonable numbers, and the result, 15.7 dB, is not a respectable value for dynamic range. If the radio’s maximum range is 50 miles, then the IF will clip at ranges less than 1.5 miles, and this would be unacceptable. The solution is to provide a means for reducing the gain ...
Precision, Low Power INSTRUMENTATION AMPLIFIER INA118
... The INA118 is a low power, general purpose instrumentation amplifier offering excellent accuracy. Its versatile 3-op amp design and small size make it ideal for a wide range of applications. Current-feedback input circuitry provides wide bandwidth even at high gain (70kHz at G = 100). A single exter ...
... The INA118 is a low power, general purpose instrumentation amplifier offering excellent accuracy. Its versatile 3-op amp design and small size make it ideal for a wide range of applications. Current-feedback input circuitry provides wide bandwidth even at high gain (70kHz at G = 100). A single exter ...
Low Cost Instrumentation Amplifier AD622 FEATURES
... The gain-bandwidth product (determined by C1, C2, and the preamp transconductance) increases with programmed gain, thus optimizing frequency response. The input voltage noise is reduced to a value of 12 nV/√Hz, determined mainly by the collector current and base resistance of the input devices. ...
... The gain-bandwidth product (determined by C1, C2, and the preamp transconductance) increases with programmed gain, thus optimizing frequency response. The input voltage noise is reduced to a value of 12 nV/√Hz, determined mainly by the collector current and base resistance of the input devices. ...
EUP2983 White LED Driver For Buck-Boost Application
... input range. The unique converter topology provide a load voltage which can be greater or less than the input voltage. With the tightly regulated load current, the EUP2983 allows series connection with multiple strings of the white LEDs. The brightness of the LEDs can be adjusted through a voltage l ...
... input range. The unique converter topology provide a load voltage which can be greater or less than the input voltage. With the tightly regulated load current, the EUP2983 allows series connection with multiple strings of the white LEDs. The brightness of the LEDs can be adjusted through a voltage l ...
MAX4100/MAX4101 500MHz, Low-Power Op
... and a 0.1dB gain flatness of 65MHz. It offers differential gain and phase errors of 0.06%/0.04°, respectively. The MAX4101 features a -3dB bandwidth of 200MHz, a 0.1dB bandwidth of 50MHz, and 0.07%/0.04° differential gain and phase. Available in small 8-pin SO and µMAX packages, these ICs are ideall ...
... and a 0.1dB gain flatness of 65MHz. It offers differential gain and phase errors of 0.06%/0.04°, respectively. The MAX4101 features a -3dB bandwidth of 200MHz, a 0.1dB bandwidth of 50MHz, and 0.07%/0.04° differential gain and phase. Available in small 8-pin SO and µMAX packages, these ICs are ideall ...
74LS02
... 14-Lead Plastic Dual-In-Line Package (PDIP), JEDEC MS-001, 0.300 Wide Package Number N14A ...
... 14-Lead Plastic Dual-In-Line Package (PDIP), JEDEC MS-001, 0.300 Wide Package Number N14A ...
AD829 Data Sheet
... capacitance. Table I and the graph of Figure 28 show the optimum compensation capacitance and the resulting slew rate for a desired noise gain. For gains between 1 and 20, CCOMP can be chosen to keep the small signal bandwidth relatively constant. The minimum gain which will still provide stability ...
... capacitance. Table I and the graph of Figure 28 show the optimum compensation capacitance and the resulting slew rate for a desired noise gain. For gains between 1 and 20, CCOMP can be chosen to keep the small signal bandwidth relatively constant. The minimum gain which will still provide stability ...
MT-079: Analog Multipliers
... cells, while Q3A and Q3B are the linearizing transistors for both cells. There is also an operational amplifier acting as a differential current to single-ended voltage converter, but for higher speed applications, the cross-coupled collectors of Q1 and Q2 form a differential open collector current ...
... cells, while Q3A and Q3B are the linearizing transistors for both cells. There is also an operational amplifier acting as a differential current to single-ended voltage converter, but for higher speed applications, the cross-coupled collectors of Q1 and Q2 form a differential open collector current ...
