Stone-roof conservation Tarek Teba
... Also, the study focuses on vault roofs, studies their behaviour as well as the main problems and failures which lead to many types of collapse they had. The structural study intersects with a theoretical review for the conservation achievements and techniques applied to the stone vaults as well as t ...
... Also, the study focuses on vault roofs, studies their behaviour as well as the main problems and failures which lead to many types of collapse they had. The structural study intersects with a theoretical review for the conservation achievements and techniques applied to the stone vaults as well as t ...
Slide 1 What do we mean when we say "house style" or
... The railroad created many new jobs to run the trains, mine the coal, make steel tracks and trains, and run the services. The people who worked these jobs sometimes lived in whole new towns created almost overnight. Industry was making other changes in the architecture of towns. As industries grew fr ...
... The railroad created many new jobs to run the trains, mine the coal, make steel tracks and trains, and run the services. The people who worked these jobs sometimes lived in whole new towns created almost overnight. Industry was making other changes in the architecture of towns. As industries grew fr ...
From the diaphragm arches to the ribbed vaults. An hypothesis for
... single ones. They can be placed parallel to the walls of the room or diagonally, springing from adjacent walls. At the Tornerias mosque in Toledo (2nd half of the 11th C.), it can be found an outstanding sample of the first solution, that divides the ceiling into nine square sections or bays, that o ...
... single ones. They can be placed parallel to the walls of the room or diagonally, springing from adjacent walls. At the Tornerias mosque in Toledo (2nd half of the 11th C.), it can be found an outstanding sample of the first solution, that divides the ceiling into nine square sections or bays, that o ...
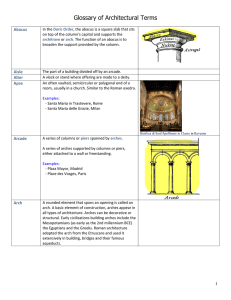
Glossary of Architectural Terms
... A ceiling or roof consisting of a continuous semicircular or pointed arch. Also known as a tunnel vault. ...
... A ceiling or roof consisting of a continuous semicircular or pointed arch. Also known as a tunnel vault. ...
Ch 18 Gothic Art Notes
... ambulatory and from the thin masonry walls framing the chapels. The rib vaults distinguishing feature is the crossed, or diagonal arches under its groins, as seen in Saint Denis’ ambulatory and chapels. These arches, or ribs, form the armature or skeletal framework for constructing the vault. Gothic ...
... ambulatory and from the thin masonry walls framing the chapels. The rib vaults distinguishing feature is the crossed, or diagonal arches under its groins, as seen in Saint Denis’ ambulatory and chapels. These arches, or ribs, form the armature or skeletal framework for constructing the vault. Gothic ...
Romanesque art in Barcelona The Romanesque Feudalism
... divided into different kingdoms of taifas. In this new situation of Andalusia Caliphate the Counts started a military pressure against these taifas that revert with monetary compensation. On the other hand, militarization and insecurity of land led to the acceleration of feudalism. Taking advantage ...
... divided into different kingdoms of taifas. In this new situation of Andalusia Caliphate the Counts started a military pressure against these taifas that revert with monetary compensation. On the other hand, militarization and insecurity of land led to the acceleration of feudalism. Taking advantage ...
Buildings to Know- Romanesque and Queen Anne
... appears fortress-like, while inside it is warm and comfortable with lots of clear-finish woodwork. Richardson designed the house as a load-bearing brick structure with a cladding of granite on the front and side, and brick with limestone trim on the rear. The house is laid out along the perimeter of ...
... appears fortress-like, while inside it is warm and comfortable with lots of clear-finish woodwork. Richardson designed the house as a load-bearing brick structure with a cladding of granite on the front and side, and brick with limestone trim on the rear. The house is laid out along the perimeter of ...
Characteristics of Gothic churches and cathedrals
... to create a powerful impression on the approaching worshipper, demonstrating both the might of God, and the might of the institution that it represents. One of the best known and most typical of such façades is that of Notre Dame de Paris. Central to the façade is the main portal, often flanked by a ...
... to create a powerful impression on the approaching worshipper, demonstrating both the might of God, and the might of the institution that it represents. One of the best known and most typical of such façades is that of Notre Dame de Paris. Central to the façade is the main portal, often flanked by a ...
History of Architecture
... The word groin refers to the edge between the intersecting vaults. Sometimes the arches of groin vaults are pointed instead of round. In comparison with a barrel vault, a groin vault provides good economies of material and labour. The thrust is concentrated along the groins so the vault need only ...
