BAND THEORY OF SOLIDS
... In the energy band, the allowed energies are almost continuous. These energy bands are in general, separated by regions, which have no allowed energy levels. These regions are known as "forbidden bands" or 'energy gaps'. The amount of splitting is not the same for different levels. The levels filled ...
... In the energy band, the allowed energies are almost continuous. These energy bands are in general, separated by regions, which have no allowed energy levels. These regions are known as "forbidden bands" or 'energy gaps'. The amount of splitting is not the same for different levels. The levels filled ...
Solid State Physics
... Electron concentration is uniform throughout the spaces in between atoms. ...
... Electron concentration is uniform throughout the spaces in between atoms. ...
Final Exam Review Answers
... • According to Hund’s rule, when electrons occupy orbitals of equal energy, one electron enters each orbit until • a. all the orbitals contain one electron, with spins parallel. • b. all the orbitals contain one electron, with opposite spins. • c. there are two electrons in each orbital. • d. electr ...
... • According to Hund’s rule, when electrons occupy orbitals of equal energy, one electron enters each orbit until • a. all the orbitals contain one electron, with spins parallel. • b. all the orbitals contain one electron, with opposite spins. • c. there are two electrons in each orbital. • d. electr ...
pdf-file - Max Planck Institut für Quantenoptik
... and Saudi Arabia, have observed, for the first time, the quantum-mechanical behaviour occurring at the location in a noble gas atom where, shortly before, an electron had been ejected from its orbit. The researchers achieved this result using light pulses which last only slightly longer than 100 att ...
... and Saudi Arabia, have observed, for the first time, the quantum-mechanical behaviour occurring at the location in a noble gas atom where, shortly before, an electron had been ejected from its orbit. The researchers achieved this result using light pulses which last only slightly longer than 100 att ...
Atomic Theory Handout CNS 8
... Bohr began to work on the problem of the atom's structure. Ernest Rutherford had recently suggested the atom had a miniature, dense nucleus surrounded by a cloud of nearly weightless electrons. There were a few problems with the model, however. For example, according to classical physics, the electr ...
... Bohr began to work on the problem of the atom's structure. Ernest Rutherford had recently suggested the atom had a miniature, dense nucleus surrounded by a cloud of nearly weightless electrons. There were a few problems with the model, however. For example, according to classical physics, the electr ...
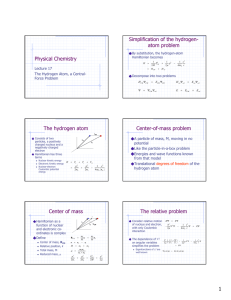
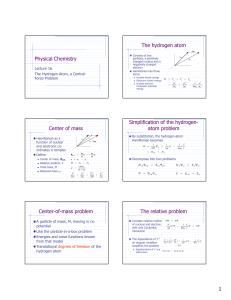
1 Hydrogen Atom: Wave Function Hydrogen Atom
... Quantum Numbers for Allowed Electron States in an Atom ...
... Quantum Numbers for Allowed Electron States in an Atom ...
Reactions I Can..
... 1. Describe the historic importance of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table. 2. List two of the problems with Mendeleev’s table. 3. Identify the key contribution of Henry Moseley to the modern periodic table 4. Identify groups and periods on the Periodic Table 5. Identify key sections of the periodic table in ...
... 1. Describe the historic importance of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table. 2. List two of the problems with Mendeleev’s table. 3. Identify the key contribution of Henry Moseley to the modern periodic table 4. Identify groups and periods on the Periodic Table 5. Identify key sections of the periodic table in ...
Atoms
... 2. List two of the problems with Mendeleev’s table. 3. Identify the key contribution of Henry Moseley to the modern periodic table 4. Identify groups and periods on the Periodic Table 5. Identify key sections of the periodic table including orbital blocks, metal vs. nonmetal, alkali metals, alkaline ...
... 2. List two of the problems with Mendeleev’s table. 3. Identify the key contribution of Henry Moseley to the modern periodic table 4. Identify groups and periods on the Periodic Table 5. Identify key sections of the periodic table including orbital blocks, metal vs. nonmetal, alkali metals, alkaline ...
Midterm Review File
... 25. If an atom has an electron configuration of 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p2, how many valence electrons does it have? ...
... 25. If an atom has an electron configuration of 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p2, how many valence electrons does it have? ...
Ch. 5 Electrons in Atoms
... an atom, it would violate Heisenberg, so it would instead form a an entire atom probability cloud - Uncertainty coupled with duality of light and matter led to Schroedinger’s equations ...
... an atom, it would violate Heisenberg, so it would instead form a an entire atom probability cloud - Uncertainty coupled with duality of light and matter led to Schroedinger’s equations ...
Deconstructed HS-PS1-2
... to chemical reactions involving main group elements and combustion reactions.] ...
... to chemical reactions involving main group elements and combustion reactions.] ...
Schrödinger`s Wave Mechanical Model
... 2. Electrons do not follow a set circular orbit a specific distance from the nucleus, but the electrons are free to travel anywhere within their respective energy level/region. 3. Energy level was described as a region of highest probability of finding an electron in a given place with a specific am ...
... 2. Electrons do not follow a set circular orbit a specific distance from the nucleus, but the electrons are free to travel anywhere within their respective energy level/region. 3. Energy level was described as a region of highest probability of finding an electron in a given place with a specific am ...
Quantum Physics Cumulative Review
... an orbit with -5.25 eV of energy. You discover that the atom emits two visible lines in its spectrum when the outermost electron is excited, with wavelengths of 420 nm and 690 nm respectively. a) Draw an energy level diagram showing the different possible orbits for the electron that show up in the ...
... an orbit with -5.25 eV of energy. You discover that the atom emits two visible lines in its spectrum when the outermost electron is excited, with wavelengths of 420 nm and 690 nm respectively. a) Draw an energy level diagram showing the different possible orbits for the electron that show up in the ...
Notes on Atoms and Molecules
... A molecule which contains only one atom is called monatomic Example: Noble gases like Helium (He), Neon (Ne), Argon (Ar) etc. ...
... A molecule which contains only one atom is called monatomic Example: Noble gases like Helium (He), Neon (Ne), Argon (Ar) etc. ...
Electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6.Electronic configurations describe electrons as each moving independently in an orbital, in an average field created by all other orbitals. Mathematically, configurations are described by Slater determinants or configuration state functions.According to the laws of quantum mechanics, for systems with only one electron, an energy is associated with each electron configuration and, upon certain conditions, electrons are able to move from one configuration to another by the emission or absorption of a quantum of energy, in the form of a photon.Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements. The concept is also useful for describing the chemical bonds that hold atoms together. In bulk materials, this same idea helps explain the peculiar properties of lasers and semiconductors.