Ketone ester effects on metabolism and
... this elevation of free fatty acids result in the elevation of the PPAR transcription factors with many undesirable effects which include diabetes and atherosclerosis (8). Feeding a high fat ketogenic diet, of the Mayo Clinic type, results in large increases in blood cholesterol and LDL cholesterol p ...
... this elevation of free fatty acids result in the elevation of the PPAR transcription factors with many undesirable effects which include diabetes and atherosclerosis (8). Feeding a high fat ketogenic diet, of the Mayo Clinic type, results in large increases in blood cholesterol and LDL cholesterol p ...
The Metabolism of the Amino Acids of Escherichia
... of Entodinium caudatum immediately after separation from the growth medium, namely Bacterium 31, Bacterium D, 7 ~ 2 21 , G 13/1 and 23 c 3 / 2 (White, 1966) had survival percentages of 7-82% and were therefore not particularly resistant to killing. It is possible, especially with Bacterium 31 which ...
... of Entodinium caudatum immediately after separation from the growth medium, namely Bacterium 31, Bacterium D, 7 ~ 2 21 , G 13/1 and 23 c 3 / 2 (White, 1966) had survival percentages of 7-82% and were therefore not particularly resistant to killing. It is possible, especially with Bacterium 31 which ...
X-ray Crystallographic Structure of Ibuprofen Bound to Human
... The fatty acid-binding proteins (FABPs) are a family of nine structurally related proteins, which bind to long-chain fatty acids with high affinity. Fatty acid binding proteins were first discovered in 1972, while conducting studies on the factors that regulate the uptake of intestinal fatty acids i ...
... The fatty acid-binding proteins (FABPs) are a family of nine structurally related proteins, which bind to long-chain fatty acids with high affinity. Fatty acid binding proteins were first discovered in 1972, while conducting studies on the factors that regulate the uptake of intestinal fatty acids i ...
BANGALORE UNIVERSITY Department of Chemistry
... As per the directive from the Bangalore University, the Chemistry syllabus for the B. Sc., degree course (CBCS) had to be prepared. Guidelines for this were provided by the University. In the Department of Studies in Chemistry, Central College, with the help of the Chemistry Teachers’ Forum, a Core ...
... As per the directive from the Bangalore University, the Chemistry syllabus for the B. Sc., degree course (CBCS) had to be prepared. Guidelines for this were provided by the University. In the Department of Studies in Chemistry, Central College, with the help of the Chemistry Teachers’ Forum, a Core ...
Treating heart attack with different food substrates
... of heart failure. The findings from several studies have shown that the socalled metabolic agents could have potential as adjunctive therapies in heart failure. These agents cause a shift in the substrate used by the heart away from free fatty acids, the oxidation of which normally provides around 7 ...
... of heart failure. The findings from several studies have shown that the socalled metabolic agents could have potential as adjunctive therapies in heart failure. These agents cause a shift in the substrate used by the heart away from free fatty acids, the oxidation of which normally provides around 7 ...
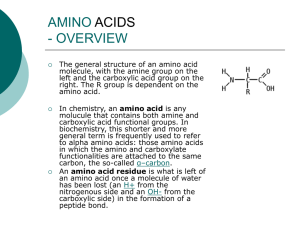
amino acids - UniMAP Portal
... general term is frequently used to refer to alpha amino acids: those amino acids in which the amino and carboxylate functionalities are attached to the same carbon, the so-called α–carbon. An amino acid residue is what is left of an amino acid once a molecule of water has been lost (an H+ from the n ...
... general term is frequently used to refer to alpha amino acids: those amino acids in which the amino and carboxylate functionalities are attached to the same carbon, the so-called α–carbon. An amino acid residue is what is left of an amino acid once a molecule of water has been lost (an H+ from the n ...
Cloning and sequence analysis of putative type II fatty
... pathway for improving oil quality and increasing oil content of peanut through biotechnology-based approaches. Fatty acid biosynthesis is catalysed by two types of fatty acid synthase (FAS). Type I FAS, as found in vertebrates, yeast and some bacteria, contains all the active sites on one or two mul ...
... pathway for improving oil quality and increasing oil content of peanut through biotechnology-based approaches. Fatty acid biosynthesis is catalysed by two types of fatty acid synthase (FAS). Type I FAS, as found in vertebrates, yeast and some bacteria, contains all the active sites on one or two mul ...
Regulation of Elovl and fatty acid metabolism
... acids (FA) do not only serve as a major source of energy, but are also crucial structural components of membranes. Additionally, fatty acids may function as signaling molecules, thus exerting key biological functions, such as regulating fatty acid metabolism (Duplus and Forest, 2002). For example, p ...