... The word groin refers to the edge between the intersecting vaults. Sometimes the arches of groin vaults are pointed instead of round. In comparison with a barrel vault, a groin vault provides good economies of material and labour. The thrust is concentrated along the groins so the vault need only ...
Romanesque Architecture Introduction Name: Introduction to
... The name gives it away. Romanesque architecture is based on Roman architectural elements. It is the rounded Roman arch that is the basis for structures built in this style. It is important to note that since the life and death of Christ, almost every major artistic and architectural movement was nam ...
... The name gives it away. Romanesque architecture is based on Roman architectural elements. It is the rounded Roman arch that is the basis for structures built in this style. It is important to note that since the life and death of Christ, almost every major artistic and architectural movement was nam ...
Introduction to Romanesque Art Romanesque art
... piers, groin vaults, large towers and decorative arcades. Each building has clearly defined forms. They are frequently of very regular, symmetrical plan; the overall appearance is one of simplicity when compared with the Gothic buildings that were to follow. The style can be identified across Europe ...
... piers, groin vaults, large towers and decorative arcades. Each building has clearly defined forms. They are frequently of very regular, symmetrical plan; the overall appearance is one of simplicity when compared with the Gothic buildings that were to follow. The style can be identified across Europe ...
características del románico
... Every building is built on robust Romanesque foundations, often so deep that allow the construction of vaults, funeral for a purpose under the apse. On these foundations the load-bearing support of the Romanesque building: the wall, the pillar and columns. - The Wall in the Roman plays a key role i ...
... Every building is built on robust Romanesque foundations, often so deep that allow the construction of vaults, funeral for a purpose under the apse. On these foundations the load-bearing support of the Romanesque building: the wall, the pillar and columns. - The Wall in the Roman plays a key role i ...
Romanesque
... After a gap of around two hundred years with no large building projects, the architects of Charlemagne’s day looked to the arched, or arcaded, system seen in Christian Roman edifices as a model. It is a logical system of stresses and buttressing, which was fairly easily engineered for large structur ...
... After a gap of around two hundred years with no large building projects, the architects of Charlemagne’s day looked to the arched, or arcaded, system seen in Christian Roman edifices as a model. It is a logical system of stresses and buttressing, which was fairly easily engineered for large structur ...
The term "Romanesque" was first applied by critics in the early
... Romanesque architecture is known by its massive quality, its thick walls, round arches, sturdy piers, groin vaults, large towers and decorative arcading. Each building has clearly defined forms and they are frequently of very regular, symmetrical plan so that the overall appearance is one of simplic ...
... Romanesque architecture is known by its massive quality, its thick walls, round arches, sturdy piers, groin vaults, large towers and decorative arcading. Each building has clearly defined forms and they are frequently of very regular, symmetrical plan so that the overall appearance is one of simplic ...
Romanesque architecture

Romanesque architecture is an architectural style of medieval Europe characterized by semi-circular arches. There is no consensus for the beginning date of the Romanesque style, with proposals ranging from the 6th to the late 10th century, this later date being the most commonly held. It developed in the 12th century into the Gothic style, marked by pointed arches. Examples of Romanesque architecture can be found across the continent, making it the first pan-European architectural style since Imperial Roman Architecture. The Romanesque style in England is traditionally referred to as Norman architecture.Combining features of ancient Roman and Byzantine buildings and other local traditions, Romanesque architecture is known by its massive quality, thick walls, round arches, sturdy pillars, groin vaults, large towers and decorative arcading. Each building has clearly defined forms, frequently of very regular, symmetrical plan; the overall appearance is one of simplicity when compared with the Gothic buildings that were to follow. The style can be identified right across Europe, despite regional characteristics and different materials.Many castles were built during this period, but they are greatly outnumbered by churches. The most significant are the great abbey churches, many of which are still standing, more or less complete and frequently in use. The enormous quantity of churches built in the Romanesque period was succeeded by the still busier period of Gothic architecture, which partly or entirely rebuilt most Romanesque churches in prosperous areas like England and Portugal. The largest groups of Romanesque survivors are in areas that were less prosperous in subsequent periods, including parts of southern France, northern Spain and rural Italy. Survivals of unfortified Romanesque secular houses and palaces, and the domestic quarters of monasteries are far rarer, but these used and adapted the features found in church buildings, on a domestic scale.