Genetic Algorithms for Optimization
... Hh: the output of h-th neuron in hidden layer Ii: the value of i-th input wih: the weight of the connection from i-th input to h-th neuron in hidden layer ...
... Hh: the output of h-th neuron in hidden layer Ii: the value of i-th input wih: the weight of the connection from i-th input to h-th neuron in hidden layer ...
5-NeuralNetworks
... • Equivalent to rules: – If output is correct do nothing. – If output is high, lower weights on active inputs – If output is low, increase weights on active inputs ...
... • Equivalent to rules: – If output is correct do nothing. – If output is high, lower weights on active inputs – If output is low, increase weights on active inputs ...
GameAI_NeuralNetworks
... Most common error measure: Mean square error, or average of the square of difference between desired and calculated output: ...
... Most common error measure: Mean square error, or average of the square of difference between desired and calculated output: ...
NeuralNets
... • Multi-layer networks can represent arbitrary functions, but an effective learning algorithm for such networks was thought to be difficult. • A typical multi-layer network consists of an input, hidden and output layer, each fully connected to the next, with activation feeding forward. output hidden ...
... • Multi-layer networks can represent arbitrary functions, but an effective learning algorithm for such networks was thought to be difficult. • A typical multi-layer network consists of an input, hidden and output layer, each fully connected to the next, with activation feeding forward. output hidden ...
Neural Networks
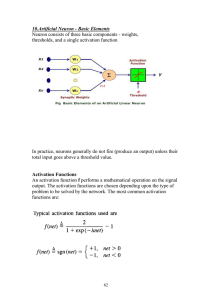
... The sigmoid function • The function used to perform this operation is the sigmoid function, • The main reason why this particular function is chosen is that its derivative, which is used in the learning law, is easily computed. • The result obtained after applying this function to the net input is ...
... The sigmoid function • The function used to perform this operation is the sigmoid function, • The main reason why this particular function is chosen is that its derivative, which is used in the learning law, is easily computed. • The result obtained after applying this function to the net input is ...
13 - classes.cs.uchicago.edu
... • Error: Sum of squares error of inputs with current weights • Compute rate of change of error wrt each weight – Which weights have greatest effect on error? – Effectively, partial derivatives of error wrt weights • In turn, depend on other weights => chain rule ...
... • Error: Sum of squares error of inputs with current weights • Compute rate of change of error wrt each weight – Which weights have greatest effect on error? – Effectively, partial derivatives of error wrt weights • In turn, depend on other weights => chain rule ...
lecture22 - University of Virginia, Department of Computer Science
... Why are modification rules more complicated? We can calculate the error of the output neuron by comparing to training data • We could use previous update rule to adjust W3,5 and W4,5 to correct that error • But how do W1,3 W1,4 W2,3 W2,4 adjust? ...
... Why are modification rules more complicated? We can calculate the error of the output neuron by comparing to training data • We could use previous update rule to adjust W3,5 and W4,5 to correct that error • But how do W1,3 W1,4 W2,3 W2,4 adjust? ...
Learning with Perceptrons and Neural Networks
... • Error: Sum of squares error of inputs with current weights • Compute rate of change of error wrt each weight – Which weights have greatest effect on error? – Effectively, partial derivatives of error wrt weights • In turn, depend on other weights => chain rule ...
... • Error: Sum of squares error of inputs with current weights • Compute rate of change of error wrt each weight – Which weights have greatest effect on error? – Effectively, partial derivatives of error wrt weights • In turn, depend on other weights => chain rule ...
Neural network architecture
... combination of the inputs. The weights are selected in the neural network framework using a ...
... combination of the inputs. The weights are selected in the neural network framework using a ...
Artificial Neural Networks
... • An input is fed into the network and the output is being calculated. • We compare the output of the network with the target output, and we get the error. • We want to minimize the error, so we greedily adjust the weights such that error for this particular input will go towards zero. • We do so us ...
... • An input is fed into the network and the output is being calculated. • We compare the output of the network with the target output, and we get the error. • We want to minimize the error, so we greedily adjust the weights such that error for this particular input will go towards zero. • We do so us ...
NeuralNets273ASpring09
... synapses which can learn how much signal is transmitted. • McCulloch and Pitt (’43) built a first abstract model of a neuron. ...
... synapses which can learn how much signal is transmitted. • McCulloch and Pitt (’43) built a first abstract model of a neuron. ...
Neural networks
... • The network topology is given • The same activation function is used at each hidden neuron and it is given • Training = calibration of weights • on-line learning (epochs) ...
... • The network topology is given • The same activation function is used at each hidden neuron and it is given • Training = calibration of weights • on-line learning (epochs) ...
Introduction to Neural Networks
... Problem: What are the errors in the hidden layer? Backpropagation Algorithm For each hidden layer (from output to input): For each unit in the layer determine how much it contributed to the errors in the previous layer. Adapt the weight according to this contribution ...
... Problem: What are the errors in the hidden layer? Backpropagation Algorithm For each hidden layer (from output to input): For each unit in the layer determine how much it contributed to the errors in the previous layer. Adapt the weight according to this contribution ...
NeuralNets
... But since things are encoded redundantly by many of them, their population can do computation reliably and fast. ...
... But since things are encoded redundantly by many of them, their population can do computation reliably and fast. ...
Specific nonlinear models
... • MLP is a composition of squash functions and scalar products. • Derivatives can be calculated by using the chain rule for derivatives of composite functions. • Complexity is O(number of weights). • Formulas are similar to those used for the forward pass, but going in contrary direction, hence the ...
... • MLP is a composition of squash functions and scalar products. • Derivatives can be calculated by using the chain rule for derivatives of composite functions. • Complexity is O(number of weights). • Formulas are similar to those used for the forward pass, but going in contrary direction, hence the ...
cs621-lect27-bp-applcation-logic-2009-10-15
... • Facts and Rules: In a certain country, people either always speak the truth or always lie. A tourist T comes to a junction in the country and finds an inhabitant S of the country standing there. One of the roads at the junction leads to the capital of the country and the other does not. S can be a ...
... • Facts and Rules: In a certain country, people either always speak the truth or always lie. A tourist T comes to a junction in the country and finds an inhabitant S of the country standing there. One of the roads at the junction leads to the capital of the country and the other does not. S can be a ...
ppt
... But since things are encoded redundantly by many of them, their population can do computation reliably and fast. ...
... But since things are encoded redundantly by many of them, their population can do computation reliably and fast. ...