Chapter 4: Quantities of Reactants and Products
... and 14 O) in the products and reactants. The law of conservation of mass says that masses of the reactants must add up to the masses of the products, 284.16 g. This looks right. 12. Define the problem: Given the balanced equation for a reaction, identify the stoichiometric coefficients in this equat ...
... and 14 O) in the products and reactants. The law of conservation of mass says that masses of the reactants must add up to the masses of the products, 284.16 g. This looks right. 12. Define the problem: Given the balanced equation for a reaction, identify the stoichiometric coefficients in this equat ...
CHAPTER 3 STOICHIOMETRY
... Solution: Let's first calculate the number of N atoms in 1.68 10 g of urea. First, we must convert grams of urea to number of molecules of urea. This calculation is similar to Problem 3.26. The molecular formula of urea shows there are two N atoms in one urea molecule, which will allow us to conve ...
... Solution: Let's first calculate the number of N atoms in 1.68 10 g of urea. First, we must convert grams of urea to number of molecules of urea. This calculation is similar to Problem 3.26. The molecular formula of urea shows there are two N atoms in one urea molecule, which will allow us to conve ...
Sample Chapter 3
... activity from a tropical plant: what is its formula, and what quantity of metabolic products will establish a safe dosage level? Thousands of biologically active compounds have been found in plants and many are used in modern medicines. For example, in 1963, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FD ...
... activity from a tropical plant: what is its formula, and what quantity of metabolic products will establish a safe dosage level? Thousands of biologically active compounds have been found in plants and many are used in modern medicines. For example, in 1963, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FD ...
Topic 1 Quantitative Chemistry Answers - slider-dpchemistry-11
... atomic masses of all the atoms that comprise the molecule. As for relative atomic mass there are no units. For example, the Mr of water H2O is (H: 2 x 1.01) + (O: 16.00) = 18.02. c) molar mass The collective name for properties that are expressed with units of mass per mole is known as molar mass. S ...
... atomic masses of all the atoms that comprise the molecule. As for relative atomic mass there are no units. For example, the Mr of water H2O is (H: 2 x 1.01) + (O: 16.00) = 18.02. c) molar mass The collective name for properties that are expressed with units of mass per mole is known as molar mass. S ...
Stoichiometry
... factor to clear the fractional coefficients 4. Verify that the equation is balanced and the coefficients are the smallest whole numbers 5. Specify physical states ...
... factor to clear the fractional coefficients 4. Verify that the equation is balanced and the coefficients are the smallest whole numbers 5. Specify physical states ...
Chapter 1
... • Amorphous metal is so tightly packed that this does not occur because the atoms of different sizes and randomly pack http://mrsec.wisc.edu/Edetc/SlideShow/slides/amorphous/glass.html Dr. S. M. Condren ...
... • Amorphous metal is so tightly packed that this does not occur because the atoms of different sizes and randomly pack http://mrsec.wisc.edu/Edetc/SlideShow/slides/amorphous/glass.html Dr. S. M. Condren ...
2 - OnCourse
... This is an empirical formula. The true chemical formula could be a whole number multiple of the empirical formula. The chemical formula of the substance analyzed could be C8H18 or any other whole number multiple. Molar mass of empirical formula 4 moles C x 12.01 g/mol C = 48.04 g C ...
... This is an empirical formula. The true chemical formula could be a whole number multiple of the empirical formula. The chemical formula of the substance analyzed could be C8H18 or any other whole number multiple. Molar mass of empirical formula 4 moles C x 12.01 g/mol C = 48.04 g C ...
Calculations and the Chemical Equation
... Relating Avogadro's number to molar mass: calculation of the mass of Avogadro's number of sodium atoms Converting moles to atoms. Converting atoms to moles. Converting moles of a substance to mass in grams. Converting kilograms to moles. Converting grams to number of atoms. Calculating formula weigh ...
... Relating Avogadro's number to molar mass: calculation of the mass of Avogadro's number of sodium atoms Converting moles to atoms. Converting atoms to moles. Converting moles of a substance to mass in grams. Converting kilograms to moles. Converting grams to number of atoms. Calculating formula weigh ...
Stoichiometric Calculations
... • you would need 3 mol of H2 to completely react with • you would produce 2 mol of NH3 ...
... • you would need 3 mol of H2 to completely react with • you would produce 2 mol of NH3 ...
