OKEMOS PUBLIC SCHOOLS
... In the space before the question, write the part of the atom which gives the characteristic listed. (Your choices are protons, neutrons, electron cloud, valence electrons, or nucleus.) _electron cloud__________________a) produces most of the atom's volume. _protons__________________b) determines the ...
... In the space before the question, write the part of the atom which gives the characteristic listed. (Your choices are protons, neutrons, electron cloud, valence electrons, or nucleus.) _electron cloud__________________a) produces most of the atom's volume. _protons__________________b) determines the ...
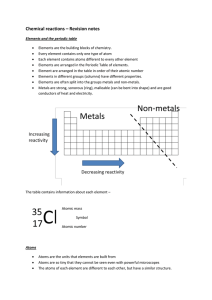
Chemical reactions revision
... Elements in different groups (columns) have different properties. Elements are often split into the groups metals and non-metals. Metals are strong, sonorous (ring), malleable (can be bent into shape) and are good conductors of heat and electricity. ...
... Elements in different groups (columns) have different properties. Elements are often split into the groups metals and non-metals. Metals are strong, sonorous (ring), malleable (can be bent into shape) and are good conductors of heat and electricity. ...
Charge Transfer in Collisions of Ions with atoms and - Indico
... This has little consequence for the fractional ion abundance for H or He but it can have a dramatic effect on the fractional abundances of the higher charge states of minor complex species (such as C, N, O,...), whose spectral lines are often used for spectroscopic diagnostics of the plasma. So we n ...
... This has little consequence for the fractional ion abundance for H or He but it can have a dramatic effect on the fractional abundances of the higher charge states of minor complex species (such as C, N, O,...), whose spectral lines are often used for spectroscopic diagnostics of the plasma. So we n ...
A Brief Review of Thomas-Fermi Theory
... in the neutral case (positivity of the pressure) [EL], [BL]. This theorem plays an important role in the stability of matter. ...
... in the neutral case (positivity of the pressure) [EL], [BL]. This theorem plays an important role in the stability of matter. ...
January 1999
... For large separation between the hydrogen molecules, the perturbation can be treated in a dipole approximation. Find an expression for the effective interaction energy and in particular find its dependence on the separation R in the limit R 2rb . ...
... For large separation between the hydrogen molecules, the perturbation can be treated in a dipole approximation. Find an expression for the effective interaction energy and in particular find its dependence on the separation R in the limit R 2rb . ...
AP Review to Share - Wappingers Central School District
... photons Calculated “size” of photon – Planck’s constant Existence of energy levels/ quantized energy states of electrons De Broglie equation; wavelength of any moving object Schrodinger’s equation; calculates probability of finding electron in a given region (orbital!) within an atom by treating ele ...
... photons Calculated “size” of photon – Planck’s constant Existence of energy levels/ quantized energy states of electrons De Broglie equation; wavelength of any moving object Schrodinger’s equation; calculates probability of finding electron in a given region (orbital!) within an atom by treating ele ...
Lesson7
... of the possible transitions between the states are allowed. The magnitude of the photon energy is not the only criteria • Consideration of things such as the need to conserve quantum spin and orbital angular momentum indicate if the transition is ...
... of the possible transitions between the states are allowed. The magnitude of the photon energy is not the only criteria • Consideration of things such as the need to conserve quantum spin and orbital angular momentum indicate if the transition is ...
Lecture 5. Radiation and energy. 1. The most important aspects of
... an atom. Because the energy levels of an atom are fixed, only certain definite amounts of energy can be absorbed (which is a difference in energy between two energy levels). ...
... an atom. Because the energy levels of an atom are fixed, only certain definite amounts of energy can be absorbed (which is a difference in energy between two energy levels). ...
Atomic Theory and the Periodic Table Atomic Theory and the
... (I.e. we cannot relate it to anything we can measure) However, Ψ2 corresponds to the electron charge density (or in terms of a particle: the probability of finding an electron in a small volume of space). We want to know about the location of the electron so ...
... (I.e. we cannot relate it to anything we can measure) However, Ψ2 corresponds to the electron charge density (or in terms of a particle: the probability of finding an electron in a small volume of space). We want to know about the location of the electron so ...
Advanced Chemistry Midterm
... 69. The half-life of a sample of a radioactive isotope is the time required for half of it to a. become stable b. undergo fission c. decay d. undergo oxidation 70. Which wave property expresses how often a wave oscillates up and down? a. frequency b. amplitude c. wavelength d. speed 71. Quanta are f ...
... 69. The half-life of a sample of a radioactive isotope is the time required for half of it to a. become stable b. undergo fission c. decay d. undergo oxidation 70. Which wave property expresses how often a wave oscillates up and down? a. frequency b. amplitude c. wavelength d. speed 71. Quanta are f ...
Atomic Spectra II
... Measure the wavelengths of these four spectral lines using the method from the diffraction laboratory, recording both color and wavelength. You will need to measure the wavelength for the first and second-order diffraction of each spectral line. quantities in an atom can assume only specific or disc ...
... Measure the wavelengths of these four spectral lines using the method from the diffraction laboratory, recording both color and wavelength. You will need to measure the wavelength for the first and second-order diffraction of each spectral line. quantities in an atom can assume only specific or disc ...
