RF5225 2.4GHz TO 2.5GHz, 802.11B/G/N WiFi FRONT END MODULE Features
... RF lines do not cross under this pin. Gerber files of RFMD PCBA designs can be provided on request. The supply voltage lines should present an RF short to the FEM by using bypass capacitors on the VCC traces. The RF5225 is a very easy part to implement , but care in circuit layout and component sele ...
... RF lines do not cross under this pin. Gerber files of RFMD PCBA designs can be provided on request. The supply voltage lines should present an RF short to the FEM by using bypass capacitors on the VCC traces. The RF5225 is a very easy part to implement , but care in circuit layout and component sele ...
Specification of bias power supply
... invert circuit (Q1-Q4) and coupled to voltage switching path (KL-LM-KH) by high frequency transformer, at last the direct pulse current voltage will be output by high frequency rectification D3 . 1.3 The power output of electricity through the current sensor after sampling as sampling signal input c ...
... invert circuit (Q1-Q4) and coupled to voltage switching path (KL-LM-KH) by high frequency transformer, at last the direct pulse current voltage will be output by high frequency rectification D3 . 1.3 The power output of electricity through the current sensor after sampling as sampling signal input c ...
OPA4243 Quad OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER POWER, Single-Supply Micro
... Rail-to-rail input signals will not cause damage or invert the output of the OPA4243. To protect against ESD and excessive input voltage (beyond the supply rails) the OPA4243 includes diodes from the input terminals to the power supply rails. Normally, these diodes are reversed biased and have negli ...
... Rail-to-rail input signals will not cause damage or invert the output of the OPA4243. To protect against ESD and excessive input voltage (beyond the supply rails) the OPA4243 includes diodes from the input terminals to the power supply rails. Normally, these diodes are reversed biased and have negli ...
LM1815
... edge of the input signal. Unlike other zero crossing detectors, the LM1815 cannot be triggered until the input signal has crossed an “arming” threshold on the positive-going portion of the waveform. The arming circuit is reset when the chip is triggered, and subsequent zero crossings are ignored unt ...
... edge of the input signal. Unlike other zero crossing detectors, the LM1815 cannot be triggered until the input signal has crossed an “arming” threshold on the positive-going portion of the waveform. The arming circuit is reset when the chip is triggered, and subsequent zero crossings are ignored unt ...
OPA4872-EP 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... provides a user-settable output amplifier gain with greater than 500-MHz large-signal bandwidth (2 VPP). The switching glitch is improved over earlier solutions using a new (patented) input stage switching approach. This technique uses current steering as the input switch while maintaining an overal ...
... provides a user-settable output amplifier gain with greater than 500-MHz large-signal bandwidth (2 VPP). The switching glitch is improved over earlier solutions using a new (patented) input stage switching approach. This technique uses current steering as the input switch while maintaining an overal ...
APD 2000 - Absolute Process Instruments
... The APD 2000 DuoPak accepts two DC voltage or current inputs and provides two optically isolated DC voltage or current outputs that are linearly related to the inputs. The input ranges and the output ranges for each channel are independent and can be specified as required. This provides an economica ...
... The APD 2000 DuoPak accepts two DC voltage or current inputs and provides two optically isolated DC voltage or current outputs that are linearly related to the inputs. The input ranges and the output ranges for each channel are independent and can be specified as required. This provides an economica ...
A Low-Power High-PSRR Current Mode Microphone Preamplifier
... ignore the term of the dependent source adds a feedback block from as shown in Fig. 2. Combining the output with gain all these effects and using Black’s formula for feedback loops, we get ...
... ignore the term of the dependent source adds a feedback block from as shown in Fig. 2. Combining the output with gain all these effects and using Black’s formula for feedback loops, we get ...
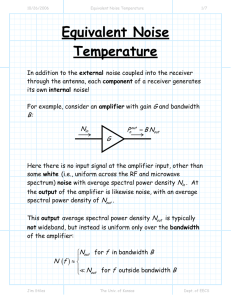
Equivalent Noise Temperature
... Equivalent Noise Temperature In addition to the external noise coupled into the receiver through the antenna, each component of a receiver generates its own internal noise! For example, consider an amplifier with gain G and bandwidth ...
