5.1
... An atomic orbital is often thought of as a region of space in which there is a high probability of finding an electron. Each energy sublevel corresponds to an orbital of a different shape, which describes where the electron is likely to ...
... An atomic orbital is often thought of as a region of space in which there is a high probability of finding an electron. Each energy sublevel corresponds to an orbital of a different shape, which describes where the electron is likely to ...
Physics 571 Lecture #27 - BYU Physics and Astronomy
... number of levels, and we have to keep track of them somehow. And besides being a historical vestige from long ago, this system is useful for knowing which states go where, what there properties are, which levels will radiate to which other levels, and so on. For two equivalent p electrons (equivalen ...
... number of levels, and we have to keep track of them somehow. And besides being a historical vestige from long ago, this system is useful for knowing which states go where, what there properties are, which levels will radiate to which other levels, and so on. For two equivalent p electrons (equivalen ...
lowdin`s remarks on the aufbau principle and a philosopher`s view of
... transition series of elements, apart from the elements Cr and Cu where further slight anomalies are believed to occur. In fact this explanation for the configuration of the scandium atom and most other first transition elements is inconsistent. If the 3d orbital has a lower energy than 4s starting a ...
... transition series of elements, apart from the elements Cr and Cu where further slight anomalies are believed to occur. In fact this explanation for the configuration of the scandium atom and most other first transition elements is inconsistent. If the 3d orbital has a lower energy than 4s starting a ...
From Last Time… - High Energy Physics
... • In an atom, the emitted electromagnetic wave carries away energy from the electron. – Electron predicted to continually lose energy. – The electron would eventually spiral into the nucleus – However most atoms are stable! ...
... • In an atom, the emitted electromagnetic wave carries away energy from the electron. – Electron predicted to continually lose energy. – The electron would eventually spiral into the nucleus – However most atoms are stable! ...
do with electron orbitals?
... What is Schrodinger Model of Hydrogen Atom? Electron is cloud of probability whose wave function (x,t) is the solution to the Schrodinger equation: ...
... What is Schrodinger Model of Hydrogen Atom? Electron is cloud of probability whose wave function (x,t) is the solution to the Schrodinger equation: ...
The Atomic Theory, and the Structure of Matter
... A simpler way to represent atoms and ions of atom is with electron dot diagrams Electron Dot Diagrams show only the outer energy level (valence shell) of an atom. Only these electrons are represented because they are responsible for an atom’s chemical properties. For example: ...
... A simpler way to represent atoms and ions of atom is with electron dot diagrams Electron Dot Diagrams show only the outer energy level (valence shell) of an atom. Only these electrons are represented because they are responsible for an atom’s chemical properties. For example: ...
Chapter 5
... (a) 1s electrons can be "found" anywhere in this solid sphere, centered on the nucleus.(b) The electron density map plots the points where electrons could be. The higher density of dots indicates the physical location in which the electron cloud is most dense.(c) Electron density (Y2) is shown as a ...
... (a) 1s electrons can be "found" anywhere in this solid sphere, centered on the nucleus.(b) The electron density map plots the points where electrons could be. The higher density of dots indicates the physical location in which the electron cloud is most dense.(c) Electron density (Y2) is shown as a ...
Chapter 5
... (a) 1s electrons can be "found" anywhere in this solid sphere, centered on the nucleus.(b) The electron density map plots the points where electrons could be. The higher density of dots indicates the physical location in which the electron cloud is most dense.(c) Electron density (Y2) is shown as a ...
... (a) 1s electrons can be "found" anywhere in this solid sphere, centered on the nucleus.(b) The electron density map plots the points where electrons could be. The higher density of dots indicates the physical location in which the electron cloud is most dense.(c) Electron density (Y2) is shown as a ...
File
... Nonmetal - Occupy the upper right hand corner of the periodic table and are generally non-lustrous and are generally poor conductors of electricity. Nucleus - The dense, central portion of an atom that contains protons and neutrons. Pauli's exclusion principle - This principle states that two electr ...
... Nonmetal - Occupy the upper right hand corner of the periodic table and are generally non-lustrous and are generally poor conductors of electricity. Nucleus - The dense, central portion of an atom that contains protons and neutrons. Pauli's exclusion principle - This principle states that two electr ...
atoms
... develop on the comb and causes bits of paper to be attracted to the comb (b) Both objects on the left carry negative charge repel each other The objects in the center lack any electrical charge and exert no force on each other ...
