Lecture 6, Parity and Charge Conjugation
... The quantum number n is called the intrinsic parity of a particle. If n= 1 the particle has even parity. If n= -1 the particle has odd parity. In addition, if the overall wavefunction of a particle (or system of particles) contains spherical harmonics (YLm) then we must take this into account to get ...
... The quantum number n is called the intrinsic parity of a particle. If n= 1 the particle has even parity. If n= -1 the particle has odd parity. In addition, if the overall wavefunction of a particle (or system of particles) contains spherical harmonics (YLm) then we must take this into account to get ...
Spacetime foam and modified dispersion relations
... Study how a Lorentz-invariant model of spacetime foam modify the propagation of particles ...
... Study how a Lorentz-invariant model of spacetime foam modify the propagation of particles ...
quant-ph
... with Θ the Heaviside function and ∆E ≥ 0. A wave packet coming from the left gets partially reflected at the step and partially transmitted. The size of the reflected and the transmitted packets can be determined by a standard textbook method of calculation (e.g., [1, 2]), the stationary analysis, r ...
... with Θ the Heaviside function and ∆E ≥ 0. A wave packet coming from the left gets partially reflected at the step and partially transmitted. The size of the reflected and the transmitted packets can be determined by a standard textbook method of calculation (e.g., [1, 2]), the stationary analysis, r ...
Chapter I
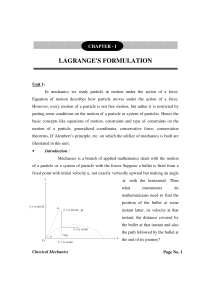
... Well, to answer such questions, mathematicians do not need any meter stick to measure the distance covered by the bullet at the instant, they don't need any speedometer to find its speed at any instant t, nor they need any clock to see the time required to cover the definite distance. In fact, they ...
... Well, to answer such questions, mathematicians do not need any meter stick to measure the distance covered by the bullet at the instant, they don't need any speedometer to find its speed at any instant t, nor they need any clock to see the time required to cover the definite distance. In fact, they ...
Anomaly driven signatures of new invisible physics
... tower of states) and therefore the mass suppression can be compensated by the large multiplicity of these fermions. In this paper we consider another possible setup, in which the anomaly cancellation occurs only within a high-energy sector (at scales not accessible by current experiments), but at lo ...
... tower of states) and therefore the mass suppression can be compensated by the large multiplicity of these fermions. In this paper we consider another possible setup, in which the anomaly cancellation occurs only within a high-energy sector (at scales not accessible by current experiments), but at lo ...
An Introduction to Applied Quantum Mechanics in the Wigner Monte
... of density functional theory (DFT) [39] and time-dependent ab-initio simulations [40]. It has shown to be a very convenient formalism when time-dependent, multi-dimensional and fully quantum simulations are necessary (see for example [41], [42] and [43]). In this work, we focus our attention on the ...
... of density functional theory (DFT) [39] and time-dependent ab-initio simulations [40]. It has shown to be a very convenient formalism when time-dependent, multi-dimensional and fully quantum simulations are necessary (see for example [41], [42] and [43]). In this work, we focus our attention on the ...
WORMHOLES WITH A PAST* 1. Introduction Although as physicists
... For fixed positive cosmological constant A (defined as 8~rG/3 times the vacuum energy density) the euclidean bounce solution is defined on a sphere of radius L where L 2 = 1/A. We will use the coordinates of a five-dimensional flat euclidean space (X, Y, Z ) in which this sphere is defined by X 2 + ...
... For fixed positive cosmological constant A (defined as 8~rG/3 times the vacuum energy density) the euclidean bounce solution is defined on a sphere of radius L where L 2 = 1/A. We will use the coordinates of a five-dimensional flat euclidean space (X, Y, Z ) in which this sphere is defined by X 2 + ...
Part II Applications of Quantum Mechanics Lent 2012
... parity reversed situation to the familiar one discussed above. We need not solve again from scratch; indeed we can recover the solution from what has already been done. The Schrödinger equation is real, and so can take the complex conjugate of the solution ψ(x) of the previous section (2.1) and get ...
... parity reversed situation to the familiar one discussed above. We need not solve again from scratch; indeed we can recover the solution from what has already been done. The Schrödinger equation is real, and so can take the complex conjugate of the solution ψ(x) of the previous section (2.1) and get ...
Contradiction within Paraxial Wave Optics and its - LAS
... Inserting Eq. (20) into Eq.(2) delivers ...
... Inserting Eq. (20) into Eq.(2) delivers ...