Molecular Quadratic Response Properties with Inclusion of Relativity Johan Henriksson
... This thesis concerns quadratic response properties and their application to properties in Jablonski diagrams such as resonant two-photon absorption and excited state absorption. Our main interest lies in optical power limiting applications, and in this context, molecules containing heavy metal atoms ...
... This thesis concerns quadratic response properties and their application to properties in Jablonski diagrams such as resonant two-photon absorption and excited state absorption. Our main interest lies in optical power limiting applications, and in this context, molecules containing heavy metal atoms ...
The Physics of Metal Clusters - Nano
... molecules and too small to resemble small pieces of crystals. Clusters, generally, do not have the same structure or atomic arrangement as a bulk solid. Clusters can change their structure with the addition of just 1 or a few atoms, while the addition of new atoms does not change the structure of bu ...
... molecules and too small to resemble small pieces of crystals. Clusters, generally, do not have the same structure or atomic arrangement as a bulk solid. Clusters can change their structure with the addition of just 1 or a few atoms, while the addition of new atoms does not change the structure of bu ...
Final Exam Review Notes
... Some numbers are very large or very small difficult to express. For example, Avogadro’s number = 602,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 an electron’s mass = 0.000 000 000 000 000 000 000 000 000 91 kg Also, it's not clear how many sig figs there are in some measurements. For example, Express 100.0 g to 3 ...
... Some numbers are very large or very small difficult to express. For example, Avogadro’s number = 602,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 an electron’s mass = 0.000 000 000 000 000 000 000 000 000 91 kg Also, it's not clear how many sig figs there are in some measurements. For example, Express 100.0 g to 3 ...
10/18/11 - Note: Once it is downloaded, click SET
... What’s involved? Periodic table, electron, atomic number Electrons are arranged in orbitals around the nucleus Things to know: -Hund’s Rule, Aufbau Principle, Pauli’s Exclusion Principle -Electron Dot- shows how many valence electrons it has. -SPDF (orbitals) S- 1- up to 2 electrons P- 3- up to 6 el ...
... What’s involved? Periodic table, electron, atomic number Electrons are arranged in orbitals around the nucleus Things to know: -Hund’s Rule, Aufbau Principle, Pauli’s Exclusion Principle -Electron Dot- shows how many valence electrons it has. -SPDF (orbitals) S- 1- up to 2 electrons P- 3- up to 6 el ...
Atomic Theory - Relativistic quantum dynamics of ions and beams
... Requires good physical intuition, or this is often at least benefitial. ...
... Requires good physical intuition, or this is often at least benefitial. ...
Spin effects in semiconductor quantum dot structures
... con4ned by two-dimensional (2D) harmonic potential, and the high-spin state is favored by exchange interaction. In this paper we use a vertical quantum dot to study the spin e ects for the simplest system, i.e., a state made out of two electrons. The spin state is then either a singlet or a triplet. ...
... con4ned by two-dimensional (2D) harmonic potential, and the high-spin state is favored by exchange interaction. In this paper we use a vertical quantum dot to study the spin e ects for the simplest system, i.e., a state made out of two electrons. The spin state is then either a singlet or a triplet. ...
DC TRANSFORMER AND DC JOSEPHSON(-LIKE) EFFECTS IN QUANTUM HALL BILAYERS
... Since the vortex motion is now parallel rather than perpendicular to the current, the (Hall) voltage drop is perpendicular to the current and the flow is dissipationless. Moving the magnetic field away from the point which gives filling factor ν exactly unity introduces extra vortices (or antivortic ...
... Since the vortex motion is now parallel rather than perpendicular to the current, the (Hall) voltage drop is perpendicular to the current and the flow is dissipationless. Moving the magnetic field away from the point which gives filling factor ν exactly unity introduces extra vortices (or antivortic ...
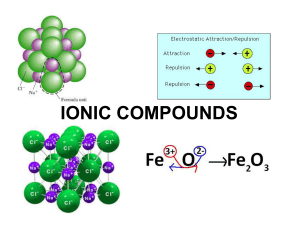
Section 8.3 Names and Formulas of Ionic Compounds Formula Unit
... two different elements (one metallic cation and one nonmetallic anion). ...
... two different elements (one metallic cation and one nonmetallic anion). ...
Balancing Chemical Equations – A Primer
... You may observe that the suffix endings of the compound names end in either ITE or ATE. This occurs when there are two polyatomics with a different charge or bonding configuration of the “same” compound. For example, there is NO2 nitrite and NO3 nitrate. The lesser on is ITE and the larger one is AT ...
... You may observe that the suffix endings of the compound names end in either ITE or ATE. This occurs when there are two polyatomics with a different charge or bonding configuration of the “same” compound. For example, there is NO2 nitrite and NO3 nitrate. The lesser on is ITE and the larger one is AT ...
