Digital Wires
... . We use averaging to find a low dimensional model of the slow center of mass motion [3]. Figure 1 shows the dynamics of this system, the dynamics of the averaged differential equation, and the dynamics of the mapping function. The original dynamics is not damped but the dynamics of the averaged dif ...
... . We use averaging to find a low dimensional model of the slow center of mass motion [3]. Figure 1 shows the dynamics of this system, the dynamics of the averaged differential equation, and the dynamics of the mapping function. The original dynamics is not damped but the dynamics of the averaged dif ...
Meeting 10 - Clark University
... how to find a solution to the equation This is a simpler equation because the constant c ax + by = d doesn’t appear in it. In fact, it’s a homogeneous equation. A homogeneous equation is one in which when d = (a, b), the greatest common divisor of all the terms have the same degree, in this case, a ...
... how to find a solution to the equation This is a simpler equation because the constant c ax + by = d doesn’t appear in it. In fact, it’s a homogeneous equation. A homogeneous equation is one in which when d = (a, b), the greatest common divisor of all the terms have the same degree, in this case, a ...
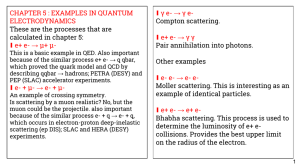
CHAPTER 5 : EXAMPLES IN QUANTUM γ e- → γ e- ∎ ELECTRODYNAMICS
... R = σ ( e e → hadrons ) / σ ( e ebar → μ μbar) . The underlying process in hadron production is e- + e+ → q + qbar. ...
... R = σ ( e e → hadrons ) / σ ( e ebar → μ μbar) . The underlying process in hadron production is e- + e+ → q + qbar. ...
Study of baryonic matter with the BM@N
... BM@N (Baryonic Matter @ Nuclotron) is the first experiment at the accelerator complex of NICA-Nuclotron-M. The aim of the BM@N experiment is to study interactions of relativistic heavy ion beams with fixed targets [5]. The Nuclotron will provide verity of beams from protons to gold ions with the kin ...
... BM@N (Baryonic Matter @ Nuclotron) is the first experiment at the accelerator complex of NICA-Nuclotron-M. The aim of the BM@N experiment is to study interactions of relativistic heavy ion beams with fixed targets [5]. The Nuclotron will provide verity of beams from protons to gold ions with the kin ...
62. Super Conduction Hopping Process on the
... gap, and isotope and pressure effects. In addition to the phase transition from insulating to super conductivity state [1, 2].The models proposed to cure these draw backs are mainly based on quantum mechanics beside generalized special relativity and plasma physics [3, 4].This new model can explain ...
... gap, and isotope and pressure effects. In addition to the phase transition from insulating to super conductivity state [1, 2].The models proposed to cure these draw backs are mainly based on quantum mechanics beside generalized special relativity and plasma physics [3, 4].This new model can explain ...
On the Control of Open Quantum Systems in the Weak Coupling Limit
... When dealing with coherent control of open quantum systems, the Hamiltonian H0 depends on the control and typically authors in the control theory literature modify equation (1) by simply replacing H0 with a time varying Hamiltonian, Hc := Hc (u), depending on the control (see e.g., papers in the spe ...
... When dealing with coherent control of open quantum systems, the Hamiltonian H0 depends on the control and typically authors in the control theory literature modify equation (1) by simply replacing H0 with a time varying Hamiltonian, Hc := Hc (u), depending on the control (see e.g., papers in the spe ...
Lecture 11 Identical particles
... However, the spin-statistics relation emerges naturally from the unification of quantum mechanics and special relativity. The rule that fermions have half-integer spin and bosons have integer spin is internally consistent: e.g. Two identical nuclei, composed of n nucleons (fermions), would have inte ...
... However, the spin-statistics relation emerges naturally from the unification of quantum mechanics and special relativity. The rule that fermions have half-integer spin and bosons have integer spin is internally consistent: e.g. Two identical nuclei, composed of n nucleons (fermions), would have inte ...
Views on Atomic Stru..
... outer region by a spherical node - a spherical shell in which the electron probability is zero ...
... outer region by a spherical node - a spherical shell in which the electron probability is zero ...
Stefano Bellucci (INFN-Laboratori Nazionali di Frascati)
... These variables are expressed via initial ones in terms of elliptic functions, so they are not very convenient for analyzing the system. Nevertheless, they allowed us to indicate the existence of two regimes, with |pФ| <2mM and |pФ| > 2mM, separated by the critical point |pФ| =2mM, where the particl ...
... These variables are expressed via initial ones in terms of elliptic functions, so they are not very convenient for analyzing the system. Nevertheless, they allowed us to indicate the existence of two regimes, with |pФ| <2mM and |pФ| > 2mM, separated by the critical point |pФ| =2mM, where the particl ...
GUIDING CENTER EQUATIONS
... center equations governing single particle motion in the presence of electromagnetic fields which vary slowly in both time and space. These equations are derived from the exact equations of motion by means of perturbation analyses, where only the firstorder terms with respect to the parameters, ρ ...
... center equations governing single particle motion in the presence of electromagnetic fields which vary slowly in both time and space. These equations are derived from the exact equations of motion by means of perturbation analyses, where only the firstorder terms with respect to the parameters, ρ ...
Motion of a Charged Particle in a Magnetic Field
... at the ends of the “bottle” to produce a strong magnetic field to pinch off the ends. • A charged particle starting at one end will spiral along the field lines until it reaches the other end, where it reverses directions and spirals back. This configuration is known as a “magnetic bottle” because c ...
... at the ends of the “bottle” to produce a strong magnetic field to pinch off the ends. • A charged particle starting at one end will spiral along the field lines until it reaches the other end, where it reverses directions and spirals back. This configuration is known as a “magnetic bottle” because c ...