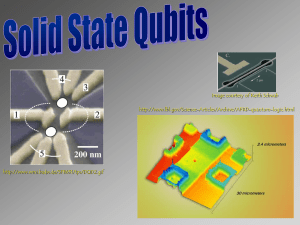
Mean-field theory of the Kondo effect in quantum dots with... Mikio Eto and Yuli V. Nazarov
... dots has attracted a lot of interest.1–5 In a quantum dot, the number of electrons N is fixed by the Coulomb blockade to integer values and can be tuned by the gate voltage. Usually the discrete spin-degenerate levels in the quantum dot are consecutively occupied, and the total spin is zero or 1/2 f ...
... dots has attracted a lot of interest.1–5 In a quantum dot, the number of electrons N is fixed by the Coulomb blockade to integer values and can be tuned by the gate voltage. Usually the discrete spin-degenerate levels in the quantum dot are consecutively occupied, and the total spin is zero or 1/2 f ...
Five Lecture Course on Basic Physics of
... • It is important that at such low temperatures a superconductor can be considered to be a single large quantum particle or molecule which is characterized by a single (BCS) wave function. • A huge amount of electrons is incorporated into a single quantum state. This is not possible for normal elect ...
... • It is important that at such low temperatures a superconductor can be considered to be a single large quantum particle or molecule which is characterized by a single (BCS) wave function. • A huge amount of electrons is incorporated into a single quantum state. This is not possible for normal elect ...
The role of electronic symmetry in charge-transfer-to
... SH兲 algorithm of Prezhdo and Rossky23 for these calculations. This method is essentially an amalgam of mean-field dynamics24 and the Tully fewest-switches surface-hopping method.25 Although the MF/SH methodology has not been as widely used as the molecular dynamics with electronic transitions 共MDET兲 ...
... SH兲 algorithm of Prezhdo and Rossky23 for these calculations. This method is essentially an amalgam of mean-field dynamics24 and the Tully fewest-switches surface-hopping method.25 Although the MF/SH methodology has not been as widely used as the molecular dynamics with electronic transitions 共MDET兲 ...
The Impact of Energy Band Diagram and Inhomogeneous
... maximize the electron-state filling term, the laser should operate close to transparency. This can be achieved by increasing the waveguide confinement factor and/or the QD coverage. Alternatively, reduced inversion levels may be achieved by long cavities but this increases the photon lifetime which ...
... maximize the electron-state filling term, the laser should operate close to transparency. This can be achieved by increasing the waveguide confinement factor and/or the QD coverage. Alternatively, reduced inversion levels may be achieved by long cavities but this increases the photon lifetime which ...
info
... All electronic structure and geometry optimization calculations were performed using Gaussian-9441 on an SGI Origin 200 workstation at the Université de Bourgogne and on both an Alpha Digital and an SGI Indigo 2 in Pisa. The threeparameter form of the Becke, Lee, Yang, and Parr functional (B3LYP),4 ...
... All electronic structure and geometry optimization calculations were performed using Gaussian-9441 on an SGI Origin 200 workstation at the Université de Bourgogne and on both an Alpha Digital and an SGI Indigo 2 in Pisa. The threeparameter form of the Becke, Lee, Yang, and Parr functional (B3LYP),4 ...
General Green`s-function formalism for transport
... magnetoconductance and GMR are found to be oscillatory functions of the nonmagnetic layer thickness5 with periods extending over several atomic planes. This is due to a periodic switching of the exchange coupling from ferromagnetic to antiferromagnetic, as a function of a spacer layer thickness. In ...
... magnetoconductance and GMR are found to be oscillatory functions of the nonmagnetic layer thickness5 with periods extending over several atomic planes. This is due to a periodic switching of the exchange coupling from ferromagnetic to antiferromagnetic, as a function of a spacer layer thickness. In ...
A Bird`s-Eye View of Density-Functional Theory
... One sometimes says that T̂ and Û are ‘universal’, while V̂ is systemdependent, or ‘nonuniversal’. We will come back to this terminology. A simple estimate of the computational complexity of this task is to imagine a real-space representation of Ψ on a mesh, in which each coordinate is discretized b ...
