IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE)
... controlled by the two gate potentials applied on either sides of the channel is calculated using the eigenenergies obtained by solving 1D time-independent Schrodinger equation for the potential profile in the channel. The various device characteristics comprising drain characteristics (I D-VDS), tra ...
... controlled by the two gate potentials applied on either sides of the channel is calculated using the eigenenergies obtained by solving 1D time-independent Schrodinger equation for the potential profile in the channel. The various device characteristics comprising drain characteristics (I D-VDS), tra ...
KHOA: HÓA HỌC - CCS - Trường Đại học Sư phạm Hà Nội
... throughout a given sample and from one sample to another. A chemical element is a substance comprised of a single type of atom. The elements are the building blocks of our nature. An element is either discovered in nature or synthesized in the laboratory in pure form that cannot be separated into s ...
... throughout a given sample and from one sample to another. A chemical element is a substance comprised of a single type of atom. The elements are the building blocks of our nature. An element is either discovered in nature or synthesized in the laboratory in pure form that cannot be separated into s ...
H - Quantum Condensed Matter Research Group
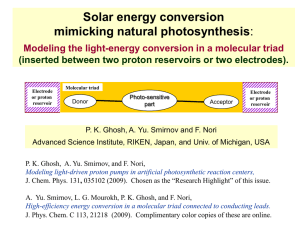
... J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 21218 (2009). Complimentary color copies of these are online. ...
... J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 21218 (2009). Complimentary color copies of these are online. ...
Thermochemistry Energy Energy is defined as the ability to do work
... Although we cannot measure the absolute state of a system, we can measure changes in the state of the system in a relative way, by measuring the work and the heat that takes place during a chemical change. As U is a function of the state of the system, it does not depend on the way the state of the ...
... Although we cannot measure the absolute state of a system, we can measure changes in the state of the system in a relative way, by measuring the work and the heat that takes place during a chemical change. As U is a function of the state of the system, it does not depend on the way the state of the ...
Photosynthesis - Quantum Condensed Matter Research Group
... • Our study models the physics in artificial photosynthesis. • (i) The numerical solutions of the coupled master equations and Langevin equation allows predictions for the quantum yield and its dependence on the surrounding medium, intrinsic properties of the donor, acceptor, photo-sensitive group, ...
... • Our study models the physics in artificial photosynthesis. • (i) The numerical solutions of the coupled master equations and Langevin equation allows predictions for the quantum yield and its dependence on the surrounding medium, intrinsic properties of the donor, acceptor, photo-sensitive group, ...
On the Convergence of Atomic Charges with the Size of the
... protonation states of acid and basic residues are predicted by using the PROPKA program27 and all titratable residues are modeled in the natural protonation states. The hydrogen-bonding environment of all histidine residues is checked in order to account for the possible hydrogen bonds surrounding t ...
... protonation states of acid and basic residues are predicted by using the PROPKA program27 and all titratable residues are modeled in the natural protonation states. The hydrogen-bonding environment of all histidine residues is checked in order to account for the possible hydrogen bonds surrounding t ...
Chemistry 11 – Course Review
... Element “X” is composed of the following naturally occurring isotopes: Isotope ...
... Element “X” is composed of the following naturally occurring isotopes: Isotope ...
Comprehensive analysis of electron correlations in
... those of a two-electron atom? In what way is the description to be modified for doubly excited states of a many-electron atom? Second, can one make the next step to understand the correlation of triply excited states? Both questions can be addressed by studying the doubly and triply excited states o ...
... those of a two-electron atom? In what way is the description to be modified for doubly excited states of a many-electron atom? Second, can one make the next step to understand the correlation of triply excited states? Both questions can be addressed by studying the doubly and triply excited states o ...
Chemistry 120
... U is a function of the state of the material only, not of the history of the sample or the path taken to prepare the state of the sample. Heat is the transfer of energy between the surroundings and the sample - the symbol for heat is q Work is the result of a force acting over a distance - the symbo ...
... U is a function of the state of the material only, not of the history of the sample or the path taken to prepare the state of the sample. Heat is the transfer of energy between the surroundings and the sample - the symbol for heat is q Work is the result of a force acting over a distance - the symbo ...
