Lecture 15: Bohr Model of the Atom
... • Johann Rydberg extends the Balmer model by finding more emission lines outside the visible region of the spectrum: ...
... • Johann Rydberg extends the Balmer model by finding more emission lines outside the visible region of the spectrum: ...
Franck-Hertz Effect in Mercury
... (Unbound states can have any energy.) The Hg atom normally will be in the lowest or ground state, with a valence electron occupancy designated by (6s)2 (two electrons in n=6, l = 0 single particle states). This has a spectroscopic designation of lS0, or (2S+1LJ), where S, L and J are system orbital, ...
... (Unbound states can have any energy.) The Hg atom normally will be in the lowest or ground state, with a valence electron occupancy designated by (6s)2 (two electrons in n=6, l = 0 single particle states). This has a spectroscopic designation of lS0, or (2S+1LJ), where S, L and J are system orbital, ...
Quantum Numbers
... • Cr should be [Ar]4s23d4 but instead it is [Ar]4s13d5 • Cu should be [Ar]4s23d9 but instead it is [Ar]4s13d10 • These deviations for Cr and Cu are attributed to the particular stability of a half-filled d subshell (the electrons are all the same spin) or a ...
... • Cr should be [Ar]4s23d4 but instead it is [Ar]4s13d5 • Cu should be [Ar]4s23d9 but instead it is [Ar]4s13d10 • These deviations for Cr and Cu are attributed to the particular stability of a half-filled d subshell (the electrons are all the same spin) or a ...
Nuclear Physics
... for a metal at several different frequencies. You then graph Kmax for photoelectrons on yaxis and frequency on x-axis. What information can you get from the slope and intercept of your data? ...
... for a metal at several different frequencies. You then graph Kmax for photoelectrons on yaxis and frequency on x-axis. What information can you get from the slope and intercept of your data? ...
Heisenbergs
... • An early attempt of the uncertainty principle appeared in a 1927 paper by Heisenberg, a German physicist who was working at Niels Bohr's institute in Copenhagen at the time, titled "On the Perceptual Content of Quantum Theoretical Kinematics and Mechanics". Jha, A. (2013, November 30). Retrieved f ...
... • An early attempt of the uncertainty principle appeared in a 1927 paper by Heisenberg, a German physicist who was working at Niels Bohr's institute in Copenhagen at the time, titled "On the Perceptual Content of Quantum Theoretical Kinematics and Mechanics". Jha, A. (2013, November 30). Retrieved f ...
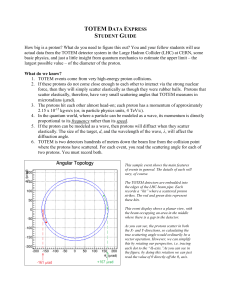
Student Guide - Quarknet
... 1. TOTEM events come from very high-energy proton collisions. 2. If these protons do not come close enough to each other to interact via the strong nuclear force, then they will simply scatter elastically as though they were rubber balls. Protons that scatter elastically, therefore, have very small ...
... 1. TOTEM events come from very high-energy proton collisions. 2. If these protons do not come close enough to each other to interact via the strong nuclear force, then they will simply scatter elastically as though they were rubber balls. Protons that scatter elastically, therefore, have very small ...
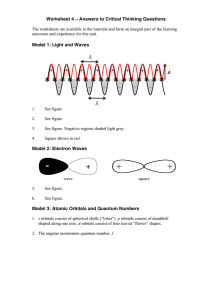
Answers to Critical Thinking Questions 4
... The 2s has one radial node and the 3s has two radial nodes. 3p have one radial node. In general, the number of radial nodes is equal to n – l - 1. ...
... The 2s has one radial node and the 3s has two radial nodes. 3p have one radial node. In general, the number of radial nodes is equal to n – l - 1. ...
Nuclear Chemistry
... nucleus it can cause the nucleus to break apart into smaller nuclei The fission reaction produces smaller nuclei as well as loose neutrons The loose neutron can strike the smaller nuclei, causing that nuclei to divide This is known as a nuclear chain reaction ...
... nucleus it can cause the nucleus to break apart into smaller nuclei The fission reaction produces smaller nuclei as well as loose neutrons The loose neutron can strike the smaller nuclei, causing that nuclei to divide This is known as a nuclear chain reaction ...
