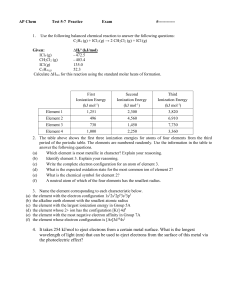
Atomic Term Symbols and Energy Splitting
... The sodium D-line gets its name because there are really two closely-spaced emissions possible, or a "doublet", as shown in Figure 1. These transitions occur at wavelengths of 5890 and 5896 Å. ...
... The sodium D-line gets its name because there are really two closely-spaced emissions possible, or a "doublet", as shown in Figure 1. These transitions occur at wavelengths of 5890 and 5896 Å. ...
Review for Exam 1
... Thus the energy eigenvalues for the rigid rotor are: ..............................E = l (l+1) ............... where (l = 0,1,2,3, ...... ) ............................. (E) .................... or .... E = J (J+1) .............. where (J = 0,1,2,3, ....... ) Often m is called ml since the value of ...
... Thus the energy eigenvalues for the rigid rotor are: ..............................E = l (l+1) ............... where (l = 0,1,2,3, ...... ) ............................. (E) .................... or .... E = J (J+1) .............. where (J = 0,1,2,3, ....... ) Often m is called ml since the value of ...
Name: Period : ______ Chemistry – Chapter 13 – Electrons in
... sublevels that could be in main level 6? ____ What is the maximum number of orbitals that could be in main level 6? _____What is the maximum number of electrons that could be in main level 6? _____ 11. If n represents the main level give a mathematical formula in terms of n for the maximum number of ...
... sublevels that could be in main level 6? ____ What is the maximum number of orbitals that could be in main level 6? _____What is the maximum number of electrons that could be in main level 6? _____ 11. If n represents the main level give a mathematical formula in terms of n for the maximum number of ...
Chemistry Study Guide
... 6. What kind of bond is NaCl? Ionic CO2 Covalent N2 Covalent 7. Which group forms acids with H+ ion? Halogens (Group 17) 8. How many valence electrons are in a Group 1 element? 1 Group 13? 3 9. How do positive and negative ions form? Positive ions form when an atom loses an electron, negative ions f ...
... 6. What kind of bond is NaCl? Ionic CO2 Covalent N2 Covalent 7. Which group forms acids with H+ ion? Halogens (Group 17) 8. How many valence electrons are in a Group 1 element? 1 Group 13? 3 9. How do positive and negative ions form? Positive ions form when an atom loses an electron, negative ions f ...
4.2_The_Quantum_Model_of_the_Atom1
... The Schrödinger Wave Equation • In 1926, Austrian physicist Erwin Schrödinger developed an equation that treated electrons in atoms as waves. • Together with the Heisenberg uncertainty principle, the Schrödinger wave equation laid the foundation for modern quantum theory. • Quantum theory describes ...
... The Schrödinger Wave Equation • In 1926, Austrian physicist Erwin Schrödinger developed an equation that treated electrons in atoms as waves. • Together with the Heisenberg uncertainty principle, the Schrödinger wave equation laid the foundation for modern quantum theory. • Quantum theory describes ...
1. Crystal Properties and Growth of Semiconductors
... radiation emanating from them Bohr postulates: 1) Electron exists in certain stable circular orbits about the nucleus and does not give off radiation 2) Electron may shift to an orbit of higher or lower energy by absorbing or emitting a photon of energy hf 3) Angular momentum is quantized p =m v r = ...
... radiation emanating from them Bohr postulates: 1) Electron exists in certain stable circular orbits about the nucleus and does not give off radiation 2) Electron may shift to an orbit of higher or lower energy by absorbing or emitting a photon of energy hf 3) Angular momentum is quantized p =m v r = ...
Figure 7.18 The 3d orbitals
... Figure 7.8 Three series of spectral lines of atomic hydrogen. Balmer is in the visible region and the other series, which have names also, are in uv or ir area of E-M radiation. The Bohr Model of Hydrogen atom 1. H atoms have only certain allowable energy levels called stationary states. 2. At ...
... Figure 7.8 Three series of spectral lines of atomic hydrogen. Balmer is in the visible region and the other series, which have names also, are in uv or ir area of E-M radiation. The Bohr Model of Hydrogen atom 1. H atoms have only certain allowable energy levels called stationary states. 2. At ...
How do you tell if a molecule is paramagnetic or diamagnetic
... oxygen for example. According to VB theory, each oxygen atom has 3 sp2 hybrid orbitals, there is one sigma-bond formed by the overlap of a pair of sp2 hybrid orbitals from each atom, one pi-bond formed by the overlap of atomic p-orbitals and each oxygen atom has 2 non-bonding pairs in 2 sp2 hybrid o ...