Effect of size and dimensionality on the magnetic moment of
... chain increases, the broadening of the levels reduces the difference in s-d mixing between odd and even atom chains. Thus, one witnesses the disappearance of the quantum size effect. The results in Fig. 2 can also be used to answer another important question concerning the adequacy of modeling infin ...
... chain increases, the broadening of the levels reduces the difference in s-d mixing between odd and even atom chains. Thus, one witnesses the disappearance of the quantum size effect. The results in Fig. 2 can also be used to answer another important question concerning the adequacy of modeling infin ...
BASIC IDEAS of QUANTUM MECHANICS I. QUANTUM STATES
... As a concrete set of ideas, and a philosophical view, it really began with Newtonian mechanics (although it is not clear what Newton would have thought of it - he perhaps took a far more provisional attitude to his work than others later did). Here is will often give another name to this philosophic ...
... As a concrete set of ideas, and a philosophical view, it really began with Newtonian mechanics (although it is not clear what Newton would have thought of it - he perhaps took a far more provisional attitude to his work than others later did). Here is will often give another name to this philosophic ...
Chapter 7
... • Ionic solutions and molten ionic compounds conduct electricity. • Ions are charged and so they can conduct electricity very well. • When a voltage is applied the cation migrates to the negative electrode and the anion towards the positive one, thus creating a current. ...
... • Ionic solutions and molten ionic compounds conduct electricity. • Ions are charged and so they can conduct electricity very well. • When a voltage is applied the cation migrates to the negative electrode and the anion towards the positive one, thus creating a current. ...
MU08-CHAPTER6.doc
... that especially arouse our curiosity. These constants never have been given any plausible explanation, instead been surrounded by an aurora of mysticism, entities of matter regarded as being of supernatural nature, not possible to be explain in a rational way. One also are taking about “hidden param ...
... that especially arouse our curiosity. These constants never have been given any plausible explanation, instead been surrounded by an aurora of mysticism, entities of matter regarded as being of supernatural nature, not possible to be explain in a rational way. One also are taking about “hidden param ...
Effective electron-atom interactions and virial coefficients in alkali
... G; denotes the Green’s function of two non-interacting particles. In the low-density limit (which is considered throughout this paper), the general interaction kernel K is given by the interaction potential V and from (2.2) the following ladder equation is ...
... G; denotes the Green’s function of two non-interacting particles. In the low-density limit (which is considered throughout this paper), the general interaction kernel K is given by the interaction potential V and from (2.2) the following ladder equation is ...
DFT - ermes@unt
... treat exactly - independent electrons approximations To appreciate the origin of this point of view, it is helpful to separate the different Coulombic contributions (classical and interacting) to the description of the electronic system ...
... treat exactly - independent electrons approximations To appreciate the origin of this point of view, it is helpful to separate the different Coulombic contributions (classical and interacting) to the description of the electronic system ...
IB Chemistry Review. Unit I. Topics 2
... 16. The element that has a valence configuration of 4s is _________. 17. Which of the following elements has a ground-state electron configuration different from the predicted one? 18. How many different principal quantum numbers can be found in the ground state electron configuration of nickel? 19. ...
... 16. The element that has a valence configuration of 4s is _________. 17. Which of the following elements has a ground-state electron configuration different from the predicted one? 18. How many different principal quantum numbers can be found in the ground state electron configuration of nickel? 19. ...
Atomic orbital
An atomic orbital is a mathematical function that describes the wave-like behavior of either one electron or a pair of electrons in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus. The term may also refer to the physical region or space where the electron can be calculated to be present, as defined by the particular mathematical form of the orbital.Each orbital in an atom is characterized by a unique set of values of the three quantum numbers n, ℓ, and m, which respectively correspond to the electron's energy, angular momentum, and an angular momentum vector component (the magnetic quantum number). Any orbital can be occupied by a maximum of two electrons, each with its own spin quantum number. The simple names s orbital, p orbital, d orbital and f orbital refer to orbitals with angular momentum quantum number ℓ = 0, 1, 2 and 3 respectively. These names, together with the value of n, are used to describe the electron configurations of atoms. They are derived from the description by early spectroscopists of certain series of alkali metal spectroscopic lines as sharp, principal, diffuse, and fundamental. Orbitals for ℓ > 3 continue alphabetically, omitting j (g, h, i, k, …).Atomic orbitals are the basic building blocks of the atomic orbital model (alternatively known as the electron cloud or wave mechanics model), a modern framework for visualizing the submicroscopic behavior of electrons in matter. In this model the electron cloud of a multi-electron atom may be seen as being built up (in approximation) in an electron configuration that is a product of simpler hydrogen-like atomic orbitals. The repeating periodicity of the blocks of 2, 6, 10, and 14 elements within sections of the periodic table arises naturally from the total number of electrons that occupy a complete set of s, p, d and f atomic orbitals, respectively.