Lecture 2 - Columbia University
... (3) Understand the Laws leading to the Dalton’s atomic theory of matter: from Laws (observations) to structures Law: A scientific law is a summary of a large number of scientific facts in a compact yet broad and sweeping statement. Law of conservation of mass: Mass is neither created nor destroyed ...
... (3) Understand the Laws leading to the Dalton’s atomic theory of matter: from Laws (observations) to structures Law: A scientific law is a summary of a large number of scientific facts in a compact yet broad and sweeping statement. Law of conservation of mass: Mass is neither created nor destroyed ...
Balancing Chemical Reactions
... chemical reactions then allows one to determine stoichiometry calculations by understanding the ratio between reactants and/or products. This worksheet includes some rules and guidelines to help you balance chemical equations. ...
... chemical reactions then allows one to determine stoichiometry calculations by understanding the ratio between reactants and/or products. This worksheet includes some rules and guidelines to help you balance chemical equations. ...
Chapter 18: The Representative Elements
... configurations ns2np3 (n is the period number) Oxidation states that range from -3 to +5 The metallic character of the group increases down the group ...
... configurations ns2np3 (n is the period number) Oxidation states that range from -3 to +5 The metallic character of the group increases down the group ...
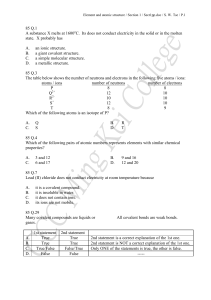
85 Q.1 A substance X melts at 1600oC. Its does
... their atoms have the same number of electron shells. their atoms have the same number of electrons in their outermost shells. their atoms have the same electronic arrangement. ...
... their atoms have the same number of electron shells. their atoms have the same number of electrons in their outermost shells. their atoms have the same electronic arrangement. ...
CH1 Student Revision Guides pdf
... An s orbital can contain two electrons, the px, py and pz orbitals can each hold two electrons making six electrons in all. Topic 1.1(m) Learning Outcome: recall the appropriate s, p and d orbital occupations for elements 1 - 36 (using 'arrows in boxes' or otherwise) and relate these to position in ...
... An s orbital can contain two electrons, the px, py and pz orbitals can each hold two electrons making six electrons in all. Topic 1.1(m) Learning Outcome: recall the appropriate s, p and d orbital occupations for elements 1 - 36 (using 'arrows in boxes' or otherwise) and relate these to position in ...
Chap. 4 AQUEOUS RXNS O
... 6. The sum of all O.N. in a neutral compound is 0, otherwise ΣO.N. = ion charge ...
... 6. The sum of all O.N. in a neutral compound is 0, otherwise ΣO.N. = ion charge ...
Chapter 6 Collisions of Charged Particles
... to develop this aspect of electromagnetic interactions in enough detail for many practical purposes. The first factor is that the details of atomic structure become far less influential in collisions at energies much higher than the binding energies of atoms (which is about ten ...
... to develop this aspect of electromagnetic interactions in enough detail for many practical purposes. The first factor is that the details of atomic structure become far less influential in collisions at energies much higher than the binding energies of atoms (which is about ten ...
Chapter 3
... indicates indicates the element indicates 4 O atoms hydrogen (H) 3 H atoms indicates the element phosphorous (P) ...
... indicates indicates the element indicates 4 O atoms hydrogen (H) 3 H atoms indicates the element phosphorous (P) ...
doc: Oxidation Numbers
... Oxidation Numbers It is often useful to follow chemical reactions by looking at changes in the oxidation numbers of the atoms in each compound during the reaction. Oxidation numbers also play an important role in the naming of chemical compounds. By definition, the oxidation number of an atom is the ...
... Oxidation Numbers It is often useful to follow chemical reactions by looking at changes in the oxidation numbers of the atoms in each compound during the reaction. Oxidation numbers also play an important role in the naming of chemical compounds. By definition, the oxidation number of an atom is the ...
From a few to many electrons in quantum dots under strong
... Due to the growing interest in solid-state nanostructures, driven by basic research and potential technological considerations, two-dimensional 共2D兲 N-electron semiconductor quantum dots 共QDs兲 in field-free conditions and under applied magnetic fields 共B兲 have been extensively studied in the last fe ...
... Due to the growing interest in solid-state nanostructures, driven by basic research and potential technological considerations, two-dimensional 共2D兲 N-electron semiconductor quantum dots 共QDs兲 in field-free conditions and under applied magnetic fields 共B兲 have been extensively studied in the last fe ...
Sections 4 - Columbia Physics
... 2. Tritium, 3 H, is highly radioactive and decays with a half-life of 12.3 years to 3 He by the emission of an electron and an electron anti-neutrino from its nucleus. The electron’s average kinetic energy is 5.7 keV. Explain why its departure can be treated as sudden in the sense that the electron ...
... 2. Tritium, 3 H, is highly radioactive and decays with a half-life of 12.3 years to 3 He by the emission of an electron and an electron anti-neutrino from its nucleus. The electron’s average kinetic energy is 5.7 keV. Explain why its departure can be treated as sudden in the sense that the electron ...
High-order impulse approximation for calculating pulsed-field recombination F. Robicheaux
... The classical and quantum angular momentum distribution after the electric-field pulse are plotted in Fig. 2; the distribution is only for the part of the packet with energy less than 3.4 cm21 below threshold. The quantum distribution is plotted for the first-order impulse approximation, Dz50 and d ...
... The classical and quantum angular momentum distribution after the electric-field pulse are plotted in Fig. 2; the distribution is only for the part of the packet with energy less than 3.4 cm21 below threshold. The quantum distribution is plotted for the first-order impulse approximation, Dz50 and d ...
Electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6.Electronic configurations describe electrons as each moving independently in an orbital, in an average field created by all other orbitals. Mathematically, configurations are described by Slater determinants or configuration state functions.According to the laws of quantum mechanics, for systems with only one electron, an energy is associated with each electron configuration and, upon certain conditions, electrons are able to move from one configuration to another by the emission or absorption of a quantum of energy, in the form of a photon.Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements. The concept is also useful for describing the chemical bonds that hold atoms together. In bulk materials, this same idea helps explain the peculiar properties of lasers and semiconductors.