... oxygen for example. According to VB theory, each oxygen atom has 3 sp2 hybrid orbitals, there is one sigma-bond formed by the overlap of a pair of sp2 hybrid orbitals from each atom, one pi-bond formed by the overlap of atomic p-orbitals and each oxygen atom has 2 non-bonding pairs in 2 sp2 hybrid o ...
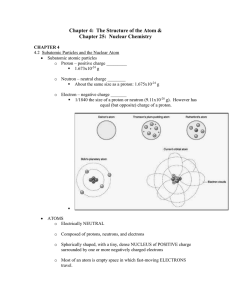
Chapter 4: The Structure of the Atom &
... o Above the band of stability – too many _____________; Below the band of stability – too many _______________ or too few ______________ o BETA DECAY: For elements above the band of stability (too many neutrons) A NEUTRON will decay into a PROTON (stays in the nucleus) and an ELECTRON (leaves the ...
... o Above the band of stability – too many _____________; Below the band of stability – too many _______________ or too few ______________ o BETA DECAY: For elements above the band of stability (too many neutrons) A NEUTRON will decay into a PROTON (stays in the nucleus) and an ELECTRON (leaves the ...
Section 1 - Tutor
... Section 30.5 The Quantum Mechanical Picture of the Hydrogen Atom 26. According to the quantum mechanical picture of the atom, which one of the following is a true statement concerning the ground state electron in a hydrogen atom? (a) The ground state electron has zero kinetic energy. (b) The groun ...
... Section 30.5 The Quantum Mechanical Picture of the Hydrogen Atom 26. According to the quantum mechanical picture of the atom, which one of the following is a true statement concerning the ground state electron in a hydrogen atom? (a) The ground state electron has zero kinetic energy. (b) The groun ...
Slide 1 - Southwest High School
... will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students except by instructors using the accompanying text in their classes. All recipients of this work are expected to abide by these restrictions and to honor the intended ...
... will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students except by instructors using the accompanying text in their classes. All recipients of this work are expected to abide by these restrictions and to honor the intended ...
ATOMIC STRUCTURE
... magnets spinning on their axes. When two electrons occupy the same orbital, they have opposite spin. Table 2-3 shows the distribution of electrons in principal energy levels I through 4. Electron Configuration. The electron configuration of an atom describes the arrangement of electrons in principal ...
... magnets spinning on their axes. When two electrons occupy the same orbital, they have opposite spin. Table 2-3 shows the distribution of electrons in principal energy levels I through 4. Electron Configuration. The electron configuration of an atom describes the arrangement of electrons in principal ...
A FERMI SEA OF HEAVY ELECTRONS
... projects out all doubly-occupied atomic states. A great deal of misinformation is in the literature about this projection process, and we should emphasize two points: First, that it can be derived as a non-singular canonical transformation; and second, any perturbative admixture between the two subs ...
... projects out all doubly-occupied atomic states. A great deal of misinformation is in the literature about this projection process, and we should emphasize two points: First, that it can be derived as a non-singular canonical transformation; and second, any perturbative admixture between the two subs ...
Chapter7 Exercises - Berkeley City College
... momentum number l, and the magnetic quantum number ml. 1. The principal quantum number n describes the principle energy levels of the orbitals and hence the energy of the electron that will eventually occupy these orbital. The values for the principal quantum number n are restricted to positive inte ...
... momentum number l, and the magnetic quantum number ml. 1. The principal quantum number n describes the principle energy levels of the orbitals and hence the energy of the electron that will eventually occupy these orbital. The values for the principal quantum number n are restricted to positive inte ...
Name - Quia
... Producing a gas d. Evaporation e. Rusting Iron f. Burning paper g. Fruit rotting 40. Describe how temperature relates to kinetic energy. If the temperature goes up or down, what happens to kinetic energy? 41. Name several factors that determine the speed of the atoms and molecules of a particular su ...
... Producing a gas d. Evaporation e. Rusting Iron f. Burning paper g. Fruit rotting 40. Describe how temperature relates to kinetic energy. If the temperature goes up or down, what happens to kinetic energy? 41. Name several factors that determine the speed of the atoms and molecules of a particular su ...
Slide 1 - KaiserScience
... The lowest energy level is called the ground state; the others are excited states. ...
... The lowest energy level is called the ground state; the others are excited states. ...
Electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6.Electronic configurations describe electrons as each moving independently in an orbital, in an average field created by all other orbitals. Mathematically, configurations are described by Slater determinants or configuration state functions.According to the laws of quantum mechanics, for systems with only one electron, an energy is associated with each electron configuration and, upon certain conditions, electrons are able to move from one configuration to another by the emission or absorption of a quantum of energy, in the form of a photon.Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements. The concept is also useful for describing the chemical bonds that hold atoms together. In bulk materials, this same idea helps explain the peculiar properties of lasers and semiconductors.