Direct Search of Dark Matter in High
... Elastic scattering cross section One can derive the SI cross section by using the SI effective ...
... Elastic scattering cross section One can derive the SI cross section by using the SI effective ...
Handout
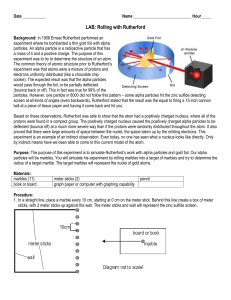
... Based on these observations, Rutherford was able to show that the atom had a positively charged nucleus, where all of the protons were found in a compact group. The positively charged nucleus caused the positively charged alpha particles to be deflected (bounce off) at a much more severe way than if ...
... Based on these observations, Rutherford was able to show that the atom had a positively charged nucleus, where all of the protons were found in a compact group. The positively charged nucleus caused the positively charged alpha particles to be deflected (bounce off) at a much more severe way than if ...
A. Atomic and Nuclear Structure
... force that operates at extremely short distances. The strong nuclear force is believed to result from attractions between even smaller particles (quarks) that compose the neutrons and protons. 3. Electrons The charge of the electron (- 1) is equal in magnitude to the charge of the proton but is nega ...
... force that operates at extremely short distances. The strong nuclear force is believed to result from attractions between even smaller particles (quarks) that compose the neutrons and protons. 3. Electrons The charge of the electron (- 1) is equal in magnitude to the charge of the proton but is nega ...
ppt - JINR
... gluons, light quarks relatively small momentum: pT 1 2 GeV / c make up for most of the multilplicity ...
... gluons, light quarks relatively small momentum: pT 1 2 GeV / c make up for most of the multilplicity ...
ppt
... happening (“if stress is large enough”) Elastic strain: deformation that can disappear in the absence of applied force Plastic strain: permanent deformation accumulated since initial state Total strain: total deformation since initial state Plastic flow: when yield condition is met, how elastic stra ...
... happening (“if stress is large enough”) Elastic strain: deformation that can disappear in the absence of applied force Plastic strain: permanent deformation accumulated since initial state Total strain: total deformation since initial state Plastic flow: when yield condition is met, how elastic stra ...
Unit 1 Atomic Structure, Periodic Properties and Nuclear Chemistry
... 5. Suppose you could grind a sample of the element copper into smaller and smaller particles. The smallest particle that could no longer be divided, yet still has the chemical properties of copper, is the _________________________________________ 6. About how many atoms of copper when placed side by ...
... 5. Suppose you could grind a sample of the element copper into smaller and smaller particles. The smallest particle that could no longer be divided, yet still has the chemical properties of copper, is the _________________________________________ 6. About how many atoms of copper when placed side by ...
Stress-energy tensor and conservation
... Consider a gas composed of weakly or noninteracting identical particles each of mass m that do not form a perfect fluid (e.g. a real gas of atoms whose separation is many times the mean free path). They have a phase space density f (xi , pi ; t) which is the number of particles per unit volume in 3- ...
... Consider a gas composed of weakly or noninteracting identical particles each of mass m that do not form a perfect fluid (e.g. a real gas of atoms whose separation is many times the mean free path). They have a phase space density f (xi , pi ; t) which is the number of particles per unit volume in 3- ...
QCD and Nuclei
... Match to highly sophisticated ‘standard nuclear physics approach’ refined since decades: Weinberg F-corollary “ … it allows one to show in a fairly convincing way that what they've been doing all along is the correct first step in a consistent approximation scheme” ...
... Match to highly sophisticated ‘standard nuclear physics approach’ refined since decades: Weinberg F-corollary “ … it allows one to show in a fairly convincing way that what they've been doing all along is the correct first step in a consistent approximation scheme” ...
Lecture 3.
... resulting ions act as condensation nuclei, around which a mist will form (because the mixture is on the point of condensation). The high energies of alpha and beta particles mean that a trail is left, due to many ions being produced along the path of the charged particle. These tracks have distincti ...
... resulting ions act as condensation nuclei, around which a mist will form (because the mixture is on the point of condensation). The high energies of alpha and beta particles mean that a trail is left, due to many ions being produced along the path of the charged particle. These tracks have distincti ...
Atomic Notes
... • This is because an uncombined atom ALWAYS has the same number of (+) charged protons and (-) charged electrons. • So…the atomic umber also tells us the number of electrons in that atom. Use this to help you remember… ...
... • This is because an uncombined atom ALWAYS has the same number of (+) charged protons and (-) charged electrons. • So…the atomic umber also tells us the number of electrons in that atom. Use this to help you remember… ...
rtnedhistlnkedchp - Churinga Publishing Home Page
... done) and measuring its wavelength to ascertain whether redshift has occurred. If redshift has occurred, the increase of wavelength can only have been caused by transit through space, because the Moon has practically no velocity with respect to Earth. This model allowed the definitions of physics to ...
... done) and measuring its wavelength to ascertain whether redshift has occurred. If redshift has occurred, the increase of wavelength can only have been caused by transit through space, because the Moon has practically no velocity with respect to Earth. This model allowed the definitions of physics to ...
The Higgs Boson - University of Surrey
... which the Lagrangian is invariant under a continuous group of local transformations". The best introduction to the Langrangian in mathematical physics I know of is in Roger Penrose's magisterial "The Road to Reality" (2004). Joseph Lagrange was an Italian nobleman who succeeded Leonhard Euler as Dir ...
... which the Lagrangian is invariant under a continuous group of local transformations". The best introduction to the Langrangian in mathematical physics I know of is in Roger Penrose's magisterial "The Road to Reality" (2004). Joseph Lagrange was an Italian nobleman who succeeded Leonhard Euler as Dir ...
Characterization of Nano Materials using Electron Microscopy
... sample by elastic scattering. BSE are often used in analytical SEM along with the spectra made from the characteristic x-rays. Because the intensity of the BSE signal is strongly related to the atomic number (Z) of the specimen, BSE images can provide information about the distribution of different ...
... sample by elastic scattering. BSE are often used in analytical SEM along with the spectra made from the characteristic x-rays. Because the intensity of the BSE signal is strongly related to the atomic number (Z) of the specimen, BSE images can provide information about the distribution of different ...
Electron scattering

Electron scattering occurs when electrons are deviated from their original trajectory. This is due to the electrostatic forces within matter interaction or, if an external magnetic field is present, the electron may be deflected by the Lorentz force. This scattering typically happens with solids such as metals, semiconductors and insulators; and is a limiting factor in integrated circuits and transistors.The application of electron scattering is such that it can be used as a high resolution microscope for hadronic systems, that allows the measurement of the distribution of charges for nucleons and nuclear structure. The scattering of electrons has allowed us to understand that protons and neutrons are made up of the smaller elementary subatomic particles called quarks.Electrons may be scattered through a solid in several ways:Not at all: no electron scattering occurs at all and the beam passes straight through.Single scattering: when an electron is scattered just once.Plural scattering: when electron(s) scatter several times.Multiple scattering: when electron(s) scatter very many times over.The likelihood of an electron scattering and the proliferance of the scattering is a probability function of the specimen thickness to the mean free path.