Photon gas as a classical medium
... takes the simple meaning of the Compton wavelength of a photon in a plasma In the relativistic theory a coordinate uncertainty in a frame of reference in which the particle is moving with energy ...
... takes the simple meaning of the Compton wavelength of a photon in a plasma In the relativistic theory a coordinate uncertainty in a frame of reference in which the particle is moving with energy ...
Slide 1
... A conducting sphere initially has no net charge. A positively charged rod is then brought close to the sphere. The sphere is then connected to ground. The rod is then removed, and then the connection to ground is broken. After these steps, what is the net charge on the sphere? ...
... A conducting sphere initially has no net charge. A positively charged rod is then brought close to the sphere. The sphere is then connected to ground. The rod is then removed, and then the connection to ground is broken. After these steps, what is the net charge on the sphere? ...
How Are Electric And Magnetic Fields Used To Steer
... Force on a charged particle in a magnetic field equation: F = B q v sin θ F = force (N) B = magnetic field strength (T) q = charge on the particle (C) v = velocity of the particle (m/s) (Angle θ is between the direction of the beam and the magnetic field direction) ...
... Force on a charged particle in a magnetic field equation: F = B q v sin θ F = force (N) B = magnetic field strength (T) q = charge on the particle (C) v = velocity of the particle (m/s) (Angle θ is between the direction of the beam and the magnetic field direction) ...
Chapter 4 Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms
... • Explain how the Heisenberg uncertainty principle and the Schrödinger wave equation led to the idea of atomic orbitals. • List the four quantum numbers and describe their significance. • Relate the number of sublevels corresponding to each of an atom’s main energy levels, the number of orbitals per ...
... • Explain how the Heisenberg uncertainty principle and the Schrödinger wave equation led to the idea of atomic orbitals. • List the four quantum numbers and describe their significance. • Relate the number of sublevels corresponding to each of an atom’s main energy levels, the number of orbitals per ...
x 100 QUANTUM NUMBERS AND SYMBOLS
... 5. What type of orbital in an atom is designated by quantum numbers n=4, l =3, and ml =0? 6. A subshell in an atom has the values, n = 3, l =2. How many orbitals are there in this ...
... 5. What type of orbital in an atom is designated by quantum numbers n=4, l =3, and ml =0? 6. A subshell in an atom has the values, n = 3, l =2. How many orbitals are there in this ...
Lecture 2. First-order differential equations
... Gravity can be expressed by mg, where g is the gravitational acceleration. Air resistance can be reasonably represented by −bv, where b is a positive constant depending on the density of the air and the shape of the object, and v is the velocity of the object. We use the negative sign because air re ...
... Gravity can be expressed by mg, where g is the gravitational acceleration. Air resistance can be reasonably represented by −bv, where b is a positive constant depending on the density of the air and the shape of the object, and v is the velocity of the object. We use the negative sign because air re ...
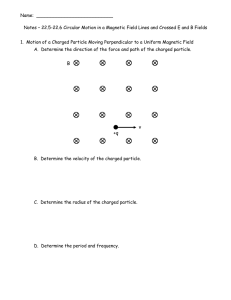
Name: Notes – 22.5-22.6 Circular Motion in a Magnetic Field Lines
... A proton with just the right velocity will pass straight through the apparatus shown below from left to right that has crossed E and B fields that are perpendicular to each other. The electric charges on the upper and lower plates are shown. ...
... A proton with just the right velocity will pass straight through the apparatus shown below from left to right that has crossed E and B fields that are perpendicular to each other. The electric charges on the upper and lower plates are shown. ...
Phys202_Final_Exam_Spr2006.doc
... 33. Two parallel wires a distance 8 m apart carry 7 A and 8 A respectively in the opposite direction. What is the force per unit length between them? a. ~1.1o b. 160 o c. 16 o d. 10 o ...
... 33. Two parallel wires a distance 8 m apart carry 7 A and 8 A respectively in the opposite direction. What is the force per unit length between them? a. ~1.1o b. 160 o c. 16 o d. 10 o ...
Powerpoint handout
... proposing that electrons in atoms could have only certain energies, and that light was given off when an electron underwent a transition from a higher energy level to a lower one. ...
... proposing that electrons in atoms could have only certain energies, and that light was given off when an electron underwent a transition from a higher energy level to a lower one. ...
Lecture notes, part 2
... = 0. If all these states are also normalized, they are said to be “orthonormal”. Case 2: degenerate. En can equal Em even if n 6= m. The proof is more complicated than the non-degenerate case. We need to use the GramSchmitt orthogonalization procedure to construct orthogonal states by taking appropr ...
... = 0. If all these states are also normalized, they are said to be “orthonormal”. Case 2: degenerate. En can equal Em even if n 6= m. The proof is more complicated than the non-degenerate case. We need to use the GramSchmitt orthogonalization procedure to construct orthogonal states by taking appropr ...
Diffusion quantum Monte Carlo
... • The variance of EL(X) approaches zero as Ψ approaches the ground state wavefunction Ψ0. σE2 =-2 ≈ -2 = 0
...
... • The variance of EL(X) approaches zero as Ψ approaches the ground state wavefunction Ψ0. σE2 =
Document
... “It is interesting to realize that essentially everything that we find in our studies of magnetism is a pure quantum effect. We may be wondering where is the point where the h=/=0 makes itself felt; after all, the classical and quantum Hamiltonians look exactly the same! It can be shown […] that the ...
... “It is interesting to realize that essentially everything that we find in our studies of magnetism is a pure quantum effect. We may be wondering where is the point where the h=/=0 makes itself felt; after all, the classical and quantum Hamiltonians look exactly the same! It can be shown […] that the ...