Vitamins B6 and B12 (Final).
... enzymes causing: 1. Deficient amino acid metabolism 2. Deficient lipid metabolism 3. Deficient neurotransmitter synthesis [serotonin, epinephrine, noradrenaline and gamma amino butyric acid (GABA) ]. (PLP is involved in the synthesis of sphingolipids, its deficiency leads to demyelination of nerves ...
... enzymes causing: 1. Deficient amino acid metabolism 2. Deficient lipid metabolism 3. Deficient neurotransmitter synthesis [serotonin, epinephrine, noradrenaline and gamma amino butyric acid (GABA) ]. (PLP is involved in the synthesis of sphingolipids, its deficiency leads to demyelination of nerves ...
The Hypothesis that the Genetic Code Originated in Coupled
... for respiration [44]. NO produced in the atmosphere could have undergone reactions leading to accumulation of nitrite and nitrate in water [45]. If primitive cells were leaky to ions, nitrite and nitrate could diffuse across membranes and be reduced to ammonia using Fe(II) or FeS [46–48]. Ethanethio ...
... for respiration [44]. NO produced in the atmosphere could have undergone reactions leading to accumulation of nitrite and nitrate in water [45]. If primitive cells were leaky to ions, nitrite and nitrate could diffuse across membranes and be reduced to ammonia using Fe(II) or FeS [46–48]. Ethanethio ...
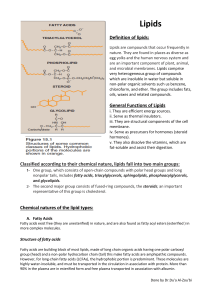
Lipids
... multifunctional, dimeric enzyme, fatty acid synthase (FAS). The biosynthesis of fatty acids involves the successive addition of two-carbon units to the growing chain. # When the fatty acid reaches a length of 16 carbons, the synthetic process is terminated. This process releasing a fully saturated m ...
... multifunctional, dimeric enzyme, fatty acid synthase (FAS). The biosynthesis of fatty acids involves the successive addition of two-carbon units to the growing chain. # When the fatty acid reaches a length of 16 carbons, the synthetic process is terminated. This process releasing a fully saturated m ...
O A RIGINAL RTICLE
... cytosol of mammalian cells or secreted by bacteria into the medium. The role of this enzyme is the degradation of SA in mammalian cells therefore it increases cellular levels of SA. However the role of these enzymes in inflammation is a largely unknown field deserving more attention [33]. In the pre ...
... cytosol of mammalian cells or secreted by bacteria into the medium. The role of this enzyme is the degradation of SA in mammalian cells therefore it increases cellular levels of SA. However the role of these enzymes in inflammation is a largely unknown field deserving more attention [33]. In the pre ...
file ini - Pusat Penelitian Biologi
... can be attributed in part to understand that these organisms have directly effects on ecosystem processes (Beare et al. 1995; Horner-Devine et al. 2004; Fierer & Jackson 2006). Phosphate solubilizing bacteria (PSB) commonly found as adaptive bacteria (Glenn & Mandelstam 1971) in most soils (Chonkar ...
... can be attributed in part to understand that these organisms have directly effects on ecosystem processes (Beare et al. 1995; Horner-Devine et al. 2004; Fierer & Jackson 2006). Phosphate solubilizing bacteria (PSB) commonly found as adaptive bacteria (Glenn & Mandelstam 1971) in most soils (Chonkar ...
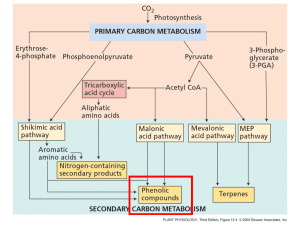
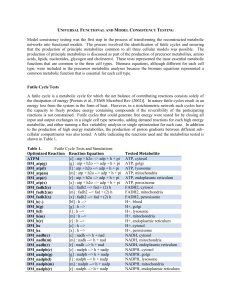
Citric Acid Cycle: Central Role in Catabolism Entry of Pyruvate into
... a thioester linkage. In the process, the -C–OH is converted to –C=O. This is catalyzed by E1. • Step 3. Catalyzed by E2. CoASH, cofactor of E2, participates in a group transfer reaction and removes the 2-carbon unit as acetylSCoA, leaving reduced lipoamide attached to E2. • Step 4. Catalyzed by E3. ...
... a thioester linkage. In the process, the -C–OH is converted to –C=O. This is catalyzed by E1. • Step 3. Catalyzed by E2. CoASH, cofactor of E2, participates in a group transfer reaction and removes the 2-carbon unit as acetylSCoA, leaving reduced lipoamide attached to E2. • Step 4. Catalyzed by E3. ...
