spin exchange optical pumping of neon and its applications
... magnetic fields. This fascination only increased with the birth of modern electronics. However the reach of magnetism extends well beyond that of electronics. The duality of the theory of magnetism and electricity proved to be a fundamental realization when special relativity was utilized to unify t ...
... magnetic fields. This fascination only increased with the birth of modern electronics. However the reach of magnetism extends well beyond that of electronics. The duality of the theory of magnetism and electricity proved to be a fundamental realization when special relativity was utilized to unify t ...
Complete Lecture Notes
... Quantum mechanics was developed in the early part of the 20th century to address the shortcomings of classical mechanics. Quantum mechanics is based on the following: • The state of matter can be described in the form of wavefunctions. • For particles confined to small scales (atomic, molecular) and ...
... Quantum mechanics was developed in the early part of the 20th century to address the shortcomings of classical mechanics. Quantum mechanics is based on the following: • The state of matter can be described in the form of wavefunctions. • For particles confined to small scales (atomic, molecular) and ...
Spin-orbit coupling effects in two
... that in the whole vectorial space of the two orthogonal vectors |0⟩ and |1⟩ there are only two possible states, no other combinations are allowed. The quantum mechanics provides us physical systems that do not endure this limitation. To distinguish the classical bit from the quantum bit, it has been ...
... that in the whole vectorial space of the two orthogonal vectors |0⟩ and |1⟩ there are only two possible states, no other combinations are allowed. The quantum mechanics provides us physical systems that do not endure this limitation. To distinguish the classical bit from the quantum bit, it has been ...
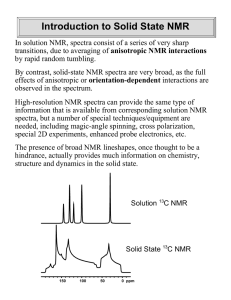
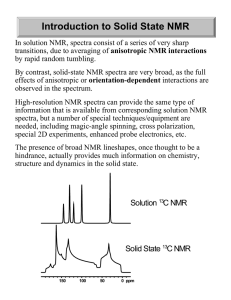
Introduction to Solid State NMR
... Origins of Solid-State NMR Original NMR experiments focused on 1H and 19F NMR, for reasons of sensitivity. However, anisotropies in the local fields of the protons broadened the 1H NMR spectra such that no spectral lines could be resolved. The only cases where useful spectra could be obtained was f ...
... Origins of Solid-State NMR Original NMR experiments focused on 1H and 19F NMR, for reasons of sensitivity. However, anisotropies in the local fields of the protons broadened the 1H NMR spectra such that no spectral lines could be resolved. The only cases where useful spectra could be obtained was f ...
Solid State NMR
... Origins of Solid-State NMR Original NMR experiments focused on 1H and 19F NMR, for reasons of sensitivity. However, anisotropies in the local fields of the protons broadened the 1H NMR spectra such that no spectral lines could be resolved. The only cases where useful spectra could be obtained was f ...
... Origins of Solid-State NMR Original NMR experiments focused on 1H and 19F NMR, for reasons of sensitivity. However, anisotropies in the local fields of the protons broadened the 1H NMR spectra such that no spectral lines could be resolved. The only cases where useful spectra could be obtained was f ...
Quantum Orders and Symmetric Spin Liquids
... help to guess that FQH liquids should have some internal orders or “patterns”. Different magical filling factors should be due to those different internal “patterns”. However, the hypothesis of internal “patterns” appears to have one difficulty – FQH states are liquids, and how can liquids have any ...
... help to guess that FQH liquids should have some internal orders or “patterns”. Different magical filling factors should be due to those different internal “patterns”. However, the hypothesis of internal “patterns” appears to have one difficulty – FQH states are liquids, and how can liquids have any ...
9 Quantum Phases and Phase Transitions of Mott
... experiments. The purpose of this article is to review recent theoretical work towards achieving this goal. We will focus mainly on the case of two spatial dimensions (d), but our methods and results often have simple generalizations to d = 3. One useful vantage point for opening this discussion is t ...
... experiments. The purpose of this article is to review recent theoretical work towards achieving this goal. We will focus mainly on the case of two spatial dimensions (d), but our methods and results often have simple generalizations to d = 3. One useful vantage point for opening this discussion is t ...
Heisenberg Spin Chains : from Quantum Groups to
... One of the main tasks of statistical mechanics is to understand macroscopic quantities such as specific heat, susceptibility, or transport properties for a fluid or a crystal in terms of microscopic elementary interactions between the constituents which are for example molecules, or ions. A fundamen ...
... One of the main tasks of statistical mechanics is to understand macroscopic quantities such as specific heat, susceptibility, or transport properties for a fluid or a crystal in terms of microscopic elementary interactions between the constituents which are for example molecules, or ions. A fundamen ...