... acids (FA) do not only serve as a major source of energy, but are also crucial structural components of membranes. Additionally, fatty acids may function as signaling molecules, thus exerting key biological functions, such as regulating fatty acid metabolism (Duplus and Forest, 2002). For example, p ...
HERE
... What are dietary Essential Amino Acids? Amino Acids whose Carbon Skeleton cannot be synthesized in the body are called ...
... What are dietary Essential Amino Acids? Amino Acids whose Carbon Skeleton cannot be synthesized in the body are called ...
overview, inorgs, trace nutrients
... learned that the symptoms were due to something missing. • The B-complex vitamins are missing in refined foods (white bread, white rice), which have had the metabolically active portions of the whole grain removed. • These vitamins are cofactors for a large number of reaction schemes that derive ene ...
... learned that the symptoms were due to something missing. • The B-complex vitamins are missing in refined foods (white bread, white rice), which have had the metabolically active portions of the whole grain removed. • These vitamins are cofactors for a large number of reaction schemes that derive ene ...
9강 - KOCW
... • All use glycolysis (net ATP = 2) to oxidize glucose and harvest chemical energy of food • In all three, NAD+ is the oxidizing agent that accepts electrons during glycolysis • The processes have different final electron acceptors: an organic molecule (such as pyruvate or acetaldehyde) in fermentati ...
... • All use glycolysis (net ATP = 2) to oxidize glucose and harvest chemical energy of food • In all three, NAD+ is the oxidizing agent that accepts electrons during glycolysis • The processes have different final electron acceptors: an organic molecule (such as pyruvate or acetaldehyde) in fermentati ...
Mechanisms of Aspartimide Formation: The Effects of Protecting
... tion is of the unimolecular AAc 1 type, in analogy with side reactions observed for glutamyl residues (11 ). However, it is now known that aspartimide formation also occurs over a wide range of acidity. Mild acids, such as trifluoroacetic acid, hydrochloric acid, or dilute HF, will catalyze asparti ...
... tion is of the unimolecular AAc 1 type, in analogy with side reactions observed for glutamyl residues (11 ). However, it is now known that aspartimide formation also occurs over a wide range of acidity. Mild acids, such as trifluoroacetic acid, hydrochloric acid, or dilute HF, will catalyze asparti ...
Algae triglycerides
... neutral lipids (20–50% DCW), mainly in the form of triacylglycerol (TAG). Unlike the glycerolipids found in membranes, TAGs do not perform a structural role but instead serve primarily as a storage form of carbon and energy. However, there is some evidence suggesting that, in algae, the TAG biosynth ...
... neutral lipids (20–50% DCW), mainly in the form of triacylglycerol (TAG). Unlike the glycerolipids found in membranes, TAGs do not perform a structural role but instead serve primarily as a storage form of carbon and energy. However, there is some evidence suggesting that, in algae, the TAG biosynth ...
PDH02 - OSU Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
... established that pea mitochondria can acyl carrier protein and the enzymes to synthesize fatty acids. Radioactivity from labeled malonic acid was found in the H protein, a lipoylcontaining enzyme involved in glycine metabolism. In Saccharomyces cerevisiae Brody, Oh, Hoja, and Schweizer (18) found th ...
... established that pea mitochondria can acyl carrier protein and the enzymes to synthesize fatty acids. Radioactivity from labeled malonic acid was found in the H protein, a lipoylcontaining enzyme involved in glycine metabolism. In Saccharomyces cerevisiae Brody, Oh, Hoja, and Schweizer (18) found th ...
Comparison of Free Total Amino Acid Compositions and
... Essential amino acid (EAA) contents in the analyzed species varied between 154.3 mg/100 g in Essential amino acid (EAA) contents in the analyzed species varied between 154.3 mg/100 g in B. craspedius and 5232.5 mg/100 g in T. microcarpus (Table 1). Eight kinds of essential amino acids were B. craspe ...
... Essential amino acid (EAA) contents in the analyzed species varied between 154.3 mg/100 g in Essential amino acid (EAA) contents in the analyzed species varied between 154.3 mg/100 g in B. craspedius and 5232.5 mg/100 g in T. microcarpus (Table 1). Eight kinds of essential amino acids were B. craspe ...
Combined fluorescence and electrochemical investigation on the
... fatty acid concentration, where A0 is the fluorescence of the probe/HSA complex before addition of the fatty acid, and A is the fluorescence after addition of the fatty acid at a certain concentration. Titration of C8 against HSA with the drug binding site I probe DNSA showed substantial reduction of ...