... develop on the comb and causes bits of paper to be attracted to the comb (b) Both objects on the left carry negative charge repel each other The objects in the center lack any electrical charge and exert no force on each other ...
Condensed Plasmoids – The Intermediate State of LENR
... The multi-electron system is approximated by computing a collection of one-electron orbitals, whereby each electron orbital is subjected to the mean electric potential and magnetic vector potential created by the total charge density and total current density of all other occupied orbitals and the n ...
... The multi-electron system is approximated by computing a collection of one-electron orbitals, whereby each electron orbital is subjected to the mean electric potential and magnetic vector potential created by the total charge density and total current density of all other occupied orbitals and the n ...
Chapter 30: Quantum Physics Chapter 31: Atomic Physics Chapter
... (a) The angular momentum in the quantum mechanical model of the hydrogen atom is zero if the quantum number is zero. In the n 1 state, the only allowed value for is 0, and hence the orbital angular momentum must be zero for n 1. (b) Yes. For n 1, there are n allowed values for the number . One ...
... (a) The angular momentum in the quantum mechanical model of the hydrogen atom is zero if the quantum number is zero. In the n 1 state, the only allowed value for is 0, and hence the orbital angular momentum must be zero for n 1. (b) Yes. For n 1, there are n allowed values for the number . One ...
Chapter 7 Ionic and Metallic Bonding
... They make positive ions (cations) If we look at the electron configuration, it makes sense to lose electrons: Na 1s22s22p63s1 1 valence electron Na1+ 1s22s22p6 This is a noble gas configuration with 8 electrons in the ...
... They make positive ions (cations) If we look at the electron configuration, it makes sense to lose electrons: Na 1s22s22p63s1 1 valence electron Na1+ 1s22s22p6 This is a noble gas configuration with 8 electrons in the ...
Quantum Theory of Hydrogen
... classical thinking in several ways): We can only give probabilities for finding an electron at some set of coordinates. The electron doesn't orbit the nucleus in any conventional sense. You should think of the pictures shown here as representing fuzzy clouds. The clouds aren't electrons, but the ...
... classical thinking in several ways): We can only give probabilities for finding an electron at some set of coordinates. The electron doesn't orbit the nucleus in any conventional sense. You should think of the pictures shown here as representing fuzzy clouds. The clouds aren't electrons, but the ...
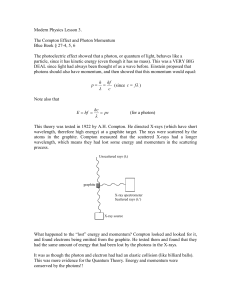
Modern Physics Lesson 3
... Conclusion: A photon is a particle of light that has energy and momentum. However, photons have no mass and travel at the speed of light, c. deBroglie Wavelength Louis deBroglie proposed in 1923 that if waves behave like particles, then particles should also behave like waves! This was the beginnin ...
... Conclusion: A photon is a particle of light that has energy and momentum. However, photons have no mass and travel at the speed of light, c. deBroglie Wavelength Louis deBroglie proposed in 1923 that if waves behave like particles, then particles should also behave like waves! This was the beginnin ...
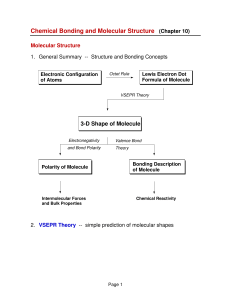
3-D Shape of Molecule
... 2. Molecular Orbitals for simple diatomic molecules (H2 and He2) in H2 the 1s atomic orbitals on the two H atoms are combined into: a bonding MO -- σ1s and an antibonding MO -- σ*1s MO energy level diagram for H2 (only the bonding MO is filled): ...
... 2. Molecular Orbitals for simple diatomic molecules (H2 and He2) in H2 the 1s atomic orbitals on the two H atoms are combined into: a bonding MO -- σ1s and an antibonding MO -- σ*1s MO energy level diagram for H2 (only the bonding MO is filled): ...
Electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6.Electronic configurations describe electrons as each moving independently in an orbital, in an average field created by all other orbitals. Mathematically, configurations are described by Slater determinants or configuration state functions.According to the laws of quantum mechanics, for systems with only one electron, an energy is associated with each electron configuration and, upon certain conditions, electrons are able to move from one configuration to another by the emission or absorption of a quantum of energy, in the form of a photon.Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements. The concept is also useful for describing the chemical bonds that hold atoms together. In bulk materials, this same idea helps explain the peculiar properties of lasers and semiconductors.