Layer-dependent quantum cooperation of electron and hole states
... The third sentence of the second paragraph should only refer to reference 2, not references 2 and 3. The correct sentence is: ‘It exhibits an extremely large uniaxial positive magnetoresistance with no saturation up to a magnetic field as high as 60 T (ref. 2), which has been attributed to perfect el ...
... The third sentence of the second paragraph should only refer to reference 2, not references 2 and 3. The correct sentence is: ‘It exhibits an extremely large uniaxial positive magnetoresistance with no saturation up to a magnetic field as high as 60 T (ref. 2), which has been attributed to perfect el ...
Blackbody Radiation and Planck`s Hypothesis of Quantized Energy
... Photons and the Photoelectric Effect Classical predictions: 1. Any beam of light of any color can eject electrons if it is intense enough. 2. The maximum kinetic energy of an ejected electron should increase as the intensity increases. Observations: 1. Light must have a certain minimum frequency in ...
... Photons and the Photoelectric Effect Classical predictions: 1. Any beam of light of any color can eject electrons if it is intense enough. 2. The maximum kinetic energy of an ejected electron should increase as the intensity increases. Observations: 1. Light must have a certain minimum frequency in ...
Course Outline Template Word Document - Physics for All
... This course is intended to be a first introduction to quantum phenomena in nature. Quatum Mechanics forms the basis of our description of nature at small scales and a clear understanding of it is required to understand phenomena ranging from atoms and chemical bonding to semiconductors and nuclear p ...
... This course is intended to be a first introduction to quantum phenomena in nature. Quatum Mechanics forms the basis of our description of nature at small scales and a clear understanding of it is required to understand phenomena ranging from atoms and chemical bonding to semiconductors and nuclear p ...
EOC_chapter28
... radiation, the subject with which quantum mechanics began. For a very simple model, consider a solid iron sphere 2.00 cm in radius. Assume that its temperature is always uniform throughout its volume. (a) Find the mass of the sphere. (b) Assume that it is at 20°C and has emissivity 0.860. Find the p ...
... radiation, the subject with which quantum mechanics began. For a very simple model, consider a solid iron sphere 2.00 cm in radius. Assume that its temperature is always uniform throughout its volume. (a) Find the mass of the sphere. (b) Assume that it is at 20°C and has emissivity 0.860. Find the p ...
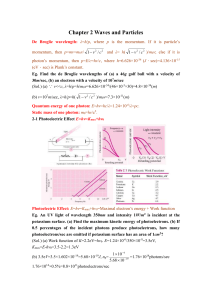
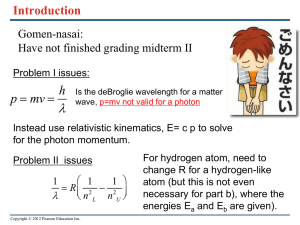
Chapter 2 Waves and Particles De Broglie wavelength: λ=h/p, where
... potassium surface. (a) Find the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons. (b) If 0.5 percentages of the incident photons produce photoelectrons, how many photoelectrons/sec are emitted if potassium surface has an area of 1cm2? (Sol.) (a) Work function of K=2.2eV=hν0. E=1.24×10-6/350×10-9=3.5eV, ...
... potassium surface. (a) Find the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons. (b) If 0.5 percentages of the incident photons produce photoelectrons, how many photoelectrons/sec are emitted if potassium surface has an area of 1cm2? (Sol.) (a) Work function of K=2.2eV=hν0. E=1.24×10-6/350×10-9=3.5eV, ...
k - Marc Madou
... Outside the 3D cube of solid the potential V(x)= and the wave function is zero anywhere outside the solid. This situation applies, for example, to totally free electrons in a metal where the ion cores do not influence their movement. Sommerfeld actually assumed that V(x) outside the conductor e ...
... Outside the 3D cube of solid the potential V(x)= and the wave function is zero anywhere outside the solid. This situation applies, for example, to totally free electrons in a metal where the ion cores do not influence their movement. Sommerfeld actually assumed that V(x) outside the conductor e ...
Chemistry I Syllabus 2011-2012
... relative mass of atoms determined? What does that indicate about the way in which they react? 3. What evidence is there for the existence of electrons and the nucleus? 4. How does the spectrum of hydrogen provide insight into a model of the structure of the atom? 5. How do the ionization energies of ...
