The case for fiscal policy
... necessary to keep spending down to prevent inflation. The interest can be paid by borrowing still more" (p. 356). Lerner (1943) summarized the answers to arguments against deficit spending by saying that the national debt does not have to keep on increasing, and that even if it does the interest doe ...
... necessary to keep spending down to prevent inflation. The interest can be paid by borrowing still more" (p. 356). Lerner (1943) summarized the answers to arguments against deficit spending by saying that the national debt does not have to keep on increasing, and that even if it does the interest doe ...
The Circular Flow of Income and Expenditure
... government would always have to balance its budget, exactly, every year. In terms of the diagram, the amount of funds flowing through the “net taxes” arrow would have to be exactly equal to the flow through the “government purchases” arrow. With the help of the financial sector, the government budge ...
... government would always have to balance its budget, exactly, every year. In terms of the diagram, the amount of funds flowing through the “net taxes” arrow would have to be exactly equal to the flow through the “government purchases” arrow. With the help of the financial sector, the government budge ...
... external demand due to global market uncertainties and the full production capacity being reached in 2013. Again, on the positive note is the diversification of the exports products portfolio as five products generated 79.0% of the total exports, compared to the 8M/13, when only FIAT exports created ...
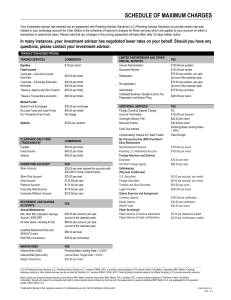
Schedule of Maximum Charges
... Certain non-FundVest funds are subject to a maximum charge of $50.00 per transaction. Those trades executed for your account with your assets through broker-dealers other than Pershing Advisor Solutions. Fees charged on anniversary of account opening. The Pershing Base Lending Rate for each currency ...
... Certain non-FundVest funds are subject to a maximum charge of $50.00 per transaction. Those trades executed for your account with your assets through broker-dealers other than Pershing Advisor Solutions. Fees charged on anniversary of account opening. The Pershing Base Lending Rate for each currency ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES MONETARY RULES FOR SMALL, OPEN, EMERGING ECONOMIES Douglas Laxton
... Finally, we gratefully acknowledge the invaluable support of Michel Juillard and Susanna Mursula in developing the procedures used in the model simulations. The views expressed here are those of the authors, and do not necessarily reflect the position of the International Monetary Fund, the Federal ...
... Finally, we gratefully acknowledge the invaluable support of Michel Juillard and Susanna Mursula in developing the procedures used in the model simulations. The views expressed here are those of the authors, and do not necessarily reflect the position of the International Monetary Fund, the Federal ...
Chapter 16 Output and the Exchange Rate in the Short Run
... Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Financial, Fiscal and Real Economic
... European fiscal and macro-economic surveillance. However, so far an integrated framework analysing fiscal, financial and real economic vulnerabilities and risks comprehensively for the Euro area is missing. This paper addresses this gap by proposing some institutional reforms. An integration of some ...
... European fiscal and macro-economic surveillance. However, so far an integrated framework analysing fiscal, financial and real economic vulnerabilities and risks comprehensively for the Euro area is missing. This paper addresses this gap by proposing some institutional reforms. An integration of some ...
Income distribution and the current account: a sectoral
... hoarding at the global level has also been identified as a contributing factor to the ‘global saving glut’, and hence the current account imbalances, prior to the Great Recession (IMF, 2006; Gruber and Kamin, 2015). Grigoli et al. (2014) in a panel estimation analysis for a sample of 165 countries f ...
... hoarding at the global level has also been identified as a contributing factor to the ‘global saving glut’, and hence the current account imbalances, prior to the Great Recession (IMF, 2006; Gruber and Kamin, 2015). Grigoli et al. (2014) in a panel estimation analysis for a sample of 165 countries f ...
A survey of the world economy September 16th 2006
... Of course there is more than one respectable way of doing the sums. So although measured at purchasing-power parity (which takes account of lower prices in poorer countries) the emerging economies now make up over half of world GDP, at market exchange rates their share is still less than 30%. But ev ...
... Of course there is more than one respectable way of doing the sums. So although measured at purchasing-power parity (which takes account of lower prices in poorer countries) the emerging economies now make up over half of world GDP, at market exchange rates their share is still less than 30%. But ev ...
Foreign Direct Investment - Faculty Directory | Berkeley-Haas
... Balance of Payment: A country’s balance-of-payment is the difference between the payments to and receipts from other countries FDI can have beneficial and negative effects on a country’s balance of payment. We look at the beneficial effects next ...
... Balance of Payment: A country’s balance-of-payment is the difference between the payments to and receipts from other countries FDI can have beneficial and negative effects on a country’s balance of payment. We look at the beneficial effects next ...
foreign direct investment (FDI) (p. 194)
... facilities in countries where demand is great enough to warrant its own production facilities. In the final standardized product stage, increased competition creates pressures to reduce production costs. In response, a company builds production capacity in low-cost developing nations to serve its ma ...
... facilities in countries where demand is great enough to warrant its own production facilities. In the final standardized product stage, increased competition creates pressures to reduce production costs. In response, a company builds production capacity in low-cost developing nations to serve its ma ...