Alternative Coverage of moles, molarity, and Chemical Calculations
... To aid in chemical calculations, chemists use a unit called a mole. The quantity of a substance whose mass in grams is numerically equal to the formula mass of the substance is called a mole. The abbreviation for mole is mol and is often used whenever a specific quantity of moles is written, for exa ...
... To aid in chemical calculations, chemists use a unit called a mole. The quantity of a substance whose mass in grams is numerically equal to the formula mass of the substance is called a mole. The abbreviation for mole is mol and is often used whenever a specific quantity of moles is written, for exa ...
Chapter 3 HWsolutions (from Handout)
... Strategy: Looking at the balanced equation, how do we compare the amounts of Cl 2 and SiCl4? We can compare them based on the mole ratio from the balanced equation. Solution: Because the balanced equation is given in the problem, the mole ratio between Cl 2 and SiCl4 is known: 2 moles Cl2 1 mole S ...
... Strategy: Looking at the balanced equation, how do we compare the amounts of Cl 2 and SiCl4? We can compare them based on the mole ratio from the balanced equation. Solution: Because the balanced equation is given in the problem, the mole ratio between Cl 2 and SiCl4 is known: 2 moles Cl2 1 mole S ...
Chapter 6 Quantities in Chemical Reactions
... Now that we have introduced the mole and practiced using it as a conversion factor, we ask the obvious question: why is the mole that particular number of things? Why is it 6.022 × 1023 and not 1 × 1023 or even 1 × 1020? The number in a mole, Avogadro’s number, is related to the relative sizes of th ...
... Now that we have introduced the mole and practiced using it as a conversion factor, we ask the obvious question: why is the mole that particular number of things? Why is it 6.022 × 1023 and not 1 × 1023 or even 1 × 1020? The number in a mole, Avogadro’s number, is related to the relative sizes of th ...
Ch. 12 Stoichiometry
... How many molecules of NH3 are needed to produce 2.34 x 1022 molecules of N2F4? How many grams of HF are produced from a reaction of 4.56 x 1023 molecules of F2 with excess NH3? What volume of HF, at STP, can be produced from 345g of NH3? How many molecules of N2F4 can be produce from 45.6L of F2 , a ...
... How many molecules of NH3 are needed to produce 2.34 x 1022 molecules of N2F4? How many grams of HF are produced from a reaction of 4.56 x 1023 molecules of F2 with excess NH3? What volume of HF, at STP, can be produced from 345g of NH3? How many molecules of N2F4 can be produce from 45.6L of F2 , a ...
Stoichiometry
... Ex: Calculate the number of grams of oxygen required to react exactly with 4.30 mol of propane, C3H8, in the reaction by the following balanced equation: C3H8(g) + 5O2(g) 3CO2(g) + 4H2O(g) 5 mol O2 32.0 g O2 4.30 mol C3H8 x _____________ x __________ 1 mol C3H8 1 mol O2 ...
... Ex: Calculate the number of grams of oxygen required to react exactly with 4.30 mol of propane, C3H8, in the reaction by the following balanced equation: C3H8(g) + 5O2(g) 3CO2(g) + 4H2O(g) 5 mol O2 32.0 g O2 4.30 mol C3H8 x _____________ x __________ 1 mol C3H8 1 mol O2 ...
Chapter 10
... Step 2 is to identify the limiting reactant. This requires a balanced chemical equation so that the mole ratio of the reacting substances can be identified. 2 Na + 2 H2O → H2 + 2 NaOH For every 2 mol of Na that react, 2 mol of H2O react, a 2:2 or 1:1 ratio. Thus, the 1.04 mol Na will be the limiting ...
... Step 2 is to identify the limiting reactant. This requires a balanced chemical equation so that the mole ratio of the reacting substances can be identified. 2 Na + 2 H2O → H2 + 2 NaOH For every 2 mol of Na that react, 2 mol of H2O react, a 2:2 or 1:1 ratio. Thus, the 1.04 mol Na will be the limiting ...
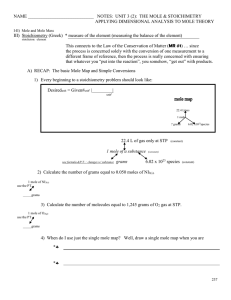
Unit 3 2 Basic Mole Conversions and Mole Maps
... This connects to the Law of the Conservation of Matter (MR #1) … since the process is concerned solely with the conversion of one measurement to a different frame of reference, then the process is really concerned with ensuring that whatever you “put into the reaction”, you somehow, “get out” with p ...
