the problem book
... determine the condition that quantizes their energy, assuming non-relativistic motion. Compute the quantized energy and angular momentum spectra. [8 pt] ...
... determine the condition that quantizes their energy, assuming non-relativistic motion. Compute the quantized energy and angular momentum spectra. [8 pt] ...
4.8 Integrals using grad, div, and curl
... Calculating the vector product of the nabla operator and a function with several components f~(~x) we get the curl ~ × f~. curlf~ = rotf~ = ∇ Note that the curl is applied to a vector and the result is a vector. One essential aspect of the curl is the solution of area integrals (Stokes integral equa ...
... Calculating the vector product of the nabla operator and a function with several components f~(~x) we get the curl ~ × f~. curlf~ = rotf~ = ∇ Note that the curl is applied to a vector and the result is a vector. One essential aspect of the curl is the solution of area integrals (Stokes integral equa ...
\chapter{Introduction}
... To write a thesis on the vacuum is, from a naive point of view, to write a thesis on nothing at all. Classically one could define the vacuum as a box containing no matter or particles whatsoever or, more rigorously, a subspace $V$ of the $\mathbb{R}^3$ such that $N(V)=0$, where $N$ denotes the numbe ...
... To write a thesis on the vacuum is, from a naive point of view, to write a thesis on nothing at all. Classically one could define the vacuum as a box containing no matter or particles whatsoever or, more rigorously, a subspace $V$ of the $\mathbb{R}^3$ such that $N(V)=0$, where $N$ denotes the numbe ...
x - Piazza
... Note that more than one wave function can have the same energy. When more than one wave function has the same energy, those quantum states are said to be degenerate. Degeneracy results from symmetries of the potential energy function that describes the system. A perturbation of the potential energy ...
... Note that more than one wave function can have the same energy. When more than one wave function has the same energy, those quantum states are said to be degenerate. Degeneracy results from symmetries of the potential energy function that describes the system. A perturbation of the potential energy ...
(a) Describe in your own words how to solve a linear equation using
... (a) Describe in your own words how to solve a linear equation using the equality properties. Demonstrate the process with an example. bNext, replace the equal sign in your example with an inequality by using the less than or greater than sign. Then solve the inequality. (c) What similarities do y ...
... (a) Describe in your own words how to solve a linear equation using the equality properties. Demonstrate the process with an example. bNext, replace the equal sign in your example with an inequality by using the less than or greater than sign. Then solve the inequality. (c) What similarities do y ...
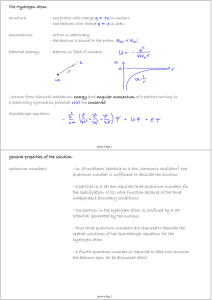
general properties of the solution: quantum numbers:
... in the Hydrogen atom with n being the principal quantum number Spatial quantum numbers of the Hydrogen atom: - principal quantum number: - orbital quantum number: - magnetic quantum number: - dependence of wave function on quantum numbers: ...
... in the Hydrogen atom with n being the principal quantum number Spatial quantum numbers of the Hydrogen atom: - principal quantum number: - orbital quantum number: - magnetic quantum number: - dependence of wave function on quantum numbers: ...
Moore`s Law No Moore?
... • Replace SiO2 with a new dielectric (a nonconductor of direct electric current) known as “high-K”. However it is not compatible with their current gate electrode. ...
... • Replace SiO2 with a new dielectric (a nonconductor of direct electric current) known as “high-K”. However it is not compatible with their current gate electrode. ...
ANGULAR MOMENTUM So far, we have studied simple models in
... m h = projection of L onto z-axis For each eigenvalue of L2, there are (2l+1) eigenfunctions of L2 with the same value of l, but different values of m. Therefore, the degeneracy is (2l+1). The Spherical Harmonic functions are important in the central force problem--in which a particle moves under a ...
... m h = projection of L onto z-axis For each eigenvalue of L2, there are (2l+1) eigenfunctions of L2 with the same value of l, but different values of m. Therefore, the degeneracy is (2l+1). The Spherical Harmonic functions are important in the central force problem--in which a particle moves under a ...