VITAMINS
... Salt. Vitamin K is transported along with LDL and is stored mainly in liver and , to a lesser extent, in other tissues. Biochemical functions The functions of vitamin K are concerned with blood clotting process. It brings about the post-translational (after protein biosynthesis in the cell) modific ...
... Salt. Vitamin K is transported along with LDL and is stored mainly in liver and , to a lesser extent, in other tissues. Biochemical functions The functions of vitamin K are concerned with blood clotting process. It brings about the post-translational (after protein biosynthesis in the cell) modific ...
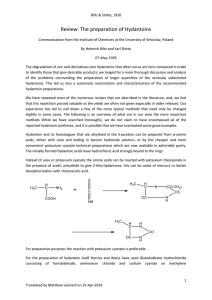
Review: The preparation of Hydantoins
... gave 20 g of pure product, (quantitative yield = 28.9 g). The yield increased to 24 g of pure hydantoin when the mother liquor was evaporated from hydantoic ester and the residue with 50 mL of fuming concentrated hydrochloric acid and 5 g of crude product was thus obtained by recrystallization. Prep ...
... gave 20 g of pure product, (quantitative yield = 28.9 g). The yield increased to 24 g of pure hydantoin when the mother liquor was evaporated from hydantoic ester and the residue with 50 mL of fuming concentrated hydrochloric acid and 5 g of crude product was thus obtained by recrystallization. Prep ...
Factors affecting human decomposition
... ammonia, thiols and pyruvic acid. In the presence of iron a black precipitate ferrous sulphide will be produced. The anaerobic conditions of a grave promote formation of considerable quantities of sulphide. Thiols or mercaptans are decomposition gases containing the –SH (sulphydryl group). These are ...
... ammonia, thiols and pyruvic acid. In the presence of iron a black precipitate ferrous sulphide will be produced. The anaerobic conditions of a grave promote formation of considerable quantities of sulphide. Thiols or mercaptans are decomposition gases containing the –SH (sulphydryl group). These are ...
Introduction into Metabolism and Energy Exchange in Human
... Anabolism is the sum total of metabolic pathways concerned with combining building block compounds into the complex macromolecules required by the organism. Anabolic processes require energy inputs. Energy can be supplied in two ways: 1) by ATP transferred from the catabolic pathways; 2) in some cas ...
... Anabolism is the sum total of metabolic pathways concerned with combining building block compounds into the complex macromolecules required by the organism. Anabolic processes require energy inputs. Energy can be supplied in two ways: 1) by ATP transferred from the catabolic pathways; 2) in some cas ...
Plant and Soil
... oxidize succinate, malate, fumarate or pyruvate but it oxidized glucose and fructose (Table 3). No significant organic acid-dependent 02 consumption was observed with PI21 cells grown on glucose. The presence of a catabolite repressionlike phenomenon (Lafreni6re et al., 1987) was investigated by gro ...
... oxidize succinate, malate, fumarate or pyruvate but it oxidized glucose and fructose (Table 3). No significant organic acid-dependent 02 consumption was observed with PI21 cells grown on glucose. The presence of a catabolite repressionlike phenomenon (Lafreni6re et al., 1987) was investigated by gro ...
Mutagenesis identifies the critical amino acid residues of human
... A few nuclease structures have been solved so far. For examples, nuclease A (NucA) from Anabaena, nuclease from Serratia, E-group colicins from Escherichia coli (E. coli), I-PpoI from Physarum polycephalum, and Vvn from Vibrio vulnificus are sugar-nonspecific nucleases involved in host defense [11]. ...
... A few nuclease structures have been solved so far. For examples, nuclease A (NucA) from Anabaena, nuclease from Serratia, E-group colicins from Escherichia coli (E. coli), I-PpoI from Physarum polycephalum, and Vvn from Vibrio vulnificus are sugar-nonspecific nucleases involved in host defense [11]. ...
6b How to ID an Unk organism
... temperature they prefer. Organisms that grow well in room temperature as well as body temperature might be opportunistic pathogens. These tubes can also be used to determine their pattern of growth in broth. THIOGLYCOLATE TUBES (OXYGEN REQUIREMENT) This medium has an oxygen gradient, which means tha ...
... temperature they prefer. Organisms that grow well in room temperature as well as body temperature might be opportunistic pathogens. These tubes can also be used to determine their pattern of growth in broth. THIOGLYCOLATE TUBES (OXYGEN REQUIREMENT) This medium has an oxygen gradient, which means tha ...
1051-2734-1-SP
... is not a safety concern in itself, as long as the genes are not mobilized and transferred to other bacteria. Theoretically, probiotics possessing antibiotic resistance genes could serve as a reservoir of resistance for potential pathogens. Therefore, microorganisms intended for use as probiotics hav ...
... is not a safety concern in itself, as long as the genes are not mobilized and transferred to other bacteria. Theoretically, probiotics possessing antibiotic resistance genes could serve as a reservoir of resistance for potential pathogens. Therefore, microorganisms intended for use as probiotics hav ...
