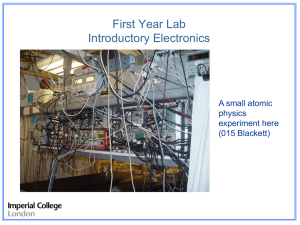
First Year Lab Introductory Electronics
... – Ground – shorts scope input to ground – kills signal, allows you to find 0V and set using Vert Position – DC – the ‘normal’ mode, what you see is what you got – AC – removes any DC component of a signal, useful for seeing a small oscillating voltage on a big DC background ...
... – Ground – shorts scope input to ground – kills signal, allows you to find 0V and set using Vert Position – DC – the ‘normal’ mode, what you see is what you got – AC – removes any DC component of a signal, useful for seeing a small oscillating voltage on a big DC background ...
ADL5391 DC to 2.0 GHz Multiplier Data Sheet (Rev. 0)
... can be done using a balun or active components, such as the AD8313, the AD8132 (both with operation down to dc), or the AD8352 (for higher drive capability). If using the ADL5391 single-ended without ac coupling capacitors, the reference voltage of 2.5 V needs to be taken into account. Voltages abov ...
... can be done using a balun or active components, such as the AD8313, the AD8132 (both with operation down to dc), or the AD8352 (for higher drive capability). If using the ADL5391 single-ended without ac coupling capacitors, the reference voltage of 2.5 V needs to be taken into account. Voltages abov ...
LMH6570 2:1 High Speed Video Multiplexer (Rev. C)
... configurations are both possible, however, all logic functions are referenced to the mid supply point. The LMH6570 features very high speed channel switching and disable times. When disabled the LMH6570 output is high impedance making MUX expansion possible by combining multiple devices. See MULTIPL ...
... configurations are both possible, however, all logic functions are referenced to the mid supply point. The LMH6570 features very high speed channel switching and disable times. When disabled the LMH6570 output is high impedance making MUX expansion possible by combining multiple devices. See MULTIPL ...
DALI sub K-14 F
... introducing audible level differences or pumping artefacts. This is done to avoid clipping of the audio signal that will cause distortion and to prevent the amplifier from being damaged. The limiter is only functional at extreme sound pressure levels. Fitted with controls for gain, cut-off frequency ...
... introducing audible level differences or pumping artefacts. This is done to avoid clipping of the audio signal that will cause distortion and to prevent the amplifier from being damaged. The limiter is only functional at extreme sound pressure levels. Fitted with controls for gain, cut-off frequency ...
74VHC163 4-Bit Binary Counter with Synchronous Clear
... counters, which facilitates easy implementation of n-bit counters without using external gates. ...
... counters, which facilitates easy implementation of n-bit counters without using external gates. ...
LTC1046 - Inductorless 5V to -5V Converter
... capability for input voltages of 6V or less. It trades off operating voltage to get higher output current. The LTC1046 provides several voltage conversion functions: the input voltage can be inverted (VOUT = – VIN), divided (VOUT = VIN/2) or multiplied (VOUT = ± nVIN). ...
... capability for input voltages of 6V or less. It trades off operating voltage to get higher output current. The LTC1046 provides several voltage conversion functions: the input voltage can be inverted (VOUT = – VIN), divided (VOUT = VIN/2) or multiplied (VOUT = ± nVIN). ...
APN0010 - GM International srl
... 10 KΩ to simulate a proximity open condition, the indication LED on unit and output LED on terminal block must be relevant with the dip-switch setting indicated in the installation sheet. Set the decade at 1 KΩ and the unit must change the status of output and LED indication. The “ON” yellow LED con ...
... 10 KΩ to simulate a proximity open condition, the indication LED on unit and output LED on terminal block must be relevant with the dip-switch setting indicated in the installation sheet. Set the decade at 1 KΩ and the unit must change the status of output and LED indication. The “ON” yellow LED con ...
Understand Low-Dropout Regulator (LDO)
... as much as 80 dB of PSRR at 10 Hz, but the PSRR can fall to as little as 20 dB at a few tens of kilohertz. Figure 10 shows the relationship between the error amplifier’s gain-bandwidth and the PSRR. This simplified example ignores parasitics from the output capacitor and the pass element. The PSRR i ...
