Chapter 7 Name Atomic Structure and Periodicity Any day you don`t
... Energy levels available to the hydrogen atom expressed in new energy equation, where “n” correlates to an energy level. ...
... Energy levels available to the hydrogen atom expressed in new energy equation, where “n” correlates to an energy level. ...
Quantum Numbers Primer The quantum numbers
... ml is the magnetic quantum number (ml = -ℓ, …, –2, -1, 0, +1, +2, …, +ℓ) (note: ℓ is lowercase L... it was used here so it is not confused with the number one). ml determines the number and orientation of the orbital. When n = 1, l must be 0. When l = 0, ml = 0. Because ml has only one value (the va ...
... ml is the magnetic quantum number (ml = -ℓ, …, –2, -1, 0, +1, +2, …, +ℓ) (note: ℓ is lowercase L... it was used here so it is not confused with the number one). ml determines the number and orientation of the orbital. When n = 1, l must be 0. When l = 0, ml = 0. Because ml has only one value (the va ...
L - BYU Physics and Astronomy
... angular momentum magnitude l =0,1,2… orbital angular momentum quantum number l=0: “s” orbital in chemistry l=1: “p” orbital in chemistry l=2: “d” orbital in chemistry ...
... angular momentum magnitude l =0,1,2… orbital angular momentum quantum number l=0: “s” orbital in chemistry l=1: “p” orbital in chemistry l=2: “d” orbital in chemistry ...
Quantum Theory
... The emission of _________ from a metal when ______________ on the metal Light had to be a certain ______________ ____for electrons to be emitted Wave theory of light said that _____________ of light should have worked This led to the concept of light as a ___________ ...
... The emission of _________ from a metal when ______________ on the metal Light had to be a certain ______________ ____for electrons to be emitted Wave theory of light said that _____________ of light should have worked This led to the concept of light as a ___________ ...
Particle Interactions - NIU - Northern Illinois University
... Beta Collisions • There are a key differences between betas and heavy ions in matter. – A large fractional energy change – Indistinguishable from e in quantum collision • Bethe formula is modified for betas. ...
... Beta Collisions • There are a key differences between betas and heavy ions in matter. – A large fractional energy change – Indistinguishable from e in quantum collision • Bethe formula is modified for betas. ...
The Standard Model - Stony Brook University
... I is isospin, where the number of particles in a family is 2I + 1 I3 is isospin component, which is related to sequence of a particle in a family, on the interval if (-I, I) ...
... I is isospin, where the number of particles in a family is 2I + 1 I3 is isospin component, which is related to sequence of a particle in a family, on the interval if (-I, I) ...
Course essay - University of Wisconsin–Madison
... Compton scattering • Photons can transfer energy to beam of electrons. • Determined by conservation of momentum, energy. • Compton awarded 1927 Nobel prize for showing that this occurs just as two balls colliding. ...
... Compton scattering • Photons can transfer energy to beam of electrons. • Determined by conservation of momentum, energy. • Compton awarded 1927 Nobel prize for showing that this occurs just as two balls colliding. ...
Modern Model of the Atom
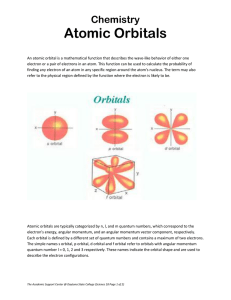
... Do not confuse with orbits! The electrons are NOT “orbiting” the nucleus. We cannot predict the actual location of an electron like we can predict planets orbiting the sun! Different orbital shapes: s, p, d, f (lowest to highest energy) ...
... Do not confuse with orbits! The electrons are NOT “orbiting” the nucleus. We cannot predict the actual location of an electron like we can predict planets orbiting the sun! Different orbital shapes: s, p, d, f (lowest to highest energy) ...
Fundamentals of Atomic Structure
... different elements are different in some fundamental way. Chemical compounds are formed when atoms of different elements combine with each other. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms. Chemical reactions involve reorganization of the atomschanges in the way they ar ...
... different elements are different in some fundamental way. Chemical compounds are formed when atoms of different elements combine with each other. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms. Chemical reactions involve reorganization of the atomschanges in the way they ar ...
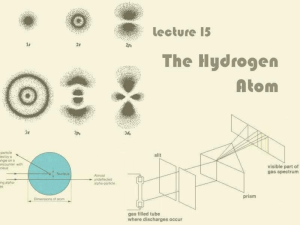
Lecture 15: The Hydrogen Atom
... He proposed that the electrons are embedded in a positively charged ‘pudding’ ...
... He proposed that the electrons are embedded in a positively charged ‘pudding’ ...
4.2 - Science with Mrs. Vaness
... model,” electrons were stuck into a lump of ____________ charge, similar to raisins stuck in dough. – The Rutherford Atomic Model – Based on his experimental results, Rutherford suggested a new theory of the atom. – He proposed that the atom is mostly___________ _________. – He concluded that all th ...
... model,” electrons were stuck into a lump of ____________ charge, similar to raisins stuck in dough. – The Rutherford Atomic Model – Based on his experimental results, Rutherford suggested a new theory of the atom. – He proposed that the atom is mostly___________ _________. – He concluded that all th ...
Chapter 7 Section 1 - School District 27J
... way that would give the maximum number of parallel spins (maximum number of unpaired electrons). Analogy: Students could fill each seat of a school bus, ...
... way that would give the maximum number of parallel spins (maximum number of unpaired electrons). Analogy: Students could fill each seat of a school bus, ...
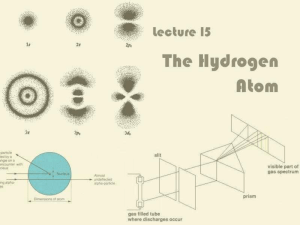
Lecture 15: The Hydrogen Atom
... It only absorbs or emits photons with precisely the right energies dictated by energy conservation ...
... It only absorbs or emits photons with precisely the right energies dictated by energy conservation ...
MSE 221 Quantum Physics of Materials
... Finite Well—Infinite wall, 1D, 3D, separation of variables, harmonic oscillator, ionic bonding, bondenergy diagram Coulomb Potential—Multi-electron atom, Hartree, many atom solid Pauli Principle—Antisymmetric eigenfunctions, covalent bonding in H2, F2, N2, O2, sp3 hydrids, Hund’s rule Molecular Orbi ...
... Finite Well—Infinite wall, 1D, 3D, separation of variables, harmonic oscillator, ionic bonding, bondenergy diagram Coulomb Potential—Multi-electron atom, Hartree, many atom solid Pauli Principle—Antisymmetric eigenfunctions, covalent bonding in H2, F2, N2, O2, sp3 hydrids, Hund’s rule Molecular Orbi ...
Electron scattering

Electron scattering occurs when electrons are deviated from their original trajectory. This is due to the electrostatic forces within matter interaction or, if an external magnetic field is present, the electron may be deflected by the Lorentz force. This scattering typically happens with solids such as metals, semiconductors and insulators; and is a limiting factor in integrated circuits and transistors.The application of electron scattering is such that it can be used as a high resolution microscope for hadronic systems, that allows the measurement of the distribution of charges for nucleons and nuclear structure. The scattering of electrons has allowed us to understand that protons and neutrons are made up of the smaller elementary subatomic particles called quarks.Electrons may be scattered through a solid in several ways:Not at all: no electron scattering occurs at all and the beam passes straight through.Single scattering: when an electron is scattered just once.Plural scattering: when electron(s) scatter several times.Multiple scattering: when electron(s) scatter very many times over.The likelihood of an electron scattering and the proliferance of the scattering is a probability function of the specimen thickness to the mean free path.