MM74HC4046 CMOS Phase Lock Loop - Elektronik
... This detector is a digital memory network. It consists of four flip-flops and some gating logic, a three state output and a phase pulse output as shown in Figure 6. This comparator acts only on the positive edges of the input signals and is thus independent of signal duty cycle. Phase comparator II ...
... This detector is a digital memory network. It consists of four flip-flops and some gating logic, a three state output and a phase pulse output as shown in Figure 6. This comparator acts only on the positive edges of the input signals and is thus independent of signal duty cycle. Phase comparator II ...
Chapter28
... For a good p-n junction made of silicon, the ratio RR/RF should be equal to or greater than 1000:1. Although not shown, the resistance measured between the collector and emitter should read high or infinite for both connections of the meter leads. ...
... For a good p-n junction made of silicon, the ratio RR/RF should be equal to or greater than 1000:1. Although not shown, the resistance measured between the collector and emitter should read high or infinite for both connections of the meter leads. ...
Chapter 6: Voltage Regulator
... in input voltage or load current caused by a change in load resistance, the decrease is sensed by R1 and R2. A feedback voltage obtained from voltage divider R1 and R2 is applied to the op-amp’s non-inverting input and compared to the Zener voltage to control the drive current to the transistor. ...
... in input voltage or load current caused by a change in load resistance, the decrease is sensed by R1 and R2. A feedback voltage obtained from voltage divider R1 and R2 is applied to the op-amp’s non-inverting input and compared to the Zener voltage to control the drive current to the transistor. ...
Load Cell Measurement using the CS3001/02/11/12
... noise in the converter is dominated by quantization noise and will be spread from DC to one half the output word rate. This was illustrated with the plot of the CS5513 noise in Figure 3. The CS5512 and CS5513 use the same modulator-filter design with the only difference being the clock source used t ...
... noise in the converter is dominated by quantization noise and will be spread from DC to one half the output word rate. This was illustrated with the plot of the CS5513 noise in Figure 3. The CS5512 and CS5513 use the same modulator-filter design with the only difference being the clock source used t ...
MAX9169/MAX9170 4-Port LVDS and LVTTL-to-LVDS Repeaters General Description Features
... operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated in the operational sections of the specifications is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability. ...
... operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated in the operational sections of the specifications is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability. ...
Chapter 6: Voltage Regulator
... in input voltage or load current caused by a change in load resistance, the decrease is sensed by R1 and R2. A feedback voltage obtained from voltage divider R1 and R2 is applied to the op-amp’s non-inverting input and compared to the Zener voltage to control the drive current to the transistor. ...
... in input voltage or load current caused by a change in load resistance, the decrease is sensed by R1 and R2. A feedback voltage obtained from voltage divider R1 and R2 is applied to the op-amp’s non-inverting input and compared to the Zener voltage to control the drive current to the transistor. ...
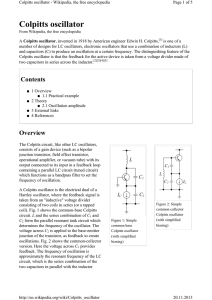
Colpitts oscillator
... consists of a gain device (such as a bipolar junction transistor, field effect transistor, operational amplifier, or vacuum tube) with its output connected to its input in a feedback loop containing a parallel LC circuit (tuned circuit) which functions as a bandpass filter to set the frequency of os ...
... consists of a gain device (such as a bipolar junction transistor, field effect transistor, operational amplifier, or vacuum tube) with its output connected to its input in a feedback loop containing a parallel LC circuit (tuned circuit) which functions as a bandpass filter to set the frequency of os ...
Analysis of fully differential amplifiers
... (from VIN to VOUT) and the VOCM error amplifier. The operation of the VOCM error amplifier is the simpler of the two and will be considered first. It may help to review the simplified schematic shown in Reference 1. VOUT+ and VOUT – are filtered and summed by an internal RC network. The VOCM amplifi ...
... (from VIN to VOUT) and the VOCM error amplifier. The operation of the VOCM error amplifier is the simpler of the two and will be considered first. It may help to review the simplified schematic shown in Reference 1. VOUT+ and VOUT – are filtered and summed by an internal RC network. The VOCM amplifi ...
MAX1719/MAX1720/MAX1721 SOT23, Switched-Capacitor Voltage Inverters with Shutdown General Description
... The ultra-small MAX1719/MAX1720/MAX1721 monolithic, CMOS charge-pump inverters accept input voltages ranging from +1.5V to +5.5V. The MAX1720 operates at 12kHz, and the MAX1719/MAX1721 operate at 125kHz. High efficiency, small external components, and logiccontrolled shutdown make these devices idea ...
