Titles and Abstracts
... operators and the corresponding coherent states can be obtained. This generalization includes systems where also the width of the coherent states is time-dependent as they occur for harmonic oscillators with time-dependent frequency or systems in contact with a dissipative environment. The key point ...
... operators and the corresponding coherent states can be obtained. This generalization includes systems where also the width of the coherent states is time-dependent as they occur for harmonic oscillators with time-dependent frequency or systems in contact with a dissipative environment. The key point ...
Aalborg Universitet Zero Point Energy and the Dirac Equation Forouzbakhsh, Farshid
... magnetic-color changes too. Therefore the electric fields do not decay in the structure of a photon. In general, a photon has been formed of two parts; 1A large number of negative color charges and magnetic color. Magnetic color maintains color charges in a tube-like distribution, so negative magnet ...
... magnetic-color changes too. Therefore the electric fields do not decay in the structure of a photon. In general, a photon has been formed of two parts; 1A large number of negative color charges and magnetic color. Magnetic color maintains color charges in a tube-like distribution, so negative magnet ...
particle physics
... not all the expected energy was in the emitted electron It was later more directly observed He concluded that some other particle took some of the energy and called it the neutrino (small neutral particle) The neutrino is almost massless and only reacts via the weak interaction And we also need an a ...
... not all the expected energy was in the emitted electron It was later more directly observed He concluded that some other particle took some of the energy and called it the neutrino (small neutral particle) The neutrino is almost massless and only reacts via the weak interaction And we also need an a ...
The variational principle and simple properties of the ground
... of the ground-state wave function of a one-body Hamiltonian corresponding to a particle with no internal degrees of freedom and moving in a field defined by a potential V(r). In particular, it is shown that the ground-state wave function can be taken to be real and non-negative, and that it cannot b ...
... of the ground-state wave function of a one-body Hamiltonian corresponding to a particle with no internal degrees of freedom and moving in a field defined by a potential V(r). In particular, it is shown that the ground-state wave function can be taken to be real and non-negative, and that it cannot b ...
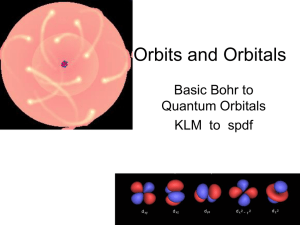
Orbits and Orbitals
... • No orbital can have more than 2 e- in it. (one spin up, one spin down) • Orbitals are half filled (with spins in the same direction) before they are doubly filled. • Orbitals are filled from lowest energy to highest energy. ...
... • No orbital can have more than 2 e- in it. (one spin up, one spin down) • Orbitals are half filled (with spins in the same direction) before they are doubly filled. • Orbitals are filled from lowest energy to highest energy. ...
Aspen-Winter08-summary
... M À TeV Scale – No Observable Flavor Violating Effects Beyond Renormalizable Standard Model If M Near TeV Scale or Additional State Which Carry Flavor Near the Weak Scale – Potential Conflict With Observation ...
... M À TeV Scale – No Observable Flavor Violating Effects Beyond Renormalizable Standard Model If M Near TeV Scale or Additional State Which Carry Flavor Near the Weak Scale – Potential Conflict With Observation ...
De Broglie-Bohm and Feynman Path Integrals
... concepts as ‘observers,’ and why should it not be possible to understand ‘measurement’ as a particular case of some general evolution process rather than need to allocate a special postulate for it [dM02]. While many still regard the measurement problem as the principal foundational issue at the hea ...
... concepts as ‘observers,’ and why should it not be possible to understand ‘measurement’ as a particular case of some general evolution process rather than need to allocate a special postulate for it [dM02]. While many still regard the measurement problem as the principal foundational issue at the hea ...
PPT
... = detecting light that has been reflected off the object's surface light = electromagnetic wave; “visible light”= those electromagnetic waves that our eyes can detect “wavelength” of e.m. wave (distance between two successive crests) determines “color” of light wave hardly influenced by object if ...
... = detecting light that has been reflected off the object's surface light = electromagnetic wave; “visible light”= those electromagnetic waves that our eyes can detect “wavelength” of e.m. wave (distance between two successive crests) determines “color” of light wave hardly influenced by object if ...