Adobe Photoshop PDF - Perimeter Institute
... the rod sags. Ask students to explain why the rod is sagging–typically students will say “force of gravity!” 2. Place the rod on a table. Have two students apply horizontal forces on the ends while you hold the middle in place by applying an opposing horizontal force. The class observes the same s ...
... the rod sags. Ask students to explain why the rod is sagging–typically students will say “force of gravity!” 2. Place the rod on a table. Have two students apply horizontal forces on the ends while you hold the middle in place by applying an opposing horizontal force. The class observes the same s ...
Two-dimensional momentum imaging of Rydberg states using half-cycle pulse ionization
... The final velocity and angular distributions of the electrons were measured by velocity map imaging 关9兴. In this technique, the position of the electrons on the detector only depends on the asymptotic x component and y component of the velocity of the electrons. The instrument’s design includes an i ...
... The final velocity and angular distributions of the electrons were measured by velocity map imaging 关9兴. In this technique, the position of the electrons on the detector only depends on the asymptotic x component and y component of the velocity of the electrons. The instrument’s design includes an i ...
Above-threshold ionization in a strong dc electric field
... had the same total energy and the same spatial distribution as the initial quantum state. The classical equations of motion were then solved with the IR field first ramped on and then ramped back off. This gave results that have almost no similarity to the experiment. First, the classical calculatio ...
... had the same total energy and the same spatial distribution as the initial quantum state. The classical equations of motion were then solved with the IR field first ramped on and then ramped back off. This gave results that have almost no similarity to the experiment. First, the classical calculatio ...
Magnetic-Field-Induced Kondo Effects in Coulomb Blockade Systems
... into a Fermi sea of itinerant electrons. These electrons are provided by the leads attached to the dot. The orbital mixing in the case of quantum dot corresponds to the electron tunneling through the junctions connecting the dot with leads. Voltage Vg applied to a gate – an electrode coupled to the ...
... into a Fermi sea of itinerant electrons. These electrons are provided by the leads attached to the dot. The orbital mixing in the case of quantum dot corresponds to the electron tunneling through the junctions connecting the dot with leads. Voltage Vg applied to a gate – an electrode coupled to the ...
Has the Periodic Table Been Successfully Axiomatized?
... In fact, at no point in the evolution of Mendeleev’s periodic tables, over half of which were published,8 did Mendeleev ever adopt such a view (van Spronsen, 1969). If one considers the group of alkali metals, for example, and one asks the question of how many elements occur before the repetition of ...
... In fact, at no point in the evolution of Mendeleev’s periodic tables, over half of which were published,8 did Mendeleev ever adopt such a view (van Spronsen, 1969). If one considers the group of alkali metals, for example, and one asks the question of how many elements occur before the repetition of ...
Atomic orbital
An atomic orbital is a mathematical function that describes the wave-like behavior of either one electron or a pair of electrons in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus. The term may also refer to the physical region or space where the electron can be calculated to be present, as defined by the particular mathematical form of the orbital.Each orbital in an atom is characterized by a unique set of values of the three quantum numbers n, ℓ, and m, which respectively correspond to the electron's energy, angular momentum, and an angular momentum vector component (the magnetic quantum number). Any orbital can be occupied by a maximum of two electrons, each with its own spin quantum number. The simple names s orbital, p orbital, d orbital and f orbital refer to orbitals with angular momentum quantum number ℓ = 0, 1, 2 and 3 respectively. These names, together with the value of n, are used to describe the electron configurations of atoms. They are derived from the description by early spectroscopists of certain series of alkali metal spectroscopic lines as sharp, principal, diffuse, and fundamental. Orbitals for ℓ > 3 continue alphabetically, omitting j (g, h, i, k, …).Atomic orbitals are the basic building blocks of the atomic orbital model (alternatively known as the electron cloud or wave mechanics model), a modern framework for visualizing the submicroscopic behavior of electrons in matter. In this model the electron cloud of a multi-electron atom may be seen as being built up (in approximation) in an electron configuration that is a product of simpler hydrogen-like atomic orbitals. The repeating periodicity of the blocks of 2, 6, 10, and 14 elements within sections of the periodic table arises naturally from the total number of electrons that occupy a complete set of s, p, d and f atomic orbitals, respectively.