... fatty acid concentration, where A0 is the fluorescence of the probe/HSA complex before addition of the fatty acid, and A is the fluorescence after addition of the fatty acid at a certain concentration. Titration of C8 against HSA with the drug binding site I probe DNSA showed substantial reduction of ...
electron transport chain
... with no release of CO2 • Lactic acid fermentation by some fungi and bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt • Human muscle cells use lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when O2 is scarce ...
... with no release of CO2 • Lactic acid fermentation by some fungi and bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt • Human muscle cells use lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when O2 is scarce ...
Ch18.doc
... dehydrogenase (1 NADH) and one turn of the CAC: yielding 3NADH, 1FADH2 and 1 GTP. Converting NADH and FADH2 to ATPs we use 1 NADH = 2.5 ATP and 1 FADH2 = 1.5 ATP. So for one alanine: (3+1)(2.5 ATP) + 1.5 ATP + 1 ATP = 12.5 ATP. But now it will cost some ATP to get rid of the amino group: so it would ...
... dehydrogenase (1 NADH) and one turn of the CAC: yielding 3NADH, 1FADH2 and 1 GTP. Converting NADH and FADH2 to ATPs we use 1 NADH = 2.5 ATP and 1 FADH2 = 1.5 ATP. So for one alanine: (3+1)(2.5 ATP) + 1.5 ATP + 1 ATP = 12.5 ATP. But now it will cost some ATP to get rid of the amino group: so it would ...
Part II: Multiple Choice Questions
... D) H+ ions serve as the final electron acceptor. E) energy is released as H+ ions move freely across mitochondrial membranes. 32) Which of the following processes produces the most ATP per molecule of glucose oxidized? A) aerobic respiration B) alcoholic fermentation C) lactic acid fermentation D) a ...
... D) H+ ions serve as the final electron acceptor. E) energy is released as H+ ions move freely across mitochondrial membranes. 32) Which of the following processes produces the most ATP per molecule of glucose oxidized? A) aerobic respiration B) alcoholic fermentation C) lactic acid fermentation D) a ...
Lactic acid fermentation of black beans
... contents, soluble fibre and resistant starch, the main flatulence-producing factors in legumes. The natural fermentation process is performed with the endogenous flora. However, the beans contain aerobic microorganisms from air, water, soil, containers, etc, on their surfaces that can be more numero ...
... contents, soluble fibre and resistant starch, the main flatulence-producing factors in legumes. The natural fermentation process is performed with the endogenous flora. However, the beans contain aerobic microorganisms from air, water, soil, containers, etc, on their surfaces that can be more numero ...
Genome-Based Metabolic Mapping and C Flux
... autotrophic and heterotrophic growth with rapid lipid synthesis, is a promising candidate for biofuel production. Based on the newly available genome knowledge of the alga, we reconstructed the compartmentalized metabolic network consisting of 272 metabolic reactions, 270 enzymes, and 461 encoding g ...
... autotrophic and heterotrophic growth with rapid lipid synthesis, is a promising candidate for biofuel production. Based on the newly available genome knowledge of the alga, we reconstructed the compartmentalized metabolic network consisting of 272 metabolic reactions, 270 enzymes, and 461 encoding g ...
4.4 Overview of Cellular Respiration
... • The electron transport chain uses NADH and to make ATP. – high-energy electrons enter electron transport chain – energy is used to transport hydrogen ions across the inner membrane – hydrogen ions flow through a channel in the membrane creating ATP – 3 ATP created for each NADH molecule – 2 ...
... • The electron transport chain uses NADH and to make ATP. – high-energy electrons enter electron transport chain – energy is used to transport hydrogen ions across the inner membrane – hydrogen ions flow through a channel in the membrane creating ATP – 3 ATP created for each NADH molecule – 2 ...
Butyric acid
Butyric acid (from Greek βούτῡρον, meaning ""butter""), also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, abbreviated BTA, is a carboxylic acid with the structural formula CH3CH2CH2-COOH. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates. Butyric acid is found in milk, especially goat, sheep and buffalo milk, butter, parmesan cheese, and as a product of anaerobic fermentation (including in the colon and as body odor). It has an unpleasant smell and acrid taste, with a sweetish aftertaste (similar to ether). It can be detected by mammals with good scent detection abilities (such as dogs) at 10 parts per billion, whereas humans can detect it in concentrations above 10 parts per million.Butyric acid is present in, and is the main distinctive smell of, human vomit.Butyric acid was first observed (in impure form) in 1814 by the French chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul. By 1818, he had purified it sufficiently to characterize it. The name of butyric acid comes from the Latin word for butter, butyrum (or buturum), the substance in which butyric acid was first found.