... One sometimes says that T̂ and Û are ‘universal’, while V̂ is systemdependent, or ‘nonuniversal’. We will come back to this terminology. A simple estimate of the computational complexity of this task is to imagine a real-space representation of Ψ on a mesh, in which each coordinate is discretized b ...
The theoretical impact polarization of the OI 6300 ˚A red line of Earth
... at that moment, following the impact polarization theory known at that time where only the case of a permitted line had ben treated. The behavior of the impact polarization as a function of energy has common features between the different elements, as it can be seen in Fig. 4 of Bommier (2006) and i ...
... at that moment, following the impact polarization theory known at that time where only the case of a permitted line had ben treated. The behavior of the impact polarization as a function of energy has common features between the different elements, as it can be seen in Fig. 4 of Bommier (2006) and i ...
Structure and transport properties of atomic chains and molecules
... Kondo effects become dominant. This demonstrates that the current description of the semiconductor based electronic devices in terms of semi-classical physics will no longer apply at such small scales [12, 13, 14]. Nano sized contacts require a new framework of ideas, representing an important scien ...
... Kondo effects become dominant. This demonstrates that the current description of the semiconductor based electronic devices in terms of semi-classical physics will no longer apply at such small scales [12, 13, 14]. Nano sized contacts require a new framework of ideas, representing an important scien ...
Chapter 8: Ionic Compounds
... Reactivity of metals is based on the ease with which they lose valence electrons to achieve a stable octet, or noble gas configuration. Group 1A elements, [noble gas]ns1, lose their one valence electron, forming an ion with a 1+ charge. Group 2A elements, [noble gas]ns2, lose their two valence elect ...
... Reactivity of metals is based on the ease with which they lose valence electrons to achieve a stable octet, or noble gas configuration. Group 1A elements, [noble gas]ns1, lose their one valence electron, forming an ion with a 1+ charge. Group 2A elements, [noble gas]ns2, lose their two valence elect ...
TOPIC 12. THE ELEMENTS
... Many nuclear diagnostic procedures rely on using artificially produced atoms that originate from nuclear reactors such as that at Lucas Heights in Sydney. An irreplaceable gas with vital applications in magnetic resonance imaging machines is used and lost - filling party balloons! An object made fro ...
... Many nuclear diagnostic procedures rely on using artificially produced atoms that originate from nuclear reactors such as that at Lucas Heights in Sydney. An irreplaceable gas with vital applications in magnetic resonance imaging machines is used and lost - filling party balloons! An object made fro ...
Atomic orbital
An atomic orbital is a mathematical function that describes the wave-like behavior of either one electron or a pair of electrons in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus. The term may also refer to the physical region or space where the electron can be calculated to be present, as defined by the particular mathematical form of the orbital.Each orbital in an atom is characterized by a unique set of values of the three quantum numbers n, ℓ, and m, which respectively correspond to the electron's energy, angular momentum, and an angular momentum vector component (the magnetic quantum number). Any orbital can be occupied by a maximum of two electrons, each with its own spin quantum number. The simple names s orbital, p orbital, d orbital and f orbital refer to orbitals with angular momentum quantum number ℓ = 0, 1, 2 and 3 respectively. These names, together with the value of n, are used to describe the electron configurations of atoms. They are derived from the description by early spectroscopists of certain series of alkali metal spectroscopic lines as sharp, principal, diffuse, and fundamental. Orbitals for ℓ > 3 continue alphabetically, omitting j (g, h, i, k, …).Atomic orbitals are the basic building blocks of the atomic orbital model (alternatively known as the electron cloud or wave mechanics model), a modern framework for visualizing the submicroscopic behavior of electrons in matter. In this model the electron cloud of a multi-electron atom may be seen as being built up (in approximation) in an electron configuration that is a product of simpler hydrogen-like atomic orbitals. The repeating periodicity of the blocks of 2, 6, 10, and 14 elements within sections of the periodic table arises naturally from the total number of electrons that occupy a complete set of s, p, d and f atomic orbitals, respectively.