... This connects to the Law of the Conservation of Matter (MR #1) … since the process is concerned solely with the conversion of one measurement to a different frame of reference, then the process is really concerned with ensuring that whatever you “put into the reaction”, you somehow, “get out” with p ...
Chemical Quantities(mole).
... It is the volume of a gas that a mole of a gas occupies at a pressure of one atmosphere (101 kPa) and a temperature of 0.00°C. Under these conditions (STP), the volume of one mole is 22.3 L. ...
... It is the volume of a gas that a mole of a gas occupies at a pressure of one atmosphere (101 kPa) and a temperature of 0.00°C. Under these conditions (STP), the volume of one mole is 22.3 L. ...
Mead Chemistry Lap 11: Stoichiometry Chapter 12 12.1 Balanced
... Mead Chemistry Lap 11: Stoichiometry Chapter 12 12.1 Balanced Chemical Equations A. Balanced equations • Used to find how much reactant is needed • Used to predict how much product will be made • You can use amount of one substance to find the amounts of the other substances • Quantity usually in mo ...
... Mead Chemistry Lap 11: Stoichiometry Chapter 12 12.1 Balanced Chemical Equations A. Balanced equations • Used to find how much reactant is needed • Used to predict how much product will be made • You can use amount of one substance to find the amounts of the other substances • Quantity usually in mo ...
File
... us the mole ratio. • It takes 1 mole of ethanol to react with 3 moles of oxygen. This produces 2 moles of carbon dioxide and 3 moles of water. • The mole ratio will act as our conversion ...
... us the mole ratio. • It takes 1 mole of ethanol to react with 3 moles of oxygen. This produces 2 moles of carbon dioxide and 3 moles of water. • The mole ratio will act as our conversion ...
Unit_1_Introduction_to_Chemistry_Student[1]
... 1. Safety goggles must be worn at all times during a lab. This rule must be followed not matter what you are doing during the lab period. 2. Contact lenses are not allowed. Even when worn under safety goggles, since fumes from the chemicals can get under them and cause serious injuries or blindness. ...
... 1. Safety goggles must be worn at all times during a lab. This rule must be followed not matter what you are doing during the lab period. 2. Contact lenses are not allowed. Even when worn under safety goggles, since fumes from the chemicals can get under them and cause serious injuries or blindness. ...
Document
... • If 3.84 moles of C2H2 are burned, how many moles of O2 are needed?(9.6 mol) •How many moles of C2H2 are needed to produce 8.95 mole of H2O? (8.95 mol) •If 2.47 moles of C2H2 are burned, how many moles of CO2 are formed? (4.94 mol) ...
... • If 3.84 moles of C2H2 are burned, how many moles of O2 are needed?(9.6 mol) •How many moles of C2H2 are needed to produce 8.95 mole of H2O? (8.95 mol) •If 2.47 moles of C2H2 are burned, how many moles of CO2 are formed? (4.94 mol) ...
mass mass calc
... In a particular lab set up, 50.0 g of oxygen gas are available for the combustion of 25.0 g of carbon.. a) Calculate the number of moles of oxygen gas and carbon solid that are each available to react. b) Calculate the number of moles of oxygen gas that will actually be needed to react with all of t ...
... In a particular lab set up, 50.0 g of oxygen gas are available for the combustion of 25.0 g of carbon.. a) Calculate the number of moles of oxygen gas and carbon solid that are each available to react. b) Calculate the number of moles of oxygen gas that will actually be needed to react with all of t ...
Chem 11 Stoichiometry (mol-mol) Using the formulas we have
... reactant. Using other mole-quantity relationships, we can introduce mass, volume, and particles into our calculations (this is what we will be getting to in the next few classes). Example 1: How many moles of ammonia are produced when 0.60 mol of nitrogen reacts with hydrogen? Solution 1: We will wo ...
... reactant. Using other mole-quantity relationships, we can introduce mass, volume, and particles into our calculations (this is what we will be getting to in the next few classes). Example 1: How many moles of ammonia are produced when 0.60 mol of nitrogen reacts with hydrogen? Solution 1: We will wo ...
















![Unit_1_Introduction_to_Chemistry_Student[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/022016930_1-98bbde1835e65f7e36a50862854faaef-300x300.png)