... The ultra-small MAX1719/MAX1720/MAX1721 monolithic, CMOS charge-pump inverters accept input voltages ranging from +1.5V to +5.5V. The MAX1720 operates at 12kHz, and the MAX1719/MAX1721 operate at 125kHz. High efficiency, small external components, and logiccontrolled shutdown make these devices idea ...
Basic Characteristics Data
... resonance of the filter or inductance. ¡Install a correspondence filter, if it is required to meet a noise standard or if the surge voltage may be applied to the unit. ¡Install a primary decoupling capacitor CY, with more than 470pF, near the input pins (within 50mm from the pins). ¡When the total c ...
... resonance of the filter or inductance. ¡Install a correspondence filter, if it is required to meet a noise standard or if the surge voltage may be applied to the unit. ¡Install a primary decoupling capacitor CY, with more than 470pF, near the input pins (within 50mm from the pins). ¡When the total c ...
ML15.121 - PULS Power Supply
... A compact size, light weight, simple mounting onto the DIN-rail and the utilization of only quality components are what makes the MiniLine power supplies so easy to use and install within seconds. ...
... A compact size, light weight, simple mounting onto the DIN-rail and the utilization of only quality components are what makes the MiniLine power supplies so easy to use and install within seconds. ...
LTC6103 - Dual High Voltage, High Side Current Sense Amplifier
... the maximum output dynamic range is available. Output dynamic range is limited by both the maximum allowed output current and the maximum allowed output voltage, as well as the minimum practical output signal. If less dynamic range is required, then RIN can be increased accordingly, reducing the max ...
... the maximum output dynamic range is available. Output dynamic range is limited by both the maximum allowed output current and the maximum allowed output voltage, as well as the minimum practical output signal. If less dynamic range is required, then RIN can be increased accordingly, reducing the max ...
LM3916 Dot/Bar Display Driver
... LM3916 is set up with 10V full scale across its voltage divider, the turn-on point for the first LED is only 450 mV. A simple silicon diode rectifier won’t work well at the low end due to the 600 mV diode threshold. The half-wave peak detector in Figure 3 uses a PNP emitter-follower in front of the ...
... LM3916 is set up with 10V full scale across its voltage divider, the turn-on point for the first LED is only 450 mV. A simple silicon diode rectifier won’t work well at the low end due to the 600 mV diode threshold. The half-wave peak detector in Figure 3 uses a PNP emitter-follower in front of the ...
MAX5152/MAX5153 Low-Power, Dual, 13-Bit Voltage-Output DACs with Configurable Outputs _______________General Description
... 16-pin QSOP and DIP packages. Access to the inverting input allows for specific gain configurations, remote sensing, and high output current capability, making these devices ideally suited for industrial process controls. These devices are also well suited for digitally programmable (4–20mA) current ...
... 16-pin QSOP and DIP packages. Access to the inverting input allows for specific gain configurations, remote sensing, and high output current capability, making these devices ideally suited for industrial process controls. These devices are also well suited for digitally programmable (4–20mA) current ...
CBC early test report - Mark Raymond
... Figure 3.1.3 shows a measurement of three of the bias generator voltage dependences on I2C register setting. VPC and VPLUS are implemented by mirroring a current into a resistor, and the voltage range covered is consistent with what is expected from simulation. VPAFB is not a simple voltage setting ...
... Figure 3.1.3 shows a measurement of three of the bias generator voltage dependences on I2C register setting. VPC and VPLUS are implemented by mirroring a current into a resistor, and the voltage range covered is consistent with what is expected from simulation. VPAFB is not a simple voltage setting ...
STK672-632AN-E
... 1-3.[CWB (Motor direction setting)] When CWB=0: The motor rotates in the clockwise direction. When CWB=1: The motor rotates in the counterclockwise direction. See the timing charts for details on the operation of the outputs. Note: Do not allow CWB input to vary during the 6.25s interval before and ...
... 1-3.[CWB (Motor direction setting)] When CWB=0: The motor rotates in the clockwise direction. When CWB=1: The motor rotates in the counterclockwise direction. See the timing charts for details on the operation of the outputs. Note: Do not allow CWB input to vary during the 6.25s interval before and ...