Molekylfysik - Leiden Univ
... Because of the electron charge and the positive charge |Ze| of the nucleus, the Coulomb potential energy V(r) has to be taken into account in the energetics of the system. ...
... Because of the electron charge and the positive charge |Ze| of the nucleus, the Coulomb potential energy V(r) has to be taken into account in the energetics of the system. ...
The regularities of the Rydberg energy levels of many
... separately in one-valence electron atoms (ions); while in WBEPM theory, through separation of the weakest bound electron and non-weakest bound electrons, one can solve the one-electron Schrödinger equation of the weakest bound electron. This is very convenient for the discussion about the excited st ...
... separately in one-valence electron atoms (ions); while in WBEPM theory, through separation of the weakest bound electron and non-weakest bound electrons, one can solve the one-electron Schrödinger equation of the weakest bound electron. This is very convenient for the discussion about the excited st ...
Monday, Oct. 30, 2006
... • While the D’s are connected to HV sources, there is no electric field inside the chamber due to Faraday effect • Strong electric field exists only in the gap between the D’s • An ion source is placed in the gap • The path is circular due to the perpendicular magnetic field • Ion does not feel any ...
... • While the D’s are connected to HV sources, there is no electric field inside the chamber due to Faraday effect • Strong electric field exists only in the gap between the D’s • An ion source is placed in the gap • The path is circular due to the perpendicular magnetic field • Ion does not feel any ...
electric field spectroscopy of ultracold polar molecular dimers
... know, is to encode the electron’s interaction with all the other electrons in the parent ion. The entire series of energy levels is described by a simple formula that is flexible enough to apply to any atom. What I would like to do here is to derive an analogue of the Rydberg formula for an electric ...
... know, is to encode the electron’s interaction with all the other electrons in the parent ion. The entire series of energy levels is described by a simple formula that is flexible enough to apply to any atom. What I would like to do here is to derive an analogue of the Rydberg formula for an electric ...
Phase Transitions of Dirac Electrons Observed in Bismuth
... subfields of physics. They have also led to important applications, e.g. the MRI machine and ever-faster and smaller solid-state transistors. At very high energies, the Schrödinger equation is supplanted by the Dirac equation, which describes neutrinos (particles that travel at the speed of light), ...
... subfields of physics. They have also led to important applications, e.g. the MRI machine and ever-faster and smaller solid-state transistors. At very high energies, the Schrödinger equation is supplanted by the Dirac equation, which describes neutrinos (particles that travel at the speed of light), ...
Unit 2 note
... Rutherford’s orbital atomic model could not explain the chemical properties of elements. For example, why do metal elements, or compounds that contain metals, give off characteristic colours when heated in a flame? Explaining what leads to the chemical properties of elements requires a model that be ...
... Rutherford’s orbital atomic model could not explain the chemical properties of elements. For example, why do metal elements, or compounds that contain metals, give off characteristic colours when heated in a flame? Explaining what leads to the chemical properties of elements requires a model that be ...
A Primer for Electro-Weak Induced Low Energy Nuclear Reactions
... show that neutrons are born with very small momentum (ultra cold) because their production is collective through a large number of protons coherently oscillating over a macroscopic region of the mono layer surface. Since the nuclear absorption cross-section of ultra low momentum neutrons is extremel ...
... show that neutrons are born with very small momentum (ultra cold) because their production is collective through a large number of protons coherently oscillating over a macroscopic region of the mono layer surface. Since the nuclear absorption cross-section of ultra low momentum neutrons is extremel ...
Electron scattering

Electron scattering occurs when electrons are deviated from their original trajectory. This is due to the electrostatic forces within matter interaction or, if an external magnetic field is present, the electron may be deflected by the Lorentz force. This scattering typically happens with solids such as metals, semiconductors and insulators; and is a limiting factor in integrated circuits and transistors.The application of electron scattering is such that it can be used as a high resolution microscope for hadronic systems, that allows the measurement of the distribution of charges for nucleons and nuclear structure. The scattering of electrons has allowed us to understand that protons and neutrons are made up of the smaller elementary subatomic particles called quarks.Electrons may be scattered through a solid in several ways:Not at all: no electron scattering occurs at all and the beam passes straight through.Single scattering: when an electron is scattered just once.Plural scattering: when electron(s) scatter several times.Multiple scattering: when electron(s) scatter very many times over.The likelihood of an electron scattering and the proliferance of the scattering is a probability function of the specimen thickness to the mean free path.