Chemotaxis Assays for Marine and Freshwater Amoeba Jessica
... Afterwards, 50µl, 100µl or 200µl of fresh amoeba culture were inoculated at the center of the petri dish and left overnight for cell migration. Agarose plug assay. Rectangular polystyrene petri dishes (50mm X 75mm) were used for this assay. Specifically, chemoattractant-infused SWCM2 was solidified ...
... Afterwards, 50µl, 100µl or 200µl of fresh amoeba culture were inoculated at the center of the petri dish and left overnight for cell migration. Agarose plug assay. Rectangular polystyrene petri dishes (50mm X 75mm) were used for this assay. Specifically, chemoattractant-infused SWCM2 was solidified ...
Degradation of Sphingolipids - Edward Dennis
... • Sphingosine can be phosphorylated by sphingosine kinases, ubiquitous enzymes in the cytosol, ER and nucleus to make sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P). • Sphingosine-1-phosphate, a lysophospholipid, acts as a potent messenger molecule that operates both intra- and inter-cellularly. • Within the cell, i ...
... • Sphingosine can be phosphorylated by sphingosine kinases, ubiquitous enzymes in the cytosol, ER and nucleus to make sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P). • Sphingosine-1-phosphate, a lysophospholipid, acts as a potent messenger molecule that operates both intra- and inter-cellularly. • Within the cell, i ...
Physiology of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in anaerobic glucose
... confirmed in experimentsin which a weak acid (acetate or propionate) was added to the medium feed. This resulted in a reduction in yield and an increase in specific ethanol production. Both yeasts required approximately 35 mg oleic acid (g biomass)-' for optimal growth. Lower or higher concentration ...
... confirmed in experimentsin which a weak acid (acetate or propionate) was added to the medium feed. This resulted in a reduction in yield and an increase in specific ethanol production. Both yeasts required approximately 35 mg oleic acid (g biomass)-' for optimal growth. Lower or higher concentration ...
An overview of food, environmentally and industrially important
... methods with a history of more than 100 years. In the first part of the 20th century, it ranked second only to ethanol fermentation. In 1861 butanol production through microbial fermentation was reported for the first time by Pasteur. This was followed by Schardinger in 1905 reporting production of ...
... methods with a history of more than 100 years. In the first part of the 20th century, it ranked second only to ethanol fermentation. In 1861 butanol production through microbial fermentation was reported for the first time by Pasteur. This was followed by Schardinger in 1905 reporting production of ...
Lipid PowerPoint
... C=C double bonds in the fatty acids plant & fish fats vegetable oils liquid at room temperature ...
... C=C double bonds in the fatty acids plant & fish fats vegetable oils liquid at room temperature ...
Determination of 17 AQC derivatized Amino acids in
... highly reactive amine derivatization reagent can be used in an easy one step procedure.6 The compound reacts with amino acids to form stable urea derivatives which are readily amenable for analysis by reversed phase HPLC. Primary and secondary amino acids are derivatized quickly and they are stable ...
... highly reactive amine derivatization reagent can be used in an easy one step procedure.6 The compound reacts with amino acids to form stable urea derivatives which are readily amenable for analysis by reversed phase HPLC. Primary and secondary amino acids are derivatized quickly and they are stable ...
1 Anaerobic Respiration
... to make yogurt, bread, wine, and biofuels. Human muscle cells also use fermentation. This occurs when muscle cells cannot get oxygen fast enough to meet their energy needs through aerobic respiration. There are two types of fermentation: lactic acid fermentation and alcoholic fermentation. Both type ...
... to make yogurt, bread, wine, and biofuels. Human muscle cells also use fermentation. This occurs when muscle cells cannot get oxygen fast enough to meet their energy needs through aerobic respiration. There are two types of fermentation: lactic acid fermentation and alcoholic fermentation. Both type ...
Lecture 6
... The 2 ATP’s produced during glycolysis are only a small fraction of the potential energy available from glucose. Under anaerobic conditions, animals convert glucose into 2 molecules of lactate. Much of the potential energy of the glucose molecule remains untapped. Under Aerobic conditions a much mor ...
... The 2 ATP’s produced during glycolysis are only a small fraction of the potential energy available from glucose. Under anaerobic conditions, animals convert glucose into 2 molecules of lactate. Much of the potential energy of the glucose molecule remains untapped. Under Aerobic conditions a much mor ...
gelfand-singapore
... You are given the data available to the researchers of the genetic code by early 1960’s, just before an experimental procedure for direct analysis of amino acids encoded by specific codons (nucleotide triplets) has been developed. These data are slightly idealized; in particular, numerical data are ...
... You are given the data available to the researchers of the genetic code by early 1960’s, just before an experimental procedure for direct analysis of amino acids encoded by specific codons (nucleotide triplets) has been developed. These data are slightly idealized; in particular, numerical data are ...
Question paper - Unit F334 - Chemistry of materials
... The student also measured a value of –0.44 V for the standard electrode potential, E –o–, of the Fe2+(aq) / Fe(s) half-cell. The student then used the two E –o– measurements to conclude incorrectly: ‘Cr3+(aq) is a stronger oxidising agent than Fe2+(aq) because the electronegativity of Cr is larger t ...
