Quantum Theory of the Atom
... A. Quantum Mechanical Model is the current description of electrons in atoms. 1. It does not describe the electron’s path around the nucleus ...
... A. Quantum Mechanical Model is the current description of electrons in atoms. 1. It does not describe the electron’s path around the nucleus ...
Quantum ElectroDynamics
... • Random motion does not constitute a current • An applied electric field results in a small drift velocity superimposed on the random motion • This drift gives a net movement of charge – an electric current, I ...
... • Random motion does not constitute a current • An applied electric field results in a small drift velocity superimposed on the random motion • This drift gives a net movement of charge – an electric current, I ...
Lecture 31 April 06. 2016.
... •Atoms are made up with a central nucleus of protons and neutrons surrounded by a number of electrons equal to the number of protons. • The notation we use is 2He4 •2 is the atomic number = number of protons (and electrons) •4 is the mass number = number of protons + neutrons •Note atomic mass is th ...
... •Atoms are made up with a central nucleus of protons and neutrons surrounded by a number of electrons equal to the number of protons. • The notation we use is 2He4 •2 is the atomic number = number of protons (and electrons) •4 is the mass number = number of protons + neutrons •Note atomic mass is th ...
CHAPTER 7: The Quantum-Mechanical Model of the Atom Energy
... Note: d, f and g subshells are little complicated to understand from the picture. Just know about the total number of orbitals (and maximum electron occupancy) in d, f and g subshells (see table 7.2). ...
... Note: d, f and g subshells are little complicated to understand from the picture. Just know about the total number of orbitals (and maximum electron occupancy) in d, f and g subshells (see table 7.2). ...
Heisenburg uncertainty principle
... forces both have infinite range but gravity is 1036 times weaker at a given distance The strong and weak forces are both short range forces (<10-14 m) The weak force is 108 times weaker than the strong force within a nucleus ...
... forces both have infinite range but gravity is 1036 times weaker at a given distance The strong and weak forces are both short range forces (<10-14 m) The weak force is 108 times weaker than the strong force within a nucleus ...
Diagnostics of complex plasmas using a dust grains
... What is a dusty plasma? • a low temperature plasma containing small particles of diameters in nanometer and micrometer range • particles acquire a net negative charge (at equilibrium floating potential) • particles levitated in sheaths where electric force ...
... What is a dusty plasma? • a low temperature plasma containing small particles of diameters in nanometer and micrometer range • particles acquire a net negative charge (at equilibrium floating potential) • particles levitated in sheaths where electric force ...
Chapter 12: Basic Review Worksheet
... 1. In general, what do we mean by a chemical bond? Name the principal types of chemical bonds. 2. What do we mean by ionic bonding? Give an example of a substance whose particles are held together by ionic bonding. 3. What do we mean by covalent bonding and polar covalent bonding? How are these two ...
... 1. In general, what do we mean by a chemical bond? Name the principal types of chemical bonds. 2. What do we mean by ionic bonding? Give an example of a substance whose particles are held together by ionic bonding. 3. What do we mean by covalent bonding and polar covalent bonding? How are these two ...
Early Atomic Models
... had the following properties: 1. Emitted by a wide variety of cathodes 2. About 2000 times smaller than hydrogen The new atomic model had the negative electrons (raisins) imbedded in a sea of positive charge (bun). Sometimes called the Plum Pudding Model. ...
... had the following properties: 1. Emitted by a wide variety of cathodes 2. About 2000 times smaller than hydrogen The new atomic model had the negative electrons (raisins) imbedded in a sea of positive charge (bun). Sometimes called the Plum Pudding Model. ...
Chapter 2 Particle properties of waves
... number of possible standing waves. The average energy per degree of freedom of an entity that is a member of a system of such entities in thermal equilibrium at T is 1/2kT. K is Boltzmann’s constant=1.381*10-23J/k ...
... number of possible standing waves. The average energy per degree of freedom of an entity that is a member of a system of such entities in thermal equilibrium at T is 1/2kT. K is Boltzmann’s constant=1.381*10-23J/k ...
The search for invisible light - INFN-LNF
... It has been proven that any hypothetical massive particles sensitive to the weak interaction (WIMP) would naturally be able to produce the correct relic abundance, a fact that has been often dubbed as «the WIMP miracle». The above mentioned Neutralino is such a kind of particle in fact For this rea ...
... It has been proven that any hypothetical massive particles sensitive to the weak interaction (WIMP) would naturally be able to produce the correct relic abundance, a fact that has been often dubbed as «the WIMP miracle». The above mentioned Neutralino is such a kind of particle in fact For this rea ...
