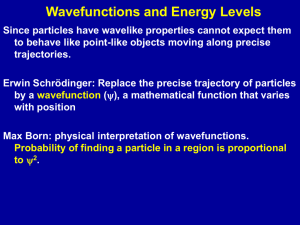
ppt
... The Schrödinger equation describes the motion of a particle of mass m moving in a region where the potential energy is described by V(x). 2 y d -h 2 m dx2 + V(x) y = E y ...
... The Schrödinger equation describes the motion of a particle of mass m moving in a region where the potential energy is described by V(x). 2 y d -h 2 m dx2 + V(x) y = E y ...
r=2l L orbits!
... field to below the critical temperature, near absolute zero, at which the transition to superconductivity takes place. It was discovered by Walther Meissner in 1933, when he measured the magnetic field surrounding two adjacent long cylindrical single crystals of tin and observed that at ?452.97°F (3 ...
... field to below the critical temperature, near absolute zero, at which the transition to superconductivity takes place. It was discovered by Walther Meissner in 1933, when he measured the magnetic field surrounding two adjacent long cylindrical single crystals of tin and observed that at ?452.97°F (3 ...
1 PHY831 - Subject Exam Dec. 14th 2011, 10am - 1pm
... (iii) The first thing to note is that T anh(3βJm2 ) for ferromagnetic interactions (i.e. J > 0) is always positive, so there are no negative m solutions to the mean field equation. This is completely different than the pair interaction case where there is symmetry in the solutions for positive and n ...
... (iii) The first thing to note is that T anh(3βJm2 ) for ferromagnetic interactions (i.e. J > 0) is always positive, so there are no negative m solutions to the mean field equation. This is completely different than the pair interaction case where there is symmetry in the solutions for positive and n ...
The Vorticity Equation and Conservation of Angular Momentum Alex
... In this form of the vorticity equation (called the barotropic potential vorticity equation) the divergence term is manifested through changes in the depth of the fluid. The physical principle behind the divergence term in either Eqn. (1) or (2) is the conservation of absolute angular momentum (Holto ...
... In this form of the vorticity equation (called the barotropic potential vorticity equation) the divergence term is manifested through changes in the depth of the fluid. The physical principle behind the divergence term in either Eqn. (1) or (2) is the conservation of absolute angular momentum (Holto ...
Black Hole
... The weak equivalence principle, also known as the universality of free fall or the Galilean equivalence principle can be stated in many ways. The strong EP includes (astronomic) bodies with gravitational binding energy (e.g., 1.74 solar-mass pulsar PSR J1903+0327, 15.3% of whose separated mass is ab ...
... The weak equivalence principle, also known as the universality of free fall or the Galilean equivalence principle can be stated in many ways. The strong EP includes (astronomic) bodies with gravitational binding energy (e.g., 1.74 solar-mass pulsar PSR J1903+0327, 15.3% of whose separated mass is ab ...
Diffusion of transverse correlations and shear viscosity in heavy ion
... Momentum fluctuation as tool to measure shear viscosity (5) Rapidity correlations to measure the shear viscosity ...
... Momentum fluctuation as tool to measure shear viscosity (5) Rapidity correlations to measure the shear viscosity ...