... The student also measured a value of –0.44 V for the standard electrode potential, E –o–, of the Fe2+(aq) / Fe(s) half-cell. The student then used the two E –o– measurements to conclude incorrectly: ‘Cr3+(aq) is a stronger oxidising agent than Fe2+(aq) because the electronegativity of Cr is larger t ...
AMINO ACIDS METABOLISM ** Dr. Mohammed Abdullateef **
... Ammonia is toxic to tissues, including the brain; some processes such as nucleotide degradation generate free ammonia. ...
... Ammonia is toxic to tissues, including the brain; some processes such as nucleotide degradation generate free ammonia. ...
Phospholipid Ester-linked Fatty Acid Biomarkers of
... apparently functionally distinctive groups of sulphate-reducing bacteria (Banat et al., 1981). If elemental sulphur is present, this may be used as terminal acceptor by sulphur-reducing bacteria (Jarrgensen, 1982; Smith & Klug, 1981). Mesophilic, eubacterial sulphur reducers that oxidize hydrogen ar ...
... apparently functionally distinctive groups of sulphate-reducing bacteria (Banat et al., 1981). If elemental sulphur is present, this may be used as terminal acceptor by sulphur-reducing bacteria (Jarrgensen, 1982; Smith & Klug, 1981). Mesophilic, eubacterial sulphur reducers that oxidize hydrogen ar ...
Phospholipids are amphipathic molecules that make up
... backbone. The phosphate may be modified by the addition of charged or polar chemical groups. Two chemical groups that may modify the phosphate, choline and serine, are shown here. Both choline and serine attach to the phosphate group at the position labeled R via the hydroxyl group indicated in gree ...
... backbone. The phosphate may be modified by the addition of charged or polar chemical groups. Two chemical groups that may modify the phosphate, choline and serine, are shown here. Both choline and serine attach to the phosphate group at the position labeled R via the hydroxyl group indicated in gree ...
Agonism with the omega-3 fatty acids α-linolenic acid
... The newly discovered G protein-coupled receptor GPR120 has recently been shown to stimulate secretion of the gut hormones glucagon-like peptide-1 and cholecystokinin upon binding of free fatty acids, thrusting it to the forefront of drug discovery efforts for treatment of type 2 diabetes as well as ...
... The newly discovered G protein-coupled receptor GPR120 has recently been shown to stimulate secretion of the gut hormones glucagon-like peptide-1 and cholecystokinin upon binding of free fatty acids, thrusting it to the forefront of drug discovery efforts for treatment of type 2 diabetes as well as ...
Bio426Lecture28Apr10
... Rhizobium is attracted to legumes through signaling by isoflavanoids released from roots. ...
... Rhizobium is attracted to legumes through signaling by isoflavanoids released from roots. ...
CHAPTER 7
... D) Lactic acid is produced when the rate of work is high. E) Energy production is limited by lactic acid accumulation. Answer: C 11. The resynthesis of ATP by the aerobic system takes place in cell organelles called _________. Answer: mitochondria 12. Anaerobic threshold is the point during exercise ...
... D) Lactic acid is produced when the rate of work is high. E) Energy production is limited by lactic acid accumulation. Answer: C 11. The resynthesis of ATP by the aerobic system takes place in cell organelles called _________. Answer: mitochondria 12. Anaerobic threshold is the point during exercise ...
Universal Functional and Model Consistency Testing
... aminotransferase reaction and the mitochondrial alanine transporter ALAtm were both removed, based on the evidence that the mitochondrial alanine transaminase is present only on gluconeogenic tissues [DeRosa and Swick, J Biol Chem (1975)] and that there were no other alanine reactions in mitochondri ...
... aminotransferase reaction and the mitochondrial alanine transporter ALAtm were both removed, based on the evidence that the mitochondrial alanine transaminase is present only on gluconeogenic tissues [DeRosa and Swick, J Biol Chem (1975)] and that there were no other alanine reactions in mitochondri ...
CHAPTER 6: Energy for Muscular Activity
... 6. Lactic acid accumulation: A) increases hydrogen ion concentration B) impedes cross bridge formation C) inhibits proper enzyme function during glycolysis D) hampers transmission of the electrical signal at the neuromuscular junction E) all of the above Answer: E 7. “Handling” lactic acid refers to ...
... 6. Lactic acid accumulation: A) increases hydrogen ion concentration B) impedes cross bridge formation C) inhibits proper enzyme function during glycolysis D) hampers transmission of the electrical signal at the neuromuscular junction E) all of the above Answer: E 7. “Handling” lactic acid refers to ...
Hepoxilin

Hepoxilins (HxA3 and HxB3) are nonclassic eicosanoid hormones involved in inflammation.