A Macroeconomic Model of a Centrally Planned Economy with
... in a particular CPL . Planners do have tremendous power to change key macro economic parameters without very much warning, and they can do so in way s which are difficult to predict . The working hypothesis behind the curren t effort is not that all planners' behavior can be explained, but that enou ...
... in a particular CPL . Planners do have tremendous power to change key macro economic parameters without very much warning, and they can do so in way s which are difficult to predict . The working hypothesis behind the curren t effort is not that all planners' behavior can be explained, but that enou ...
November 13, 2010 The Return to Fiscal Rectitude After the Recent
... would not be cyclical but long lasting and would have major consequences for the role that governments would play in the economy in years to come.7 Frequent references to the Great Depression (see Spilimbergo et. al. p. 2, and many columns by Paul Krugman) did not recognize the huge differences that ...
... would not be cyclical but long lasting and would have major consequences for the role that governments would play in the economy in years to come.7 Frequent references to the Great Depression (see Spilimbergo et. al. p. 2, and many columns by Paul Krugman) did not recognize the huge differences that ...
Setting the Stage for a National Currency in the West
... currency (examples are Afghanistan, Iraq, Lebanon, and the former Soviet Union). For details of policy, institutional, and technical issues, see, for example, Abrams and Cortes-Douglas ...
... currency (examples are Afghanistan, Iraq, Lebanon, and the former Soviet Union). For details of policy, institutional, and technical issues, see, for example, Abrams and Cortes-Douglas ...
The profit cycle and economic recession
... net national product (that’s GDP less depreciation) less v (employee compensation); c = net fixed assets (either on an historic or current cost basis); and v = employee compensation ie wages plus benefits. My measure of value is for the whole economy and not just for the corporate sector (which ...
... net national product (that’s GDP less depreciation) less v (employee compensation); c = net fixed assets (either on an historic or current cost basis); and v = employee compensation ie wages plus benefits. My measure of value is for the whole economy and not just for the corporate sector (which ...
Exercises for Chapter 26
... 3. Suppose that the government finds a major defect in one of a company’s products and demands that they take it off the market. We would expect that the a. supply of the stock and the price will both rise. b. supply of the stock and the price will both fall. c. demand for the stock and the price wi ...
... 3. Suppose that the government finds a major defect in one of a company’s products and demands that they take it off the market. We would expect that the a. supply of the stock and the price will both rise. b. supply of the stock and the price will both fall. c. demand for the stock and the price wi ...
Is the end of fiscal austerity feasible in Spain?
... We adopt the “functional finance” approach to fiscal policy, in contrast to the “sound finances” approach that characterizes the current policies recommended by the European authorities and applied by the Spanish government, with the SP as an example. According to the sound finances approach, struct ...
... We adopt the “functional finance” approach to fiscal policy, in contrast to the “sound finances” approach that characterizes the current policies recommended by the European authorities and applied by the Spanish government, with the SP as an example. According to the sound finances approach, struct ...
CHAP16
... The U.S. experience in recent years Early 1980s through early 1990s debt-GDP ratio: 25.5% in 1980, 48.9% in 1993 due to Reagan tax cuts, increases in defense ...
... The U.S. experience in recent years Early 1980s through early 1990s debt-GDP ratio: 25.5% in 1980, 48.9% in 1993 due to Reagan tax cuts, increases in defense ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES TAX POLICY AND INTERNATIONAL CAPiTAL FLOWS Martin Feldstein
... 2The evidence on savings retention coefficients estimated for regions within a single country supports the interpretation of the cross-country savings retention coefficients as true measuresof de facto international capital market segmentation. Within countries the savings retention coefficients are ...
... 2The evidence on savings retention coefficients estimated for regions within a single country supports the interpretation of the cross-country savings retention coefficients as true measuresof de facto international capital market segmentation. Within countries the savings retention coefficients are ...
Chapter 21 : What Macroeconomics Is All About?
... local currency appreciates. Note: the definition can be reversed. However, the above definition is the standard one. See Fig. 21-8, for the external value of the dollar. Why is it important to Saudi Arabia? ...
... local currency appreciates. Note: the definition can be reversed. However, the above definition is the standard one. See Fig. 21-8, for the external value of the dollar. Why is it important to Saudi Arabia? ...
The Dollar Hegemony And The US-china Monetary Disputes
... action. It also refuses to admit that the results happening in the United States are mainly because of the Chinese monetary policy. In the climax of the disputes, the U.S. Congress has even threatened to pass legislation to punish the “manipulator”, a name it labeled China, but China criticized this ...
... action. It also refuses to admit that the results happening in the United States are mainly because of the Chinese monetary policy. In the climax of the disputes, the U.S. Congress has even threatened to pass legislation to punish the “manipulator”, a name it labeled China, but China criticized this ...
Quantitative Easing and Proposals for Reform of Monetary Policy
... thus, again, the issuance of treasuries is not somehow reducing “cash” previously circulating in the private sector. Going in reverse order, the sale of treasuries by primary dealers to the Fed doesn’t necessarily raise their “cash,” since these new balances will frequently be destroyed as they are ...
... thus, again, the issuance of treasuries is not somehow reducing “cash” previously circulating in the private sector. Going in reverse order, the sale of treasuries by primary dealers to the Fed doesn’t necessarily raise their “cash,” since these new balances will frequently be destroyed as they are ...