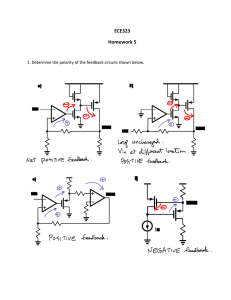
OSCILLATOR, VERY LOW FREQUENCY - 0.1Hz
... The IEC Very Low Freq. Oscillator is a fixed very low frequency sine wave oscillator which is useful for providing very slow sine wave signals for special experiments. The input is 12V.AC only and the output is 15Volt peak to peak at 5mA max. load. The starting of the oscillation is controlled by a ...
... The IEC Very Low Freq. Oscillator is a fixed very low frequency sine wave oscillator which is useful for providing very slow sine wave signals for special experiments. The input is 12V.AC only and the output is 15Volt peak to peak at 5mA max. load. The starting of the oscillation is controlled by a ...
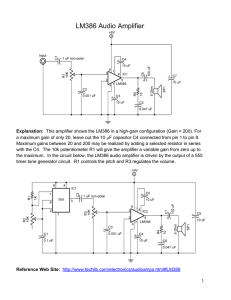
LM386 Audio Amplifier - Cornerstone Robotics
... Explanation: This amplifier shows the LM386 in a high-gain configuration (Gain = 200). For a maximum gain of only 20, leave out the 10 F capacitor C4 connected from pin 1 to pin 8. Maximum gains between 20 and 200 may be realized by adding a selected resistor in series with the C4. The 10k potentio ...
... Explanation: This amplifier shows the LM386 in a high-gain configuration (Gain = 200). For a maximum gain of only 20, leave out the 10 F capacitor C4 connected from pin 1 to pin 8. Maximum gains between 20 and 200 may be realized by adding a selected resistor in series with the C4. The 10k potentio ...
Wein Bridge Oscillators
... A better design would cause the circuit to exhibit a cons tant (not decaying) oscillation. We can attempt to update the circuit using a form of amplitude stabilization. There are a couple of available design methods, but one of the better schemes involves the introduction diodes into the circuit. A ...
... A better design would cause the circuit to exhibit a cons tant (not decaying) oscillation. We can attempt to update the circuit using a form of amplitude stabilization. There are a couple of available design methods, but one of the better schemes involves the introduction diodes into the circuit. A ...
UNIT-IV 1. List the advantages of crystal oscillator The advantages
... 3. What is the difference between Amplifier and oscillator? -> Amplifiers are circuits which transfer an input signal into an output signal. -> Oscillators produce a steady state signal e.g a square wave signal or a sinusoidal signal. 4. What are the advantages of differential Amplifier? A different ...
... 3. What is the difference between Amplifier and oscillator? -> Amplifiers are circuits which transfer an input signal into an output signal. -> Oscillators produce a steady state signal e.g a square wave signal or a sinusoidal signal. 4. What are the advantages of differential Amplifier? A different ...
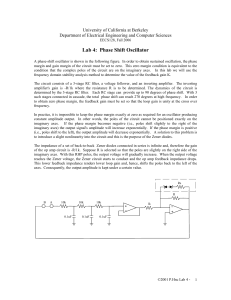
Lab 4: Phase Shift Oscillator - EECS: www
... The circuit consists of a 3-stage RC filter, a voltage follower, and an inverting amplifier. The inverting amplifier's gain is -R/1k where the resistance R is to be determined. The dynamics of the circuit is determined by the 3-stage RC filter. Each RC stage can provide up to 90 degrees of phase shi ...
... The circuit consists of a 3-stage RC filter, a voltage follower, and an inverting amplifier. The inverting amplifier's gain is -R/1k where the resistance R is to be determined. The dynamics of the circuit is determined by the 3-stage RC filter. Each RC stage can provide up to 90 degrees of phase shi ...
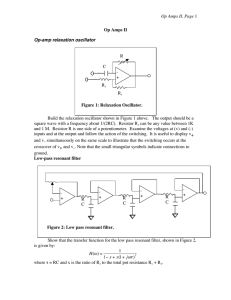
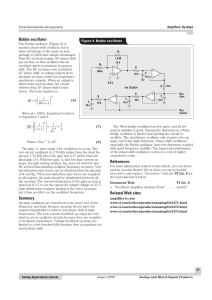
Op Amps II, Page R C -
... Next, use what you know about RC filters to find v4 in terms of v1.] When you understand the equation for the transfer function, build the circuit. It is convenient to use a TL084 with four op amps in a package. Choose RC so that the resonant frequency is 2 to 5 kHz. Tune the pot until the circuit n ...
