19-6 The Magnetic Torque on a Current Loop
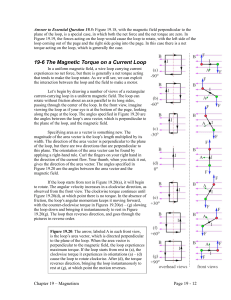
... Figure 19.21 (overhead view). The distance from each force to this axis is W / 2, each force has a magnitude of F = IHB (from equation 19.7), and the angle between the line we’re measuring the distance along and the line of the force is 90°. A factor of 2 accounts for the two identical torques, whic ...
... Figure 19.21 (overhead view). The distance from each force to this axis is W / 2, each force has a magnitude of F = IHB (from equation 19.7), and the angle between the line we’re measuring the distance along and the line of the force is 90°. A factor of 2 accounts for the two identical torques, whic ...
Frequency combs and frequency dissemination for scientific and
... to precision caesium atomic clocks. To obtain highly accurate results it is necessary to measure the frequency of light rather than its wavelength, given that time can be measured more precisely than any other physical quantity, and counting the number of cycles in a second is as accurate as the clo ...
... to precision caesium atomic clocks. To obtain highly accurate results it is necessary to measure the frequency of light rather than its wavelength, given that time can be measured more precisely than any other physical quantity, and counting the number of cycles in a second is as accurate as the clo ...
lecture1429540701
... magnitude of the change in the input measured quantity that produces an observable change in the instrument output. Like threshold, resolution is sometimes specified as an absolute value and sometimes as a percentage of f.s. deflection. One of the major factors influencing the resolution of an instr ...
... magnitude of the change in the input measured quantity that produces an observable change in the instrument output. Like threshold, resolution is sometimes specified as an absolute value and sometimes as a percentage of f.s. deflection. One of the major factors influencing the resolution of an instr ...
Low Cost, Low Power 12-Bit Differential ADC Driver AD8137
... and common-mode currents flowing to the load, as well as currents flowing through the external feedback networks and the internal common-mode feedback loop. The internal resistor tap used in the common-mode feedback loop places a 1 kΩ differential load on the output. RMS output voltages should be co ...
... and common-mode currents flowing to the load, as well as currents flowing through the external feedback networks and the internal common-mode feedback loop. The internal resistor tap used in the common-mode feedback loop places a 1 kΩ differential load on the output. RMS output voltages should be co ...
Understanding piezoelectric transformers in CCFL
... stage. The frequency range of the VCO must include the Several topologies exist for the resonant power stage shown strike and operating frequencies of the PZT. For example, in Figure 8. Input voltage range, lamp characteristics, and a frequency range of 51 to 71 kHz is required for proper PZT charac ...
... stage. The frequency range of the VCO must include the Several topologies exist for the resonant power stage shown strike and operating frequencies of the PZT. For example, in Figure 8. Input voltage range, lamp characteristics, and a frequency range of 51 to 71 kHz is required for proper PZT charac ...
A 24-GHz CMOS Direct-Conversion Sub-Harmonic Downconverter
... millimeterwave bands such as automotive radars and high data rate wireless communications. The goal of this research is to realize a high performance, low dc power, low area, 24 GHz direct-conversion mixer for phasedarray applications. In direct conversion receivers, the 1/f noise of the mixers is e ...
... millimeterwave bands such as automotive radars and high data rate wireless communications. The goal of this research is to realize a high performance, low dc power, low area, 24 GHz direct-conversion mixer for phasedarray applications. In direct conversion receivers, the 1/f noise of the mixers is e ...
Chapter 3
... A newer microprocessor-controlled impedance bridge. An older style impedance bridge that involved adjusting knobs until the needle indicated that the bridge was balanced. Ref: http://www.testequipmentconnection.com/products/908 ...
... A newer microprocessor-controlled impedance bridge. An older style impedance bridge that involved adjusting knobs until the needle indicated that the bridge was balanced. Ref: http://www.testequipmentconnection.com/products/908 ...
a 50 MHz CMOS Complete DDS AD9835
... fundamental. Noise is the rms sum of all the nonfundamental signals up to half the sampling frequency (fMCLK/2) but excluding the dc component. Signal to (Noise + Distortion) is dependent on the number of quantization levels used in the digitization process; the more levels, the smaller the quantiza ...
... fundamental. Noise is the rms sum of all the nonfundamental signals up to half the sampling frequency (fMCLK/2) but excluding the dc component. Signal to (Noise + Distortion) is dependent on the number of quantization levels used in the digitization process; the more levels, the smaller the quantiza ...
A CMOS low power, process/temperature variation tolerant RSSI
... of the right-hand side current mirror (M6 and M8) is larger than that of the left-hand side current mirror (M5 and M7). Based on Eq. (6), Iout will be at its maximum value. When the differential input voltage increases, Iout decreases. As input voltage increases, smaller size transistors (M1 and M4) ...
... of the right-hand side current mirror (M6 and M8) is larger than that of the left-hand side current mirror (M5 and M7). Based on Eq. (6), Iout will be at its maximum value. When the differential input voltage increases, Iout decreases. As input voltage increases, smaller size transistors (M1 and M4) ...
•What is NOISE? A definition: Any unwanted signal obscuring signal
... eg arrival of charges at electrode in system - induce charges on electrode T quantised in amplitude and time •Examples electrons/holes crossing potential barrier in diode or transistor electron flow in vacuum tube < in2> = 2qI.∆ f ...
... eg arrival of charges at electrode in system - induce charges on electrode T quantised in amplitude and time •Examples electrons/holes crossing potential barrier in diode or transistor electron flow in vacuum tube < in2> = 2qI.∆ f ...