Fatty Acid Metabolism
... How is the oxidation of odd-chain fatty acids different from even-chain ones? ...
... How is the oxidation of odd-chain fatty acids different from even-chain ones? ...
Publication JournalArticle (Originalarbeit in einer wissenschaftlichen
... Phosphate/chemistry/*metabolism; Vigabatrin/*chemistry; gamma-Aminobutyric Acid/analogs & derivatives/*chemistry Gamma-aminobutyric acid aminotransferase (GABA-AT) is a pyridoxal 5'-phosphate-dependent enzyme responsible for the degradation of the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA. GABA-AT is a valid ...
... Phosphate/chemistry/*metabolism; Vigabatrin/*chemistry; gamma-Aminobutyric Acid/analogs & derivatives/*chemistry Gamma-aminobutyric acid aminotransferase (GABA-AT) is a pyridoxal 5'-phosphate-dependent enzyme responsible for the degradation of the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA. GABA-AT is a valid ...
chapter 6 - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... 1. For pyruvic acid to enter the citric acid cycle, it must first be oxidized to acetyl CoA. The acetyl CoA then joins with a molecule of oxaloacetic acid to form citric acid in the citric acid cycle. After one turn of the citric acid cycle, the citric acid regenerates the oxaloacetic acid molecule ...
... 1. For pyruvic acid to enter the citric acid cycle, it must first be oxidized to acetyl CoA. The acetyl CoA then joins with a molecule of oxaloacetic acid to form citric acid in the citric acid cycle. After one turn of the citric acid cycle, the citric acid regenerates the oxaloacetic acid molecule ...
Macromolecules
... Above: left, the simplest amino acid is glycine with R = H; right, in alanine R = CH3; in other amino acids R is more complex and may be an electrically charged group that is attracted to water (it is polar or hydrophilic) or it may be a water-insoluble (fatsoluble) side-chain (which is non-polar or ...
... Above: left, the simplest amino acid is glycine with R = H; right, in alanine R = CH3; in other amino acids R is more complex and may be an electrically charged group that is attracted to water (it is polar or hydrophilic) or it may be a water-insoluble (fatsoluble) side-chain (which is non-polar or ...
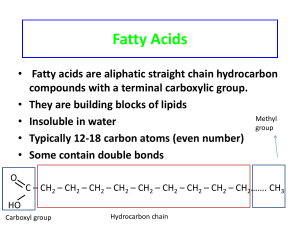
Fatty acid - thevignanam
... They were discovered in brain extracts in the 1870s and were named for the mythological Sphinx because of their enigmatic nature. ...
... They were discovered in brain extracts in the 1870s and were named for the mythological Sphinx because of their enigmatic nature. ...
Red Blood Cell Membrane Fatty Acids as a
... When there is concern about a patient’s fat intake or blood lipid levels, tests ordered are usually restricted to cholesterol, triglyceride, HDL, and LDL. Occasionally, a lipoprotein electro- phoresis or lipoprotein-a (Lp-a) are ordered. In addition to those tests listed above, at The Center we rout ...
... When there is concern about a patient’s fat intake or blood lipid levels, tests ordered are usually restricted to cholesterol, triglyceride, HDL, and LDL. Occasionally, a lipoprotein electro- phoresis or lipoprotein-a (Lp-a) are ordered. In addition to those tests listed above, at The Center we rout ...
No Slide Title
... Hemoglobin A, Sickle-Cell Hemoglobin, and Hemoglobin C Hemoglobin S Glu to Val at Position 6 on the Beta Chain Hemoglobin C Glu to Lys at Position 6 on the Beta Chain ...
... Hemoglobin A, Sickle-Cell Hemoglobin, and Hemoglobin C Hemoglobin S Glu to Val at Position 6 on the Beta Chain Hemoglobin C Glu to Lys at Position 6 on the Beta Chain ...
HYDROLYSIS OF THE PEPTIDE BOND AND AMINO ACID
... hydrolysis and was considered to be due to phosphoserine formed from the interaction of serine with oxidation products of hypophosphorous acid. In fact, when H 3P0 2 was added in similar amounts to a hydrochloric acid hydrolysis (22 hr, nOac, sealed tube), approximately 12% serine was converted to t ...
