Lecture 34: The `Density Operator
... • Using the formalism we have developed so far, the procedure is as follows: – Take an initial state vector – Evolve it according to Schrödinger's equation until the time the measurement takes place – Use the projector onto eigenstates of the observable to predict the probabilities for different res ...
... • Using the formalism we have developed so far, the procedure is as follows: – Take an initial state vector – Evolve it according to Schrödinger's equation until the time the measurement takes place – Use the projector onto eigenstates of the observable to predict the probabilities for different res ...
n-1 - KAIST
... (This fluctuating electron energy might suggest a violation of the conservation of energy, but not if the electron is exchanging energy at the Planck level with other electrons or particles) ...
... (This fluctuating electron energy might suggest a violation of the conservation of energy, but not if the electron is exchanging energy at the Planck level with other electrons or particles) ...
Chapter 7: The Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom I. The
... 1. Bohr s major idea was that the energy states of the atom were _________, and that the amount of energy in the atom was related to the electron s position in the atom. 2. The electrons travel in orbits that are at a fixed distance from the nucleus. ...
... 1. Bohr s major idea was that the energy states of the atom were _________, and that the amount of energy in the atom was related to the electron s position in the atom. 2. The electrons travel in orbits that are at a fixed distance from the nucleus. ...
atomsagain
... •If you ignore the interaction of electrons, then 3s = 3p = 3d •In fact, the inner electrons are so close to the nucleus, the nuclear charge looks like it is reduced •Unless the “outer” electron penetrates inside a bit •Behavior near the nucleus is governed by l •Small l values can go near nucleus • ...
... •If you ignore the interaction of electrons, then 3s = 3p = 3d •In fact, the inner electrons are so close to the nucleus, the nuclear charge looks like it is reduced •Unless the “outer” electron penetrates inside a bit •Behavior near the nucleus is governed by l •Small l values can go near nucleus • ...
1 8. CONSERVATION LAWS The general form of a conservation law
... We can use the resistive form of Ohm’s law to eliminate V ! B in favor of J and E . Then writing !V 2" # V = " # ( !V 2 V) $ V # " !V 2 , and using the definition of P , ...
... We can use the resistive form of Ohm’s law to eliminate V ! B in favor of J and E . Then writing !V 2" # V = " # ( !V 2 V) $ V # " !V 2 , and using the definition of P , ...
The muon
... If we know that LF number is conserved, then the decay μ → e γ cannot occur. But we know that LF number is not conserved. So the challenge is to observe the decay μ → e γ . To be continued ... ...
... If we know that LF number is conserved, then the decay μ → e γ cannot occur. But we know that LF number is not conserved. So the challenge is to observe the decay μ → e γ . To be continued ... ...
Physics 513 Topic List/Study Checksheet This should function more
... You should go through each of the major units and think about “what would be a long answer calculation that could be asked from this unit?” Note that this will be similar to the middling level long answer questions from the unit exams. In general, for a final, the physics teachers believe it would n ...
... You should go through each of the major units and think about “what would be a long answer calculation that could be asked from this unit?” Note that this will be similar to the middling level long answer questions from the unit exams. In general, for a final, the physics teachers believe it would n ...
Lecture 8a
... • The electronic Zeeman effect arises from an unpaired electron, which possesses a magnetic moment that assumes one of two orientations in an external magnetic field • The energy separation between these two states, is given as DE = hn = gbH where h, g, and b are Planck's constant, the Lande spectro ...
... • The electronic Zeeman effect arises from an unpaired electron, which possesses a magnetic moment that assumes one of two orientations in an external magnetic field • The energy separation between these two states, is given as DE = hn = gbH where h, g, and b are Planck's constant, the Lande spectro ...
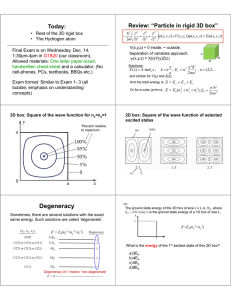
Degeneracy
... Schrodinger’s Solutions for Hydrogen If you understand the 1D quantum well (and how we went from 1D to 3D), then it is easy for you to understand Schrödinger's hydrogen atom! ...
... Schrodinger’s Solutions for Hydrogen If you understand the 1D quantum well (and how we went from 1D to 3D), then it is easy for you to understand Schrödinger's hydrogen atom! ...
Document
... (b) Although the photon has energy, it cannot transfer any energy to the surface because it has zero mass. (c) The photon carries momentum, and when it reflects off the mirror, it undergoes a change in momentum and exerts a force on the mirror. (d) Although the photon carries momentum, its change in ...
... (b) Although the photon has energy, it cannot transfer any energy to the surface because it has zero mass. (c) The photon carries momentum, and when it reflects off the mirror, it undergoes a change in momentum and exerts a force on the mirror. (d) Although the photon carries momentum, its change in ...