... Equivalent Noise Temperature In addition to the external noise coupled into the receiver through the antenna, each component of a receiver generates its own internal noise! For example, consider an amplifier with gain G and bandwidth ...
Evaluating the NE605 SO and SSOP demo-board
... it becomes important to follow good RF techniques. This application note shows the techniques used in the SO and SSOP demo-board. It does not cover the basic functionality of the NE605 but instead focuses more on the layout constraints. This application note also has a trouble-shooting chart to aid ...
... it becomes important to follow good RF techniques. This application note shows the techniques used in the SO and SSOP demo-board. It does not cover the basic functionality of the NE605 but instead focuses more on the layout constraints. This application note also has a trouble-shooting chart to aid ...
Study of Speed Enhancement of a CMOS ring VCO
... feedback, a maximum of 167 % increase in speed with feedback resistance of 33 kΩ. But in case of negative feedback to gate same speed improvement, the require feedback resistance will be nearly 200 kΩ. Since this feedback resistance is very large, so it is difficult to fabricate in integrated circui ...
... feedback, a maximum of 167 % increase in speed with feedback resistance of 33 kΩ. But in case of negative feedback to gate same speed improvement, the require feedback resistance will be nearly 200 kΩ. Since this feedback resistance is very large, so it is difficult to fabricate in integrated circui ...
HY2596A Description Features 3A 150kHz DC-DC BUCK REGULATOR
... design of switch mode power supplies. HY2596A guarantees 4% tolerance on output voltage within specified input voltages and output load conditions and 15% on the oscillator frequency. External shut-down is included with typical 100uA (typical) standby current. The output switch has cycle-by-cycle cu ...
... design of switch mode power supplies. HY2596A guarantees 4% tolerance on output voltage within specified input voltages and output load conditions and 15% on the oscillator frequency. External shut-down is included with typical 100uA (typical) standby current. The output switch has cycle-by-cycle cu ...
from ucd.ie - the RF and Microwave Research Group at UCD
... achieve high efficiency for wideband signals by properly designing the switch control signal to force the switcher to provide the majority of the required output current. However, because the digital switch control is an open loop structure, in practice, it cannot be guaranteed that the dc level pro ...
... achieve high efficiency for wideband signals by properly designing the switch control signal to force the switcher to provide the majority of the required output current. However, because the digital switch control is an open loop structure, in practice, it cannot be guaranteed that the dc level pro ...
AD8210 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... sensing, filtering at the input of the AD8210 can be beneficial in reducing differential noise, as well as transients and current ripples flowing through the input shunt resistor. An input lowpass filter can be implemented as shown in Figure 32. ...
... sensing, filtering at the input of the AD8210 can be beneficial in reducing differential noise, as well as transients and current ripples flowing through the input shunt resistor. An input lowpass filter can be implemented as shown in Figure 32. ...
Buck Current/Voltage Fed Push-Pull PWM
... To force BUCK high, force VCSAO=2.5 V, VCEAO = 2.5 V, a 25-kΩ pulldown resistor from RAMP to ground, and VCT = 0.5 V. To force BUCK low, force VCSAO = 2.5 V, VCEAO = 2.5 V, a 10-kΩ pulldown resistor from RAMP to ground, and VCT = 3.5 V. The overlap time is measured from the point at which the rising ...
... To force BUCK high, force VCSAO=2.5 V, VCEAO = 2.5 V, a 25-kΩ pulldown resistor from RAMP to ground, and VCT = 0.5 V. To force BUCK low, force VCSAO = 2.5 V, VCEAO = 2.5 V, a 10-kΩ pulldown resistor from RAMP to ground, and VCT = 3.5 V. The overlap time is measured from the point at which the rising ...
AN147 : Automated Linearization of Sensor Circuits
... excitation of the PRTD is sourced by the 2.5V voltage reference VR1 via R1. The DCP1 (digitally controlled potentiometer of the X4023x) provides for automated adjustment of the thermometer scale factor and span. Voltage monitor VMON2 monitors the current excitation by tracking the voltage. The VMON2 ...