... as much as 80 dB of PSRR at 10 Hz, but the PSRR can fall to as little as 20 dB at a few tens of kilohertz. Figure 10 shows the relationship between the error amplifier’s gain-bandwidth and the PSRR. This simplified example ignores parasitics from the output capacitor and the pass element. The PSRR i ...
TL082
... Customers represent that they have all necessary expertise in the safety and regulatory ramifications of their life support devices or systems, and acknowledge and agree that they are solely responsible for all legal, regulatory and safety-related requirements concerning their products and any use o ...
... Customers represent that they have all necessary expertise in the safety and regulatory ramifications of their life support devices or systems, and acknowledge and agree that they are solely responsible for all legal, regulatory and safety-related requirements concerning their products and any use o ...
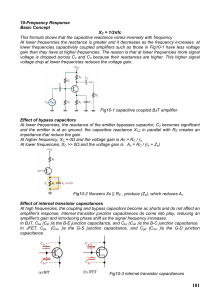
10-Frequency Response Basic Concept XC = 1/2πfc This formula
... voltage is lost due to a voltage-divider effect of the source resistance and the reactance of Cbe Fig10-4(a). When the reactance of Cbc (or Cgd ) becomes small enough, a significant amount of output signal voltage is fed back out of phase with the input (negative feedback), thus effectively reducing ...
... voltage is lost due to a voltage-divider effect of the source resistance and the reactance of Cbe Fig10-4(a). When the reactance of Cbc (or Cgd ) becomes small enough, a significant amount of output signal voltage is fed back out of phase with the input (negative feedback), thus effectively reducing ...
LF155/LF156/LF256 LF257 LF355 LF356
... Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absol ...
... Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absol ...
DAC900 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... The DAC900 has a high impedance (200kΩ) current output with a nominal range of 20mA and an output compliance of up to 1.25V. The differential outputs allow for both a differential or singleended analog signal interface. The close matching of the current outputs ensures superior dynamic performance i ...
... The DAC900 has a high impedance (200kΩ) current output with a nominal range of 20mA and an output compliance of up to 1.25V. The differential outputs allow for both a differential or singleended analog signal interface. The close matching of the current outputs ensures superior dynamic performance i ...
TPA6020A2 Audio Power Amplifier Evaluation
... TI does not warrant or represent that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any TI patent right, copyright, mask work right, or other TI intellectual property right relating to any combination, machine, or process in which TI products or services are used. Information published by ...
... TI does not warrant or represent that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any TI patent right, copyright, mask work right, or other TI intellectual property right relating to any combination, machine, or process in which TI products or services are used. Information published by ...
Amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that increases the power of a signal.It does this by taking energy from a power supply and controlling the output to match the input signal shape but with a larger amplitude. In this sense, an amplifier modulates the output of the power supply to make the output signal stronger than the input signal. An amplifier is effectively the opposite of an attenuator: while an amplifier provides gain, an attenuator provides loss.An amplifier can either be a separate piece of equipment or an electrical circuit within another device. The ability to amplify is fundamental to modern electronics, and amplifiers are extremely widely used in almost all electronic equipment. The types of amplifiers can be categorized in different ways. One is by the frequency of the electronic signal being amplified; audio amplifiers amplify signals in the audio (sound) range of less than 20 kHz, RF amplifiers amplify frequencies in the radio frequency range between 20 kHz and 300 GHz. Another is which quantity, voltage or current is being amplified; amplifiers can be divided into voltage amplifiers, current amplifiers, transconductance amplifiers, and transresistance amplifiers. A further distinction is whether the output is a linear or nonlinear representation of the input. Amplifiers can also be categorized by their physical placement in the signal chain.The first practical electronic device that amplified was the Audion (triode) vacuum tube, invented in 1906 by Lee De Forest, which led to the first amplifiers. The terms ""amplifier"" and ""amplification"" (from the Latin amplificare, 'to enlarge or expand') were first used for this new capability around 1915 when triodes became widespread. For the next 50 years, vacuum tubes were the only devices that could amplify. All amplifiers used them until the 1960s, when transistors appeared. Most amplifiers today use transistors, though tube amplifiers are still produced.