Chemical reaction
... • Solution – a mixture in which one or more substances are uniformly distributed into another • Solute – the substance dissolved in the solution (Sugar) • Solvent – the substance in which the ...
... • Solution – a mixture in which one or more substances are uniformly distributed into another • Solute – the substance dissolved in the solution (Sugar) • Solvent – the substance in which the ...
The p orbital paradox
... The formulation of the paradox begins by assuming that a single electron finds in some point of a lobe at instant t and in another point of the other lobe at some posterior instant t'. Then the paradox arises when trying to unite both points with a trajectory without passing by the nodal plane. It ...
... The formulation of the paradox begins by assuming that a single electron finds in some point of a lobe at instant t and in another point of the other lobe at some posterior instant t'. Then the paradox arises when trying to unite both points with a trajectory without passing by the nodal plane. It ...
10.3 Ligand Field Theory 10.3 Ligand Field Theory
... 10.3.3 Ligand Field Stabilization Energy - ligand field stabilization E (LFSE): difference b/w 1) total E of a coordination complex from ligand field splitting of the orbitals 2)) orbital o b tal E for o the t e sa ...
... 10.3.3 Ligand Field Stabilization Energy - ligand field stabilization E (LFSE): difference b/w 1) total E of a coordination complex from ligand field splitting of the orbitals 2)) orbital o b tal E for o the t e sa ...
Lecture 2 Hamiltonian operators for molecules CHEM6085: Density
... • The Born-Oppenheimer approximation is based on the fact that nuclei have much larger masses than the electrons • To a good approximation, one can solve the Schrödinger equation only for the electrons and assume the nuclei are frozen • We will use this approximation from now on • As a result, our w ...
... • The Born-Oppenheimer approximation is based on the fact that nuclei have much larger masses than the electrons • To a good approximation, one can solve the Schrödinger equation only for the electrons and assume the nuclei are frozen • We will use this approximation from now on • As a result, our w ...
BEC - Triumf
... d. because fuzziness only can be seen if objects are very hot. ans. b They are spread out, but over very small distance. How small depends on weight and temperature of object. room temp electron spread (fuzzed) out over 0.000 000 007 m atom is spread over 0.000 000 000 02 m hockey puck-- spread over ...
... d. because fuzziness only can be seen if objects are very hot. ans. b They are spread out, but over very small distance. How small depends on weight and temperature of object. room temp electron spread (fuzzed) out over 0.000 000 007 m atom is spread over 0.000 000 000 02 m hockey puck-- spread over ...
2nd Semester Chemistry Terms - Glancy 4TH PERIOD PHYSICAL
... 83. Covalent bond- a chemical bond in which atoms are held together by their mutual attraction for two or more electrons they share 84. Covalent compound- an element or chemical compound in which atoms are held together by covalent bonds 85. Molecule- a group of atoms held tightly together by covale ...
... 83. Covalent bond- a chemical bond in which atoms are held together by their mutual attraction for two or more electrons they share 84. Covalent compound- an element or chemical compound in which atoms are held together by covalent bonds 85. Molecule- a group of atoms held tightly together by covale ...
Understanding Electron Spin
... two "poles" will be subject to different fields. Classically one would expect all possible orientations of the dipoles so that a continuous smear would be produced on the photographic plate, but they found that the field separated the beam into two distinct parts, indicating just two possible orien ...
... two "poles" will be subject to different fields. Classically one would expect all possible orientations of the dipoles so that a continuous smear would be produced on the photographic plate, but they found that the field separated the beam into two distinct parts, indicating just two possible orien ...
Answers to Coursebook questions – Chapter J1
... Applied to the inner shell of an atom, the Pauli principle demands that the electrons occupying that state be differentiated in some way. The inner shell has no quantum numbers other than energy, and so the only quantum number that can separate two electrons is the spin. One electron can have spin u ...
... Applied to the inner shell of an atom, the Pauli principle demands that the electrons occupying that state be differentiated in some way. The inner shell has no quantum numbers other than energy, and so the only quantum number that can separate two electrons is the spin. One electron can have spin u ...
water, h2o
... When molecules form the atomic orbitals get re-arranged into new molecular orbitals to satisfy symmetry requirements. The oxygen atom 16O8 has the following atomic orbitals: 2(1s), 2(2s), 4(2p). The s orbitals are of course spherically symmetric, while the p orbitals are of the form: px = sinθ∙cosφ; ...
... When molecules form the atomic orbitals get re-arranged into new molecular orbitals to satisfy symmetry requirements. The oxygen atom 16O8 has the following atomic orbitals: 2(1s), 2(2s), 4(2p). The s orbitals are of course spherically symmetric, while the p orbitals are of the form: px = sinθ∙cosφ; ...
Electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6.Electronic configurations describe electrons as each moving independently in an orbital, in an average field created by all other orbitals. Mathematically, configurations are described by Slater determinants or configuration state functions.According to the laws of quantum mechanics, for systems with only one electron, an energy is associated with each electron configuration and, upon certain conditions, electrons are able to move from one configuration to another by the emission or absorption of a quantum of energy, in the form of a photon.Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements. The concept is also useful for describing the chemical bonds that hold atoms together. In bulk materials, this same idea helps explain the peculiar properties of lasers and semiconductors.