... excitation of the PRTD is sourced by the 2.5V voltage reference VR1 via R1. The DCP1 (digitally controlled potentiometer of the X4023x) provides for automated adjustment of the thermometer scale factor and span. Voltage monitor VMON2 monitors the current excitation by tracking the voltage. The VMON2 ...
MAX3801 3.2Gbps Adaptive Equalizer General Description Features
... The adaptive cable equalizer accepts differential CML input data at rates up to 3.2Gbps and is capable of equalizing differential or single-ended signals. It automatically adjusts to attenuation levels of up to 30dB at 1.6GHz (because of skin-effect losses in copper cable). The equalizer consists of ...
... The adaptive cable equalizer accepts differential CML input data at rates up to 3.2Gbps and is capable of equalizing differential or single-ended signals. It automatically adjusts to attenuation levels of up to 30dB at 1.6GHz (because of skin-effect losses in copper cable). The equalizer consists of ...
AD626 - Analog Devices
... The output of amplifier A2 relies on a 10 k⍀ resistor to –VS for “pull-down.” For single-supply operation, (–VS = “GND”), A2 can drive a 10 k⍀ ground referenced load to at least +4.7 V. The minimum, nominally “zero,” output voltage will be 30 mV. For dual-supply operation (±5 V), the positive output ...
... The output of amplifier A2 relies on a 10 k⍀ resistor to –VS for “pull-down.” For single-supply operation, (–VS = “GND”), A2 can drive a 10 k⍀ ground referenced load to at least +4.7 V. The minimum, nominally “zero,” output voltage will be 30 mV. For dual-supply operation (±5 V), the positive output ...
Concertmate AM/FM Radio
... the left. Speakers may be placed in any convenient position, however, for optimum stereo performance they should be separated and placed against a wall or in corners. ...
... the left. Speakers may be placed in any convenient position, however, for optimum stereo performance they should be separated and placed against a wall or in corners. ...
Drake_TR-4C HF Comms Reciever_Manual
... 3-3. BLANKER SWITCH. The noise blanker may be left on except when there is a strong signal within 5 kHz of the received signal. A strong signal which falls within the 10 kHz wide crystal filter in the noise blanker, and outside the 2.1 kHz crystal filter in the TR-4C, will operate the noise blanker ...
... 3-3. BLANKER SWITCH. The noise blanker may be left on except when there is a strong signal within 5 kHz of the received signal. A strong signal which falls within the 10 kHz wide crystal filter in the noise blanker, and outside the 2.1 kHz crystal filter in the TR-4C, will operate the noise blanker ...
Amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that increases the power of a signal.It does this by taking energy from a power supply and controlling the output to match the input signal shape but with a larger amplitude. In this sense, an amplifier modulates the output of the power supply to make the output signal stronger than the input signal. An amplifier is effectively the opposite of an attenuator: while an amplifier provides gain, an attenuator provides loss.An amplifier can either be a separate piece of equipment or an electrical circuit within another device. The ability to amplify is fundamental to modern electronics, and amplifiers are extremely widely used in almost all electronic equipment. The types of amplifiers can be categorized in different ways. One is by the frequency of the electronic signal being amplified; audio amplifiers amplify signals in the audio (sound) range of less than 20 kHz, RF amplifiers amplify frequencies in the radio frequency range between 20 kHz and 300 GHz. Another is which quantity, voltage or current is being amplified; amplifiers can be divided into voltage amplifiers, current amplifiers, transconductance amplifiers, and transresistance amplifiers. A further distinction is whether the output is a linear or nonlinear representation of the input. Amplifiers can also be categorized by their physical placement in the signal chain.The first practical electronic device that amplified was the Audion (triode) vacuum tube, invented in 1906 by Lee De Forest, which led to the first amplifiers. The terms ""amplifier"" and ""amplification"" (from the Latin amplificare, 'to enlarge or expand') were first used for this new capability around 1915 when triodes became widespread. For the next 50 years, vacuum tubes were the only devices that could amplify. All amplifiers used them until the 1960s, when transistors appeared. Most amplifiers today use transistors, though tube amplifiers are still produced.