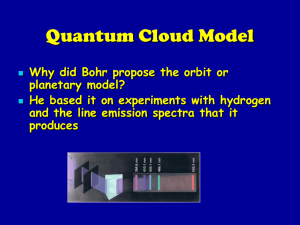
Physics Qualifying Examination – Part I 7-Minute Questions February 7, 2015
... A cold sodium atom (23Na), at rest, is isolated in a vacuum system on the Earth's surface. A laser, with λ = 589 nm (i.e., D-line or the 3s to 3p transition) shines on this atom from directly below. The atom absorbs photons and then reradiates that energy uniformly in all directions. Gravity, with a ...
... A cold sodium atom (23Na), at rest, is isolated in a vacuum system on the Earth's surface. A laser, with λ = 589 nm (i.e., D-line or the 3s to 3p transition) shines on this atom from directly below. The atom absorbs photons and then reradiates that energy uniformly in all directions. Gravity, with a ...
Chapter 25: Electric Potential Energy
... Energy concepts allow us to consider the behavior of charges in an electric field. ...
... Energy concepts allow us to consider the behavior of charges in an electric field. ...
Quantum Mechanics: Particles in Potentials
... As the quantum number increases to large values, probability of particle position approaches uniform distribution in the region [0,a]. This is the classical limit. Quantum mechanics approaches classical mechanics in the limit of large quantum numbers. As the quantum number increases to large values ...
... As the quantum number increases to large values, probability of particle position approaches uniform distribution in the region [0,a]. This is the classical limit. Quantum mechanics approaches classical mechanics in the limit of large quantum numbers. As the quantum number increases to large values ...
PHYS1220 - s3.amazonaws.com
... Free Particles The simplest wave function to describe is that of a free particle. It does not have any potential acting on it and therefore no forces. ...
... Free Particles The simplest wave function to describe is that of a free particle. It does not have any potential acting on it and therefore no forces. ...
9-3 optimizing with constraints
... Identify your givens and what you are looking for Assign a variable for each quantity involved in the problem. Write an equation involving the quantity you are trying to make as ____ or as ______ as possible (Equation to be ____________________________) 5. Write an equation that involves the restric ...
... Identify your givens and what you are looking for Assign a variable for each quantity involved in the problem. Write an equation involving the quantity you are trying to make as ____ or as ______ as possible (Equation to be ____________________________) 5. Write an equation that involves the restric ...
Lectuer 15
... - The z component of the angular momentum is determined completely by m through L z = m ħ. - The quantum number m is called the magnetic quantum number because the energy of a hydrogen atom in a magnetic field depends on m. - The (2 Ɩ + 1) – fold degeneracy in the absence of a magnetic field is spli ...
... - The z component of the angular momentum is determined completely by m through L z = m ħ. - The quantum number m is called the magnetic quantum number because the energy of a hydrogen atom in a magnetic field depends on m. - The (2 Ɩ + 1) – fold degeneracy in the absence of a magnetic field is spli ...
Problem Set 2
... and use this to compute etM . • Calculate etM using the Taylor series expansion for the exponential, as well as the series expansions for the sine and cosine. Problem 2: Consider a two-state quantum system, with Hamiltonian H = −Bx σ1 (this is the sort of thing that occurs for a spin-1/2 system subj ...
... and use this to compute etM . • Calculate etM using the Taylor series expansion for the exponential, as well as the series expansions for the sine and cosine. Problem 2: Consider a two-state quantum system, with Hamiltonian H = −Bx σ1 (this is the sort of thing that occurs for a spin-1/2 system subj ...