... Next, use what you know about RC filters to find v4 in terms of v1.] When you understand the equation for the transfer function, build the circuit. It is convenient to use a TL084 with four op amps in a package. Choose RC so that the resonant frequency is 2 to 5 kHz. Tune the pot until the circuit n ...
Op Amps II, Page
... convenient to use a TL084 with four op amps in a package. Choose RC so that the resonant frequency is 2 to 5 kHz. Tune the pot until the circuit nearly oscillates. See how close you can get. Notice how oscillations grow and die exponentially. Find the resonant frequency by feeding in a sine signal f ...
... convenient to use a TL084 with four op amps in a package. Choose RC so that the resonant frequency is 2 to 5 kHz. Tune the pot until the circuit nearly oscillates. See how close you can get. Notice how oscillations grow and die exponentially. Find the resonant frequency by feeding in a sine signal f ...
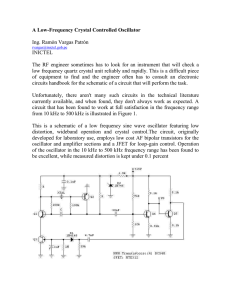
A Low-Frequency Crystal Controlled Oscillator
... the loop gain is automatically adjusted to the threshold of oscillation by means of field effect transistor Q3. Q4 linearly amplifies the signal present at the collector of Q2 and isolates the oscillator section of the circuit from the output. This stage features wideband operation and delivers a cl ...
... the loop gain is automatically adjusted to the threshold of oscillation by means of field effect transistor Q3. Q4 linearly amplifies the signal present at the collector of Q2 and isolates the oscillator section of the circuit from the output. This stage features wideband operation and delivers a cl ...
lab7
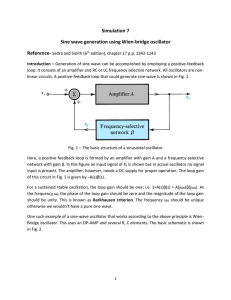
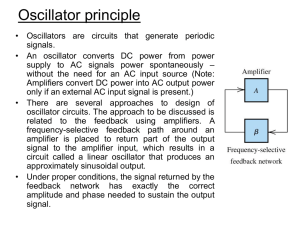
... Fig. 1 – The basic structure of a sinusoidal oscillator Here, a positive feedback loop is formed by an amplifier with gain A and a frequency-selective network with gain β. In this figure an input signal of Xs is shown but in actual oscillator no signal input is present. The amplifier, however, needs ...
... Fig. 1 – The basic structure of a sinusoidal oscillator Here, a positive feedback loop is formed by an amplifier with gain A and a frequency-selective network with gain β. In this figure an input signal of Xs is shown but in actual oscillator no signal input is present. The amplifier, however, needs ...
sheet3
... 3. Why is Hartley oscillation not suitable for low frequency work? 4. What are the conditions of oscillation in the Hartley and Colpitts Oscillators? 5. In order to sustain oscillation in a Hartley oscillator, what will be the minimum value of the feedback resistor and frequency of oscillation with ...
... 3. Why is Hartley oscillation not suitable for low frequency work? 4. What are the conditions of oscillation in the Hartley and Colpitts Oscillators? 5. In order to sustain oscillation in a Hartley oscillator, what will be the minimum value of the feedback resistor and frequency of oscillation with ...
Exp-7 - WordPress.com
... Oscillators are circuits that produce periodic waveforms without input other than perhaps a trigger. They generally use some form of active device, lamp, or crystal, surrounded by passive devices such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors, to generate the output. There are two main classes of osci ...
... Oscillators are circuits that produce periodic waveforms without input other than perhaps a trigger. They generally use some form of active device, lamp, or crystal, surrounded by passive devices such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors, to generate the output. There are two main classes of osci ...
Frequency response of feedback amplifiers
... • In real oscillator design, we usually design loop-gain magnitude slightly larger than unity at the desired frequency of oscillation. Because a higher gain magnitude results in oscillations that grow in amplitude with time, eventually, the amplitude is clipped by the amplifier so that a constant-am ...
... • In real oscillator design, we usually design loop-gain magnitude slightly larger than unity at the desired frequency of oscillation. Because a higher gain magnitude results in oscillations that grow in amplitude with time, eventually, the amplitude is clipped by the amplifier so that a constant-am ...