Deviations from exponential law and Van Hove`s “2t” limit
... The purpose of this paper is to consider the e ects that arise when the coupling constant is small but nonvanishing. This will enable us to give general estimates for deviations from exponential behavior. The paper is organized as follows. We shall rst look, in Section 2, at a simple system: we sum ...
... The purpose of this paper is to consider the e ects that arise when the coupling constant is small but nonvanishing. This will enable us to give general estimates for deviations from exponential behavior. The paper is organized as follows. We shall rst look, in Section 2, at a simple system: we sum ...
BTEC National in Applied Science Unit 01 Sample redacted web
... Key term Orbitals – regions where there is a 95% probability of locating an electron. An orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons. ...
... Key term Orbitals – regions where there is a 95% probability of locating an electron. An orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons. ...
Chapter 4 The Two Slit Experiment
... mystery is embodied in the apparent ability of a system to exhibit properties which, from a classical physics point-of-view, are mutually contradictory. We have already touched on one such instance, in which the same physical system can exhibit under different circumstances, either particle or wave- ...
... mystery is embodied in the apparent ability of a system to exhibit properties which, from a classical physics point-of-view, are mutually contradictory. We have already touched on one such instance, in which the same physical system can exhibit under different circumstances, either particle or wave- ...
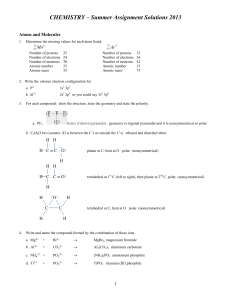
Chemistry - RESONANCE PCCP IDEAL for NTSE, IJSO, Olympiads
... Mol wt. or At. wt No. of electrons lost or gained by one molecule of the substance ...
... Mol wt. or At. wt No. of electrons lost or gained by one molecule of the substance ...
NeuroQuantology Journal
... occurred as suddenly I could no longer see as I was now in total darkness and I felt as if I were cut off from all of the other people in the room. It was as if I was now inside of a very dark cave, aand I could hear all the people in the room but they were outside of the cave. So I thought why don’ ...
... occurred as suddenly I could no longer see as I was now in total darkness and I felt as if I were cut off from all of the other people in the room. It was as if I was now inside of a very dark cave, aand I could hear all the people in the room but they were outside of the cave. So I thought why don’ ...
Supercatalysis by superexchange
... with certainty because they must be extracted from a nearinfinite set of plausible alternatives. Complicating matters still further, each individual molecular trajectory involves random changes of atomic and electronic configurations that occur on vastly different time scales. Even with modern computer ...
... with certainty because they must be extracted from a nearinfinite set of plausible alternatives. Complicating matters still further, each individual molecular trajectory involves random changes of atomic and electronic configurations that occur on vastly different time scales. Even with modern computer ...
Lecture Notes Chapters 1-7
... material is transparent or not to visible light, whether the electrons are (locally) magnetically polarised, and so on. But after this basic landscape is determined, many further phenomena develop on energy scales measured in meV that correspond to thermal energies at room temperature and below. The ...
... material is transparent or not to visible light, whether the electrons are (locally) magnetically polarised, and so on. But after this basic landscape is determined, many further phenomena develop on energy scales measured in meV that correspond to thermal energies at room temperature and below. The ...
Hydrogen Atom.
... include the components of two three-vectors: the angular momentum vector and the Laplace-Runge-Lenz vector. When the dynamical symmetry is broken, as in the case of the KleinGordon equation, the classical orbit is a precessing ellipse and the bound states with a given principle quantum number N are ...
... include the components of two three-vectors: the angular momentum vector and the Laplace-Runge-Lenz vector. When the dynamical symmetry is broken, as in the case of the KleinGordon equation, the classical orbit is a precessing ellipse and the bound states with a given principle quantum number N are ...
IGCSE Revision Question Booklet Mark Scheme
... 14.(a) ideas that hydrogen is in a group / is with the halogens only seven groups / no group O / no noble gases / fewer elements halogens are in the first group / Group 1 other elements are in one group higher (or example) modern table only has two elements in the top row / period modern ...
... 14.(a) ideas that hydrogen is in a group / is with the halogens only seven groups / no group O / no noble gases / fewer elements halogens are in the first group / Group 1 other elements are in one group higher (or example) modern table only has two elements in the top row / period modern ...
Free Energies of Cavity and Noncavity Hydrated Electrons at the
... theoretical results have suggested that interfacial hydrated ...
... theoretical results have suggested that interfacial hydrated ...
Elementary Quantum Mechanics
... Quantum mechanics is a mathematical formalism, which, on the basis of knowledge of the state of a system, at a given time, allows the calculation of the state of the system at a later time, so that the result of experiments can be predicted. In quantum mechanics, the state of a particle is described ...
... Quantum mechanics is a mathematical formalism, which, on the basis of knowledge of the state of a system, at a given time, allows the calculation of the state of the system at a later time, so that the result of experiments can be predicted. In quantum mechanics, the state of a particle is described ...
Document
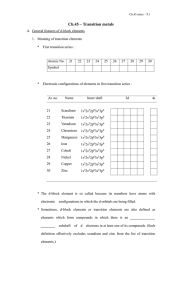
... series, the atomic radii actually ____________again. At the beginning of the series, the increase in __________ _______________ with atomic number pulls in the electron cloud, resulting in a reduction of atomic size. Since electrons are added to an inner d subshell across the series, this adds to th ...
... series, the atomic radii actually ____________again. At the beginning of the series, the increase in __________ _______________ with atomic number pulls in the electron cloud, resulting in a reduction of atomic size. Since electrons are added to an inner d subshell across the series, this adds to th ...
Atomic orbital
An atomic orbital is a mathematical function that describes the wave-like behavior of either one electron or a pair of electrons in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus. The term may also refer to the physical region or space where the electron can be calculated to be present, as defined by the particular mathematical form of the orbital.Each orbital in an atom is characterized by a unique set of values of the three quantum numbers n, ℓ, and m, which respectively correspond to the electron's energy, angular momentum, and an angular momentum vector component (the magnetic quantum number). Any orbital can be occupied by a maximum of two electrons, each with its own spin quantum number. The simple names s orbital, p orbital, d orbital and f orbital refer to orbitals with angular momentum quantum number ℓ = 0, 1, 2 and 3 respectively. These names, together with the value of n, are used to describe the electron configurations of atoms. They are derived from the description by early spectroscopists of certain series of alkali metal spectroscopic lines as sharp, principal, diffuse, and fundamental. Orbitals for ℓ > 3 continue alphabetically, omitting j (g, h, i, k, …).Atomic orbitals are the basic building blocks of the atomic orbital model (alternatively known as the electron cloud or wave mechanics model), a modern framework for visualizing the submicroscopic behavior of electrons in matter. In this model the electron cloud of a multi-electron atom may be seen as being built up (in approximation) in an electron configuration that is a product of simpler hydrogen-like atomic orbitals. The repeating periodicity of the blocks of 2, 6, 10, and 14 elements within sections of the periodic table arises naturally from the total number of electrons that occupy a complete set of s, p, d and f atomic orbitals, respectively.