AMP02 英文数据手册DataSheet 下载
... The AMP02 is the first precision instrumentation amplifier available in an 8-lead package. Gain of the AMP02 is set by a single external resistor and can range from 1 to 10,000. No gain set resistor is required for unity gain. The AMP02 includes an input protection network that allows the inputs to ...
... The AMP02 is the first precision instrumentation amplifier available in an 8-lead package. Gain of the AMP02 is set by a single external resistor and can range from 1 to 10,000. No gain set resistor is required for unity gain. The AMP02 includes an input protection network that allows the inputs to ...
A 200 MHz 23 mW High-Efficiency Inductive Link Power Supply Cir
... ABSTRACT: A 200 MHz CMOS near-field inductive link power supply (ILPS) supplying output power of 18 mW and 5 mW under supply voltage of 1.8 V and 1 V is proposed in this paper. The CMOS power supply consists of differential-driven rectifier and low-dropout regulators (LDOs). Two fully-integrated LDO ...
... ABSTRACT: A 200 MHz CMOS near-field inductive link power supply (ILPS) supplying output power of 18 mW and 5 mW under supply voltage of 1.8 V and 1 V is proposed in this paper. The CMOS power supply consists of differential-driven rectifier and low-dropout regulators (LDOs). Two fully-integrated LDO ...
Diodes
... (a) Begin with the capacitor disconnected. Observe the full-wave rectified pattern on the oscilloscope. Verify that the frequency of the pattern is 120 Hz. [Note: Because the two channels of your oscilloscope have a common ground, it is not possible to view both the input and the output of the recti ...
... (a) Begin with the capacitor disconnected. Observe the full-wave rectified pattern on the oscilloscope. Verify that the frequency of the pattern is 120 Hz. [Note: Because the two channels of your oscilloscope have a common ground, it is not possible to view both the input and the output of the recti ...
Using the TL441 with the TL441 to Generate 4mA to 20mA Output
... A common requirement of sensor conditioning systems is that they have a 4mA to 20mA output. For example, instrumentation amplifiers are frequently used to translate a pressure sensor output to a usable voltage level. In many cases, it is desirable to translate the amplifier voltage output to the ind ...
... A common requirement of sensor conditioning systems is that they have a 4mA to 20mA output. For example, instrumentation amplifiers are frequently used to translate a pressure sensor output to a usable voltage level. In many cases, it is desirable to translate the amplifier voltage output to the ind ...
Amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that increases the power of a signal.It does this by taking energy from a power supply and controlling the output to match the input signal shape but with a larger amplitude. In this sense, an amplifier modulates the output of the power supply to make the output signal stronger than the input signal. An amplifier is effectively the opposite of an attenuator: while an amplifier provides gain, an attenuator provides loss.An amplifier can either be a separate piece of equipment or an electrical circuit within another device. The ability to amplify is fundamental to modern electronics, and amplifiers are extremely widely used in almost all electronic equipment. The types of amplifiers can be categorized in different ways. One is by the frequency of the electronic signal being amplified; audio amplifiers amplify signals in the audio (sound) range of less than 20 kHz, RF amplifiers amplify frequencies in the radio frequency range between 20 kHz and 300 GHz. Another is which quantity, voltage or current is being amplified; amplifiers can be divided into voltage amplifiers, current amplifiers, transconductance amplifiers, and transresistance amplifiers. A further distinction is whether the output is a linear or nonlinear representation of the input. Amplifiers can also be categorized by their physical placement in the signal chain.The first practical electronic device that amplified was the Audion (triode) vacuum tube, invented in 1906 by Lee De Forest, which led to the first amplifiers. The terms ""amplifier"" and ""amplification"" (from the Latin amplificare, 'to enlarge or expand') were first used for this new capability around 1915 when triodes became widespread. For the next 50 years, vacuum tubes were the only devices that could amplify. All amplifiers used them until the 1960s, when transistors appeared. Most amplifiers today use transistors, though tube amplifiers are still produced.