... hydrolysis and was considered to be due to phosphoserine formed from the interaction of serine with oxidation products of hypophosphorous acid. In fact, when H 3P0 2 was added in similar amounts to a hydrochloric acid hydrolysis (22 hr, nOac, sealed tube), approximately 12% serine was converted to t ...
Pentose Phosphate Pathway (aka Hexose monophosphate shunt)
... • G6PD is the most regulated enzyme: inhibition by NADPH, expression is dependent on insulin thus it is only expressed at high glucose concentration • Since the non-oxidative pathway is reversible, the direction is dependent on the need of the cell for ATP / acetyl CoA (energy / fatty acid synthesis ...
... • G6PD is the most regulated enzyme: inhibition by NADPH, expression is dependent on insulin thus it is only expressed at high glucose concentration • Since the non-oxidative pathway is reversible, the direction is dependent on the need of the cell for ATP / acetyl CoA (energy / fatty acid synthesis ...
powerpoint
... chains of insulin (21 aa) • All of the molecules of a given protein have the same sequence • Proteins can be sequenced in two ways: - direct amino acid sequencing - indirect sequencing of the encoding gene (DNA) ...
... chains of insulin (21 aa) • All of the molecules of a given protein have the same sequence • Proteins can be sequenced in two ways: - direct amino acid sequencing - indirect sequencing of the encoding gene (DNA) ...
Lecture 35 - Lipid Metabolism 1
... active conformation is dephosphorylated) and allosteric mechanisms (citrate binding stimulates activity, palmitoyl-CoA inhibits activity). ...
... active conformation is dephosphorylated) and allosteric mechanisms (citrate binding stimulates activity, palmitoyl-CoA inhibits activity). ...
GLUCOGENIC & KETOGENIC AMINO ACIDS
... CoA and succinyl CoA, rendering it both ketogenic and glucogenic. 2. Valine yields succinyl CoA and is glucogenic. 3. Leucine is ketogenic, being metabolized to acetoacetate and acetyl CoA. ...
... CoA and succinyl CoA, rendering it both ketogenic and glucogenic. 2. Valine yields succinyl CoA and is glucogenic. 3. Leucine is ketogenic, being metabolized to acetoacetate and acetyl CoA. ...
Lipogenesis (2014)
... Palmitic acid - the end product of FA synthesis in cytoplasm can be elongated in mitochondria by the addition of two carbon atoms to give other long chain saturated FA e.g. stearic acid Unsaturation: occur also in mitochondria by desaturase enzyme to give unsaturated fatty acids e.g. oleic acid ...
... Palmitic acid - the end product of FA synthesis in cytoplasm can be elongated in mitochondria by the addition of two carbon atoms to give other long chain saturated FA e.g. stearic acid Unsaturation: occur also in mitochondria by desaturase enzyme to give unsaturated fatty acids e.g. oleic acid ...
Analysis of Amino and Fatty Acids Composition of Senna alata Seed
... the major constituent (34.26%), followed by saturated fatty acid; palmitic acid (13.73%). The oil was having more unsaturated fatty acid (51.90%) than the saturated fatty acid (43.34%). The linoleic acid content is lower that the report of [17] as (45.5%) while the oleic acid content was reported as ...
... the major constituent (34.26%), followed by saturated fatty acid; palmitic acid (13.73%). The oil was having more unsaturated fatty acid (51.90%) than the saturated fatty acid (43.34%). The linoleic acid content is lower that the report of [17] as (45.5%) while the oleic acid content was reported as ...
REGULATION OF ACID
... therefore, more CO2 and H2O are formed 7. CO2 stimulates respiration and CO2 is eliminated from the extracellular fluid 8. When a strong base (ex. NaOH) is added to the bicarbonate buffer solution the hydroxyl ion (OH-) from the NaOH combines with H2CO3 to form HCO3-. The weak base NaHCO3 replaces ...
... therefore, more CO2 and H2O are formed 7. CO2 stimulates respiration and CO2 is eliminated from the extracellular fluid 8. When a strong base (ex. NaOH) is added to the bicarbonate buffer solution the hydroxyl ion (OH-) from the NaOH combines with H2CO3 to form HCO3-. The weak base NaHCO3 replaces ...
S1 Genetics
... • The first proof of how genes specify proteins came from studies on the oxygen binding protein found in red blood cells: haemoglobin. • Haemoglobin is a tetramer. It is made of four polypeptide chains – two -chains and two chains. ...