LP2950/LP2951 Series of Adjustable Micropower Voltage Regulators Series General Description
... this capacitor the part will oscillate. Most types of tantalum or aluminum electrolytics work fine here; even film types work but are not recommended for reasons of cost. Many aluminum electrolytics have electrolytes that freeze at about −30˚C, so solid tantalums are recommended for operation below ...
... this capacitor the part will oscillate. Most types of tantalum or aluminum electrolytics work fine here; even film types work but are not recommended for reasons of cost. Many aluminum electrolytics have electrolytes that freeze at about −30˚C, so solid tantalums are recommended for operation below ...
STK672-630AN-E
... 1-3.[CWB (Motor direction setting)] When CWB=0: The motor rotates in the clockwise direction. When CWB=1: The motor rotates in the counterclockwise direction. See the timing charts for details on the operation of the outputs. Note: Do not allow CWB input to vary during the 6.25s interval before and ...
... 1-3.[CWB (Motor direction setting)] When CWB=0: The motor rotates in the clockwise direction. When CWB=1: The motor rotates in the counterclockwise direction. See the timing charts for details on the operation of the outputs. Note: Do not allow CWB input to vary during the 6.25s interval before and ...
MAX5088/MAX5089 2.2MHz, 2A Buck Converters with an Integrated High-Side Switch General Description
... RESET, PGOOD to SGND ........................................-0.3V to +6V BYPASS to SGND..................................................-0.3V to +2.2V VL and BYPASS Short-Circuit Duration to SGND ......Continuous Continuous Power Dissipation* (TA = +70°C) 16-Pin TQFN (derate 33mW/°C above +70°C) . ...
... RESET, PGOOD to SGND ........................................-0.3V to +6V BYPASS to SGND..................................................-0.3V to +2.2V VL and BYPASS Short-Circuit Duration to SGND ......Continuous Continuous Power Dissipation* (TA = +70°C) 16-Pin TQFN (derate 33mW/°C above +70°C) . ...
LMF100 High Performance Dual Switched Capacitor Filter
... block. Each block has 3 outputs. One output can be configured to perform either an allpass, highpass, or notch function. The other two outputs perform bandpass and lowpass functions. The center frequency of each filter stage is tuned by using an external clock or a combination of a clock and resisto ...
... block. Each block has 3 outputs. One output can be configured to perform either an allpass, highpass, or notch function. The other two outputs perform bandpass and lowpass functions. The center frequency of each filter stage is tuned by using an external clock or a combination of a clock and resisto ...
Designing of a variable frequency standalone impedance analyzer
... 2.2. Constant current source Bio-impedance can be measured using constant current source. There are many constant current sources like howland current source, current mirror based constant current source, but application of these current sources are limited to lower value of frequency and impedance ...
... 2.2. Constant current source Bio-impedance can be measured using constant current source. There are many constant current sources like howland current source, current mirror based constant current source, but application of these current sources are limited to lower value of frequency and impedance ...
Amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that increases the power of a signal.It does this by taking energy from a power supply and controlling the output to match the input signal shape but with a larger amplitude. In this sense, an amplifier modulates the output of the power supply to make the output signal stronger than the input signal. An amplifier is effectively the opposite of an attenuator: while an amplifier provides gain, an attenuator provides loss.An amplifier can either be a separate piece of equipment or an electrical circuit within another device. The ability to amplify is fundamental to modern electronics, and amplifiers are extremely widely used in almost all electronic equipment. The types of amplifiers can be categorized in different ways. One is by the frequency of the electronic signal being amplified; audio amplifiers amplify signals in the audio (sound) range of less than 20 kHz, RF amplifiers amplify frequencies in the radio frequency range between 20 kHz and 300 GHz. Another is which quantity, voltage or current is being amplified; amplifiers can be divided into voltage amplifiers, current amplifiers, transconductance amplifiers, and transresistance amplifiers. A further distinction is whether the output is a linear or nonlinear representation of the input. Amplifiers can also be categorized by their physical placement in the signal chain.The first practical electronic device that amplified was the Audion (triode) vacuum tube, invented in 1906 by Lee De Forest, which led to the first amplifiers. The terms ""amplifier"" and ""amplification"" (from the Latin amplificare, 'to enlarge or expand') were first used for this new capability around 1915 when triodes became widespread. For the next 50 years, vacuum tubes were the only devices that could amplify. All amplifiers used them until the 1960s, when transistors appeared. Most amplifiers today use transistors, though tube amplifiers are still produced.