Effect of essential and non-essential amino acid addition to a
... proline (Table 2). The effect of the addition of nonessential amino acids to diet E was negligible, even though the endogenous flow of most AA tended to decrease. In comparison with diet NF, the endogenous flow of total N in diets E and E+N was reduced by about 30%. This reduction was mainly due to ...
... proline (Table 2). The effect of the addition of nonessential amino acids to diet E was negligible, even though the endogenous flow of most AA tended to decrease. In comparison with diet NF, the endogenous flow of total N in diets E and E+N was reduced by about 30%. This reduction was mainly due to ...
Biochemical Engineering Prof. Dr. Rintu Banerjee Department of
... Now, when we are coming to the polar R group then we can find that serine threonine, cysteine, glycine, asparagines, glutamine are the polar amino acid, where glycine is the amino acid which is placed on the transition phase of polar and non polar amino acid. Now, this is the only amino acid where t ...
... Now, when we are coming to the polar R group then we can find that serine threonine, cysteine, glycine, asparagines, glutamine are the polar amino acid, where glycine is the amino acid which is placed on the transition phase of polar and non polar amino acid. Now, this is the only amino acid where t ...
Nucleotides: Synthesis and Degredation
... enzyme is aspartate transcarbamoylase (ATCase) catalyzes the condensation of carbamoyl phosphate with aspartate with the release of Pi ATCase is the major site of regulation in bacteria; it is activated by ATP and inhibited by CTP carbamoyl phosphate is an “activated” compound, so no energy input is ...
... enzyme is aspartate transcarbamoylase (ATCase) catalyzes the condensation of carbamoyl phosphate with aspartate with the release of Pi ATCase is the major site of regulation in bacteria; it is activated by ATP and inhibited by CTP carbamoyl phosphate is an “activated” compound, so no energy input is ...
Defining the molecular basis for the first potent and selective
... the rodent orthologs of FFA2 and FFA3, where C2 was found to be equipotent at mouse FFA2 (mFFA2) and mFFA3 (11). Clearly, this demonstrates a need for synthetic ligands that can differentiate between the function of these receptors in both human and rodent systems. Early attempts to identify synthet ...
... the rodent orthologs of FFA2 and FFA3, where C2 was found to be equipotent at mouse FFA2 (mFFA2) and mFFA3 (11). Clearly, this demonstrates a need for synthetic ligands that can differentiate between the function of these receptors in both human and rodent systems. Early attempts to identify synthet ...
Production of lactic acid using a new homofermentative
... 10 mmol−1 l−1 h−1 was attained (Fig. 1C). Therefore, to better understand the behaviour of CBRD01, it was of interest to discuss its fermentation profile in two phases (phase 1, 0–12 h; phase 2, 12–24 h). The total glucose consumption at 24 h was 94.06 mmol l−1 (Table 3). Although the lactate yield ...
... 10 mmol−1 l−1 h−1 was attained (Fig. 1C). Therefore, to better understand the behaviour of CBRD01, it was of interest to discuss its fermentation profile in two phases (phase 1, 0–12 h; phase 2, 12–24 h). The total glucose consumption at 24 h was 94.06 mmol l−1 (Table 3). Although the lactate yield ...
Splanchnic exchange of glucose, amino acids and free disease
... While it is known that patients with chronic inflammatory bowel disease in the active phase have disturbances in their nutritional and metabolic status, the precise nature of these alterations has been unclear. The observations in the present study show that carbohydrate, as well as lipid and protei ...
... While it is known that patients with chronic inflammatory bowel disease in the active phase have disturbances in their nutritional and metabolic status, the precise nature of these alterations has been unclear. The observations in the present study show that carbohydrate, as well as lipid and protei ...
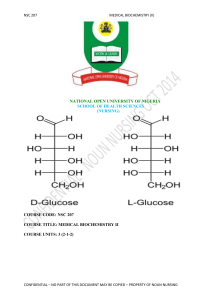
NSC 207 - National Open University of Nigeria
... The glycolytic pathway has a dual role (i) It degrades glucose to generate ATP and (ii) It provides building blocks for synthetic reactions. The rate of conversion of glucose into pyruvate is regulated to meet these 2 major cellular needs. Enzymes catalyzing essentially irreversible reactions are po ...
... The glycolytic pathway has a dual role (i) It degrades glucose to generate ATP and (ii) It provides building blocks for synthetic reactions. The rate of conversion of glucose into pyruvate is regulated to meet these 2 major cellular needs. Enzymes catalyzing essentially irreversible reactions are po ...
Correlations between the Amino Acid and Nucleotide Composition
... I967) that some plant virus nucleic acids, when put into Escherischia coli cell-free protein-producing systems (Nirenberg & Matthaei, I960, induce the formation of proteins like those produced in the host plant. These experiments have not yet been confirmed, and similar experiments with several othe ...
... I967) that some plant virus nucleic acids, when put into Escherischia coli cell-free protein-producing systems (Nirenberg & Matthaei, I960, induce the formation of proteins like those produced in the host plant. These experiments have not yet been confirmed, and similar experiments with several othe ...