... • The first proof of how genes specify proteins came from studies on the oxygen binding protein found in red blood cells: haemoglobin. • Haemoglobin is a tetramer. It is made of four polypeptide chains – two -chains and two chains. ...
Cellular Respiration Chapter 9
... Yeasts use this process to form ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide as waste products. This causes bread dough to rise This is how some alcoholic beverages are made Pyruvic Acid + NADH alcohol + CO2 + NAD+ ...
... Yeasts use this process to form ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide as waste products. This causes bread dough to rise This is how some alcoholic beverages are made Pyruvic Acid + NADH alcohol + CO2 + NAD+ ...
Direct Comparison DNA and Amino Acid Sequences Based on a
... the 5' end of the DNA sequence, we got a codon and translate it into an amino acid. Then we move on to the next codon by shifting one nucleotide in the 3' direction and translating it. By continuing this process until we reach the 3' end of the sequence, we can get the translated amino acid sequence ...
... the 5' end of the DNA sequence, we got a codon and translate it into an amino acid. Then we move on to the next codon by shifting one nucleotide in the 3' direction and translating it. By continuing this process until we reach the 3' end of the sequence, we can get the translated amino acid sequence ...
Abnormalities of Intermediary Metabolism in Barth Syndrome
... TCA Intermediates in Smith-Leml-Opitz Syndrome ...
... TCA Intermediates in Smith-Leml-Opitz Syndrome ...
Cellular Respiration PPT
... Glycolysis is the process in which one molecule of glucose(6C) is broken in half, producing two molecules of pyruvic acid(3C) Requires 2 ATP molecules to get it started, but produces 4 ATP molecules and 2 NADH molecules in return ...
... Glycolysis is the process in which one molecule of glucose(6C) is broken in half, producing two molecules of pyruvic acid(3C) Requires 2 ATP molecules to get it started, but produces 4 ATP molecules and 2 NADH molecules in return ...
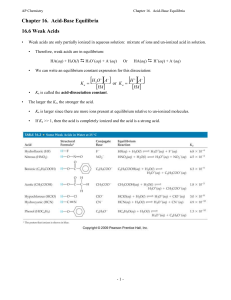
Chapter 15 Acids and Bases
... the H+ from the acid combines with the OH- from the base to make a molecule of H2O it is often helpful to think of H2O as H-OH the cation from the base combines with the anion from the acid to make a salt acid + base → salt + water HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) H+(aq)+Cl-(aq)+Na+(aq)+ ...
... the H+ from the acid combines with the OH- from the base to make a molecule of H2O it is often helpful to think of H2O as H-OH the cation from the base combines with the anion from the acid to make a salt acid + base → salt + water HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) H+(aq)+Cl-(aq)+Na+(aq)+ ...
Document
... PAF is synthesized and released by a variety of cell types that binds to surface receptors, triggering potent قويthrombotic and acute inflammatory leads to hypersensitivity & anaphylactic ردود فعل مناعيهreactions. It causes platelets to aggregate and degranulate the neutrophils and alveolar ...
... PAF is synthesized and released by a variety of cell types that binds to surface receptors, triggering potent قويthrombotic and acute inflammatory leads to hypersensitivity & anaphylactic ردود فعل مناعيهreactions. It causes platelets to aggregate and degranulate the neutrophils and alveolar ...
Metabolism
... Electron transport chain Where NADH and FADH2 are converted to ATP 1 molecule NADH from citric acid cycle = 2.5 ATP 1 molecule FADH2 = 1.5 ATP Oxygen is required Water is produced ...
... Electron transport chain Where NADH and FADH2 are converted to ATP 1 molecule NADH from citric acid cycle = 2.5 ATP 1 molecule FADH2 = 1.5 ATP Oxygen is required Water is produced ...
Chapter 1 - TamAPChemistryHart
... Practice Problem 16.15 Which of the following compounds should produce the highest pH as a 0.05 M solution: pyridine, methylamine, or nitrous acid? (methylamine) ...
... Practice Problem 16.15 Which of the following compounds should produce the highest pH as a 0.05 M solution: pyridine, methylamine, or nitrous acid? (methylamine) ...
Hepoxilin

Hepoxilins (HxA3 and HxB3) are nonclassic eicosanoid hormones involved in inflammation.