Symbols of Elements
... Images of nickel atoms are produced when nickel is magnified millions of times by a scanning tunneling microscope (STM). This instrument generates an image of the atomic structure. ...
... Images of nickel atoms are produced when nickel is magnified millions of times by a scanning tunneling microscope (STM). This instrument generates an image of the atomic structure. ...
Parts of an atoms - Mr-Durands
... Quarks—Even Smaller Particles • Scientists theorize that an arrangement of three quarks held together with the strong nuclear force produces a proton. • Another arrangement of three quarks produces a neutron ...
... Quarks—Even Smaller Particles • Scientists theorize that an arrangement of three quarks held together with the strong nuclear force produces a proton. • Another arrangement of three quarks produces a neutron ...
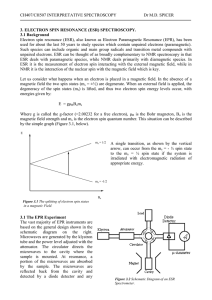
ESR Theory - Personal WWW Pages
... As seen previously, the electron spin energy levels are split by the magnetic field. In addition there is further splitting due to the four possible values of m I. Since the coupling is to a nucleus of spin I = 3/2, there should be 2n(I + 1) lines (ie 2.1.(3/2 +1) = 4 lines). The four transitions ar ...
... As seen previously, the electron spin energy levels are split by the magnetic field. In addition there is further splitting due to the four possible values of m I. Since the coupling is to a nucleus of spin I = 3/2, there should be 2n(I + 1) lines (ie 2.1.(3/2 +1) = 4 lines). The four transitions ar ...
Standard Model of Physics
... • Of the fields that we are usually accustomed to, force decreases with distance e.g. the electric field. • This does not seem to be the case for quarks. • We have posited the existence of gluons to account for the strange behavior of these particles (which we can’t see). • When it is attempted to s ...
... • Of the fields that we are usually accustomed to, force decreases with distance e.g. the electric field. • This does not seem to be the case for quarks. • We have posited the existence of gluons to account for the strange behavior of these particles (which we can’t see). • When it is attempted to s ...
Quantum Theory
... • Principle Quantum Number: • The principle quantum number, symbolized by “n”, indicates the main energy level occupied by the electron. • Values of “n” are positive integers only: 1,2,3 . . . • An electron for which n=1 occupies the first, or lowest, main energy level and is located closest to the ...
... • Principle Quantum Number: • The principle quantum number, symbolized by “n”, indicates the main energy level occupied by the electron. • Values of “n” are positive integers only: 1,2,3 . . . • An electron for which n=1 occupies the first, or lowest, main energy level and is located closest to the ...
No Slide Title - Weizmann Institute of Science
... • Two-path interference by scattering off a single free quantum particle in a superposition of two locations is possible. • Interference is suppressed by initial momentum spread of the probe particle or by measurement ...
... • Two-path interference by scattering off a single free quantum particle in a superposition of two locations is possible. • Interference is suppressed by initial momentum spread of the probe particle or by measurement ...
Chapter 5/6 Notes
... Predicting properties using other elements data: Example: Predict the density of Aluminum given: Density: Ga = 5.9 g/cm3 & B = 2.3 g/cm3 ...
... Predicting properties using other elements data: Example: Predict the density of Aluminum given: Density: Ga = 5.9 g/cm3 & B = 2.3 g/cm3 ...
Impact of Large-Mixing-Angle Neutrino Oscillations
... particle having nearly the same predicted mass of, ...
... particle having nearly the same predicted mass of, ...
Electron scattering

Electron scattering occurs when electrons are deviated from their original trajectory. This is due to the electrostatic forces within matter interaction or, if an external magnetic field is present, the electron may be deflected by the Lorentz force. This scattering typically happens with solids such as metals, semiconductors and insulators; and is a limiting factor in integrated circuits and transistors.The application of electron scattering is such that it can be used as a high resolution microscope for hadronic systems, that allows the measurement of the distribution of charges for nucleons and nuclear structure. The scattering of electrons has allowed us to understand that protons and neutrons are made up of the smaller elementary subatomic particles called quarks.Electrons may be scattered through a solid in several ways:Not at all: no electron scattering occurs at all and the beam passes straight through.Single scattering: when an electron is scattered just once.Plural scattering: when electron(s) scatter several times.Multiple scattering: when electron(s) scatter very many times over.The likelihood of an electron scattering and the proliferance of the scattering is a probability function of the specimen thickness to the mean free path.