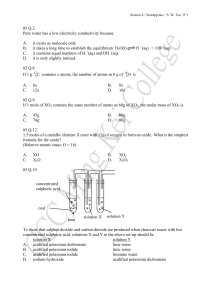
85 Q.2 Pure water has a low electricity conductivity because A. it
... ethanoic acid is / are correct? (1) They give the same colour change when the same quantity to universal indicator is added. (2) They react with marble chips at the same rate when the initial temperatures are the same. (3) They require the same number of moles of sodium hydroxide for complete neutra ...
... ethanoic acid is / are correct? (1) They give the same colour change when the same quantity to universal indicator is added. (2) They react with marble chips at the same rate when the initial temperatures are the same. (3) They require the same number of moles of sodium hydroxide for complete neutra ...
The Citric acid cycle - University of Houston
... Gluconeogenesis is the process whereby precursors such as lactate, pyruvate, glycerol, and amino acids are converted to glucose. Fasting requires all the glucose to be synthesized from these non-carbohydrate precursors. Most precursors must enter the Krebs cycle at some point to be converted to oxal ...
... Gluconeogenesis is the process whereby precursors such as lactate, pyruvate, glycerol, and amino acids are converted to glucose. Fasting requires all the glucose to be synthesized from these non-carbohydrate precursors. Most precursors must enter the Krebs cycle at some point to be converted to oxal ...
INSULIN, GLUCAGON, AND DIABETES MELLITUS
... 3. plasma lipoproteins increase up to 3X - leads to atherosclerosis G. Lack of insulin stimulates ketogenesis and acidosis 1. excess fatty acids in the liver stimulates carnitine transport mechanism 2. increased fatty acids to mitochondria produces excess acetyl-CoA 3. excess acetyl-CoA is condensed ...
... 3. plasma lipoproteins increase up to 3X - leads to atherosclerosis G. Lack of insulin stimulates ketogenesis and acidosis 1. excess fatty acids in the liver stimulates carnitine transport mechanism 2. increased fatty acids to mitochondria produces excess acetyl-CoA 3. excess acetyl-CoA is condensed ...
Carbohydrates - the Complex Carbohydrate Research Center
... metabolic intermediates (ATP, coenzymes) part of DNA & RNA structural elements in cell walls of bacteria, fungi & plants exoskeleton of arthropods extracellular matrix of animals cell-cell communication/signalling ...
... metabolic intermediates (ATP, coenzymes) part of DNA & RNA structural elements in cell walls of bacteria, fungi & plants exoskeleton of arthropods extracellular matrix of animals cell-cell communication/signalling ...
MOMORDICA CHARANTIA LIPOXYGENASE ENZYME Research Article
... different stages and there are many targets for anti inflammatory action 1. The mechanisms of inflammation involve a serious of events in which the metabolism of arachidonic acid plays an important role. Prostaglandins are involved in the complex process of inflammation and are responsible for the p ...
... different stages and there are many targets for anti inflammatory action 1. The mechanisms of inflammation involve a serious of events in which the metabolism of arachidonic acid plays an important role. Prostaglandins are involved in the complex process of inflammation and are responsible for the p ...
A speculation on the origin of protein synthesis
... separately, are comma-free. The second set is less attractive in that the possible weaker base pairing occurs not only in the hf configuration but also in the F H configuration. This latter is the configuration needed to hold the growing polypeptide chain to the mRNA and one might expect it to be th ...
... separately, are comma-free. The second set is less attractive in that the possible weaker base pairing occurs not only in the hf configuration but also in the F H configuration. This latter is the configuration needed to hold the growing polypeptide chain to the mRNA and one might expect it to be th ...
Analysis of amino acids and peptide primary structure determination
... linkages (bonds) between the carboxylic acid group of one amino acid and the amino group of the next amino acid. • Amide bonds are strong and are resistant to hydrolysis, but there are enzymes that catalyze their hydrolysis (to the amino acids). H O H2N C C OH R1 ...
... linkages (bonds) between the carboxylic acid group of one amino acid and the amino group of the next amino acid. • Amide bonds are strong and are resistant to hydrolysis, but there are enzymes that catalyze their hydrolysis (to the amino acids). H O H2N C C OH R1 ...
CHAPTER 19 LIPID METABOLISM Introduction: Fats are much more
... CoA, thus having these steps in common with ketone body formation. Note that cholesterol biosynthesis occurs in the cytoplasm, whereas ketone body takes place in the mitochondria of a liver cell. The reduction of HMG CoA to form mevalonate is the next step in the biosynthesis of cholesterol and con ...
... CoA, thus having these steps in common with ketone body formation. Note that cholesterol biosynthesis occurs in the cytoplasm, whereas ketone body takes place in the mitochondria of a liver cell. The reduction of HMG CoA to form mevalonate is the next step in the biosynthesis of cholesterol and con ...
Hepoxilin

Hepoxilins (HxA3 and HxB3) are nonclassic eicosanoid hormones involved in inflammation.