... relative mass of atoms determined? What does that indicate about the way in which they react? 3. What evidence is there for the existence of electrons and the nucleus? 4. How does the spectrum of hydrogen provide insight into a model of the structure of the atom? 5. How do the ionization energies of ...
Document
... It will include questions on analysis and evaluation of practical work. Quality of written communication will also be assessed in this section. ...
... It will include questions on analysis and evaluation of practical work. Quality of written communication will also be assessed in this section. ...
Sub Unit Plan 1 Chem Periodic Table
... II.3 Elements can be classified by their properties and located on the Periodic Table as metals, nonmetals, metalloids (B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te), and noble gases. (3.1v) II.4 Elements can be differentiated by their physical properties. Physical properties of substances, such as density, conductivity, ...
... II.3 Elements can be classified by their properties and located on the Periodic Table as metals, nonmetals, metalloids (B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te), and noble gases. (3.1v) II.4 Elements can be differentiated by their physical properties. Physical properties of substances, such as density, conductivity, ...
2.8 M - Thierry Karsenti
... The following list identifies and describes the equipment necessary for all of the activities in this module. The quantities listed are required for each group. 1. Computer (With Internet Access): - A personal computer with word processing and spreadsheet software 2. Periodic Table of Elements: 3. M ...
... The following list identifies and describes the equipment necessary for all of the activities in this module. The quantities listed are required for each group. 1. Computer (With Internet Access): - A personal computer with word processing and spreadsheet software 2. Periodic Table of Elements: 3. M ...
Electronic Structure of Atoms
... quantum-mechanical property called spin. The Pauli exclusion principle states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same four quantum numbers (three for the orbital and one for the spin). Therefore, an orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons. ...
... quantum-mechanical property called spin. The Pauli exclusion principle states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same four quantum numbers (three for the orbital and one for the spin). Therefore, an orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons. ...
Chapter 10
... How do we account for 4 C—H sigma bonds 109o apart? Need to use 4 atomic orbitals — s, px, py, and pz — to form 4 new hybrid orbitals pointing in the correct direction. Dr. S. M. Condren ...
... How do we account for 4 C—H sigma bonds 109o apart? Need to use 4 atomic orbitals — s, px, py, and pz — to form 4 new hybrid orbitals pointing in the correct direction. Dr. S. M. Condren ...
3 Radiation processes 3.1 Atomic and molecular structure
... where re = e2 /me c2 = 2.8 · 10−13 cm is the classical electron radius. In the Coulomb field, the average kinetic energy is equal to the binding energy so that the electron velocity at the i-th level could be estimated as v = αc/i. For hydrogen-like ions, IZ = Z 2 IH , aZ = aH /Z. In all atoms, the ...
... where re = e2 /me c2 = 2.8 · 10−13 cm is the classical electron radius. In the Coulomb field, the average kinetic energy is equal to the binding energy so that the electron velocity at the i-th level could be estimated as v = αc/i. For hydrogen-like ions, IZ = Z 2 IH , aZ = aH /Z. In all atoms, the ...
8th Grade Science: 1st Six Weeks At-A
... periods, to explain how properties are used to classify elements. SCI.8.2D Construct tables, using repeated trials and means, to organize data and identify patterns. SCI.8.2E Analyze data to formulate reasonable explanations, communicate valid conclusions supported by the data, and predict trends. S ...
... periods, to explain how properties are used to classify elements. SCI.8.2D Construct tables, using repeated trials and means, to organize data and identify patterns. SCI.8.2E Analyze data to formulate reasonable explanations, communicate valid conclusions supported by the data, and predict trends. S ...
Electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6.Electronic configurations describe electrons as each moving independently in an orbital, in an average field created by all other orbitals. Mathematically, configurations are described by Slater determinants or configuration state functions.According to the laws of quantum mechanics, for systems with only one electron, an energy is associated with each electron configuration and, upon certain conditions, electrons are able to move from one configuration to another by the emission or absorption of a quantum of energy, in the form of a photon.Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements. The concept is also useful for describing the chemical bonds that hold atoms together. In bulk materials, this same idea helps explain the peculiar properties of lasers and semiconductors.