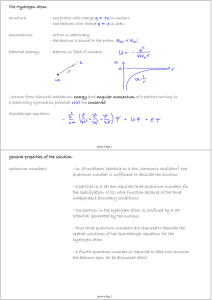
general properties of the solution: quantum numbers:
... - Lz is the component of the angular moment L along the quantization axis z - the quantization axis can be determined by an external magnetic field B pointing in the z-direction for example - ml can take 2 l + 1 different values from -l, …, 0, …, l - note that Lz is never equal to L and therefore ca ...
... - Lz is the component of the angular moment L along the quantization axis z - the quantization axis can be determined by an external magnetic field B pointing in the z-direction for example - ml can take 2 l + 1 different values from -l, …, 0, …, l - note that Lz is never equal to L and therefore ca ...
SPIN-LIQUIDS ON THE KAGOME LATTICE: CHIRAL
... The uniform phase is the ground state of the simple (half-filled) Hubbard model on the Kagome lattice when a magnetic field is applied. Since the Hubbard model is the minimal model describing typical Mott-insulating materials, this is a step towards finding the chiral spin liquid in standard electro ...
... The uniform phase is the ground state of the simple (half-filled) Hubbard model on the Kagome lattice when a magnetic field is applied. Since the Hubbard model is the minimal model describing typical Mott-insulating materials, this is a step towards finding the chiral spin liquid in standard electro ...
MRAM presentation 2010
... • In addition to charge electrons also have an inherent property called spin, either up or down. • In general most matter has equal numbers of spin up and spin down electrons which cancel any effect. • Ferromagnets are materials where there is a net spin. This tendency of electron spins to align wit ...
... • In addition to charge electrons also have an inherent property called spin, either up or down. • In general most matter has equal numbers of spin up and spin down electrons which cancel any effect. • Ferromagnets are materials where there is a net spin. This tendency of electron spins to align wit ...
Electrically induced spin resonance fluorescence. I. Theory
... oscillators, the amplitude of electron oscillations, the effective magnetic field sensed by the electron spin, and the rate at which electrons are injected from an electrode into spin oscillators. We then switch on the interaction between the spin magnetic dipole and the electromagnetic field to fin ...
... oscillators, the amplitude of electron oscillations, the effective magnetic field sensed by the electron spin, and the rate at which electrons are injected from an electrode into spin oscillators. We then switch on the interaction between the spin magnetic dipole and the electromagnetic field to fin ...
General Physics I - University of Rochester
... • Potential energy of the magnetic dipole in magnetic field splits into several levels ...
... • Potential energy of the magnetic dipole in magnetic field splits into several levels ...
Algebraic spin liquid in an exactly solvable spin model
... phases have been proposed, which are distinguished by the character of any gapless spinons and the exchange statistics of the topological “vison” excitations. Since they are new and “exotic” quantum phases of matter, it is desirable to construct solvable models with short range interactions with sta ...
... phases have been proposed, which are distinguished by the character of any gapless spinons and the exchange statistics of the topological “vison” excitations. Since they are new and “exotic” quantum phases of matter, it is desirable to construct solvable models with short range interactions with sta ...