Lecture 15 Summary
... We now consider systems that can exchange particles, in addition to energy. This will lead to the Grand Canonical Ensemble of statistical mechanics. We saw that temperature can be used to decide how energy will flow between two systems when they are brought into thermal contact. Simply put, the syst ...
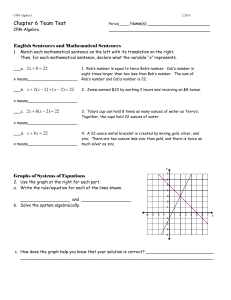
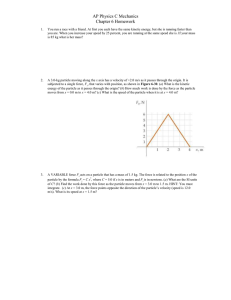
... We now consider systems that can exchange particles, in addition to energy. This will lead to the Grand Canonical Ensemble of statistical mechanics. We saw that temperature can be used to decide how energy will flow between two systems when they are brought into thermal contact. Simply put, the syst ...
Neitzke: What is a BPS state?
... The quantum theories we want to understand are describing phenomena which take place in Minkowski space E3,1 . Among other things, such a theory is supposed to have an associated Hilbert space H, whose vectors represent the possible “states” of the system. One simple example of a quantum theory whic ...
... The quantum theories we want to understand are describing phenomena which take place in Minkowski space E3,1 . Among other things, such a theory is supposed to have an associated Hilbert space H, whose vectors represent the possible “states” of the system. One simple example of a quantum theory whic ...
States and Operators in the Spacetime Algebra
... This demonstrates that the 2-sided construction of the expectation value (2.15) is an instruction to rotate and dilate the fixed σ3 axis into the spin direction. The original states of quantum mechanics therefore become operators in the STA, acting on vectors. This explains why spinors transform sin ...
... This demonstrates that the 2-sided construction of the expectation value (2.15) is an instruction to rotate and dilate the fixed σ3 axis into the spin direction. The original states of quantum mechanics therefore become operators in the STA, acting on vectors. This explains why spinors transform sin ...
Energy Methods - MIT OpenCourseWare
... could be given by r and θ. A two-degree of freedom system remains two-degree so that the number of coordinate variables required remains two. r and θ and their counterparts in other coordinate systems will be referred to as generalized coordinates. We introduce quite general notation for the relatio ...
... could be given by r and θ. A two-degree of freedom system remains two-degree so that the number of coordinate variables required remains two. r and θ and their counterparts in other coordinate systems will be referred to as generalized coordinates. We introduce quite general notation for the relatio ...
By: 3rd Period Chemistry Actinide Ionization Energy Probability
... 3rd quantum number Principal quantum number Noble Gas Especially stable, low-energy, don’t tend to combine with other elements, have s and p orbitals that are completely full ...
... 3rd quantum number Principal quantum number Noble Gas Especially stable, low-energy, don’t tend to combine with other elements, have s and p orbitals that are completely full ...
15.06.18_CAP-Edmonton-CWL
... him in 1916), and represents probably the most beautiful of all existing physical theories. L.D. Landau, E.M. Lifshitz “The Classical Theory of Fields”, sec.82 ...
... him in 1916), and represents probably the most beautiful of all existing physical theories. L.D. Landau, E.M. Lifshitz “The Classical Theory of Fields”, sec.82 ...
iGCSE Physics Specification Questions Forces and Motion 1. What
... 24. What happens if you apply a range of forces to an object such as a spring, a metal wire or an elastic band? 25. What is Hooke’s Law? How can it be demonstrated graphically? 26. What is elastic behaviour? 27. Why does an Astronaut weigh less on the Moon than on Earth but more if they were on the ...
... 24. What happens if you apply a range of forces to an object such as a spring, a metal wire or an elastic band? 25. What is Hooke’s Law? How can it be demonstrated graphically? 26. What is elastic behaviour? 27. Why does an Astronaut weigh less on the Moon than on Earth but more if they were on the ...
MAPPING BETWEEN NONLINEAR SCHRÖDINGER EQUATIONS WITH REAL AND COMPLEX POTENTIALS MARIO SALERNO
... applicative point of view. The non hermiticity is in general due to the presence of a complex potential in the Hamiltonian accounting for typical dissipative and amplification effects met in classical and quantum contexts [5, 12]. In particular, dissipative solitons [4] of the nonlinear Schrödinger ...
... applicative point of view. The non hermiticity is in general due to the presence of a complex potential in the Hamiltonian accounting for typical dissipative and amplification effects met in classical and quantum contexts [5, 12]. In particular, dissipative solitons [4] of the nonlinear Schrödinger ...